Diffusion of holes and electrons
Category
Published on
Abstract
Diffusion is a process of particles distributing themselves from regions of high- to low- concentrations. In semi-classical electronics these particles are the charge carriers (electrons and holes). The rate at which a carrier can diffuse is called diffusion constant with units of cm2/s.
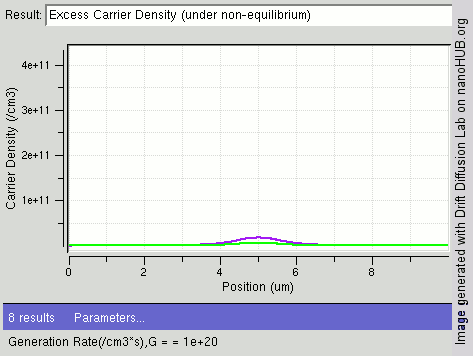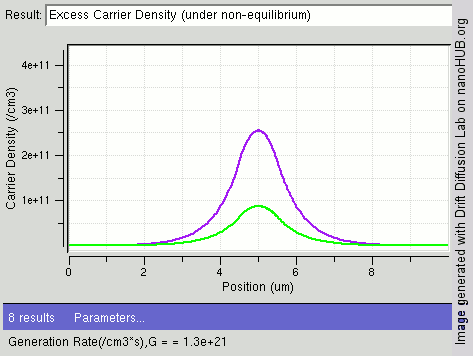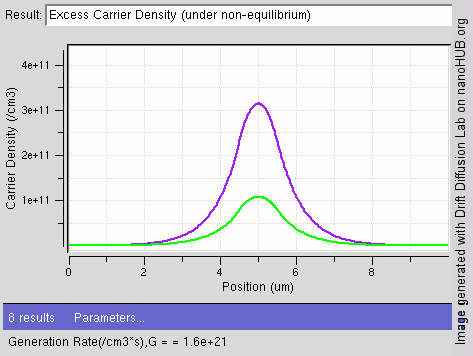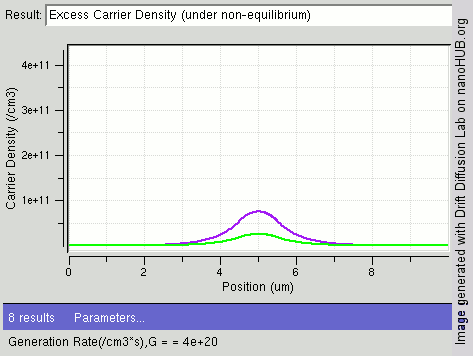
The image shows the process of steady state diffusion in an intrinsic semiconductor bar with different light shining intensity (different carrier generations rates /cm3) at the center of the bar. In general electrons have a higher rate of diffusion than holes. As more electron-hole pairs are generated, fewer excess electrons remain, diffusing away faster as compared to holes.
Credits
Image rendered using nanoHUB tool Drift Diffusion Lab (http://nanohub.org/tools/semi)
Cite this work
Researchers should cite this work as follows: