Lecture 4: Thermoelectric Effects-Physical Approach
Lecture 4: Thermoelectric Effects-Physical Approach
-
 1. NCN Summer School: July 2011 …
0
00:00/00:00
1. NCN Summer School: July 2011 …
0
00:00/00:00 -
 2. copyright 2011
58.5
00:00/00:00
2. copyright 2011
58.5
00:00/00:00 -
 3. about thermoelectricity
59.733333333333334
00:00/00:00
3. about thermoelectricity
59.733333333333334
00:00/00:00 -
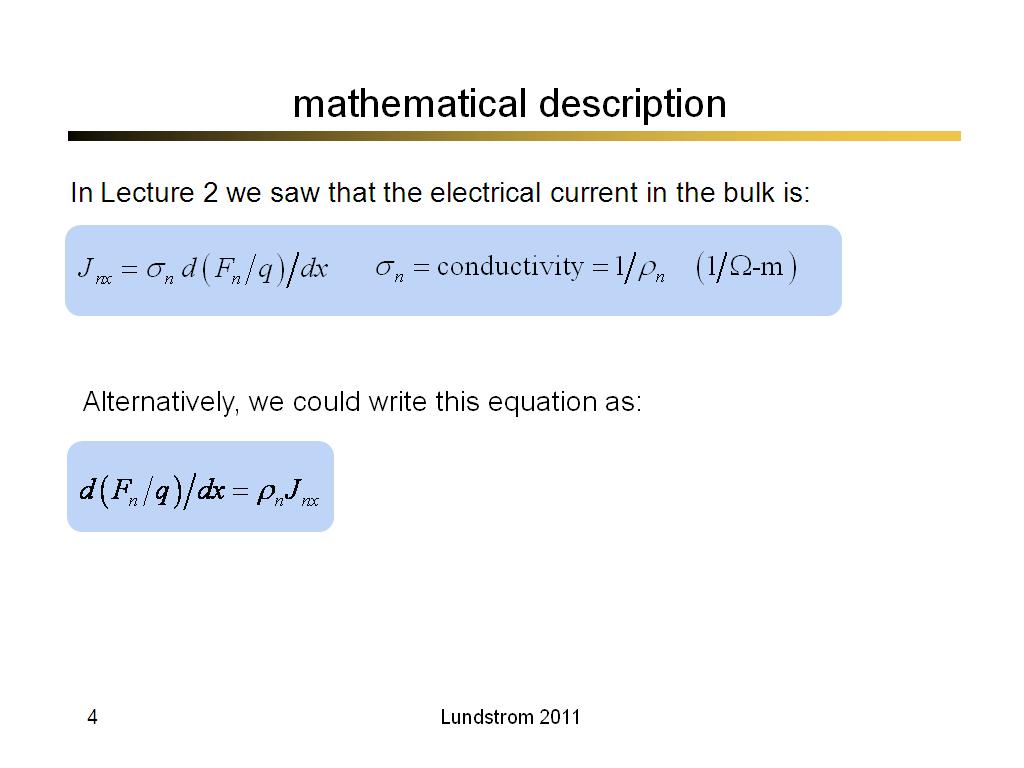
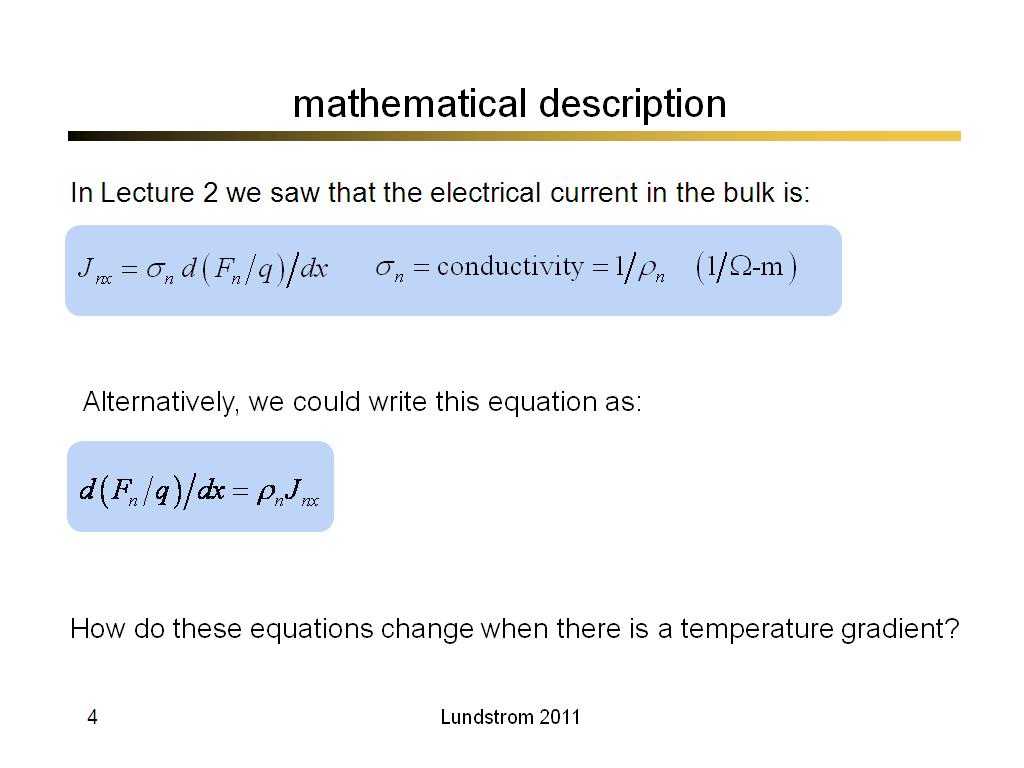 4. mathematical description
98.6
00:00/00:00
4. mathematical description
98.6
00:00/00:00 -
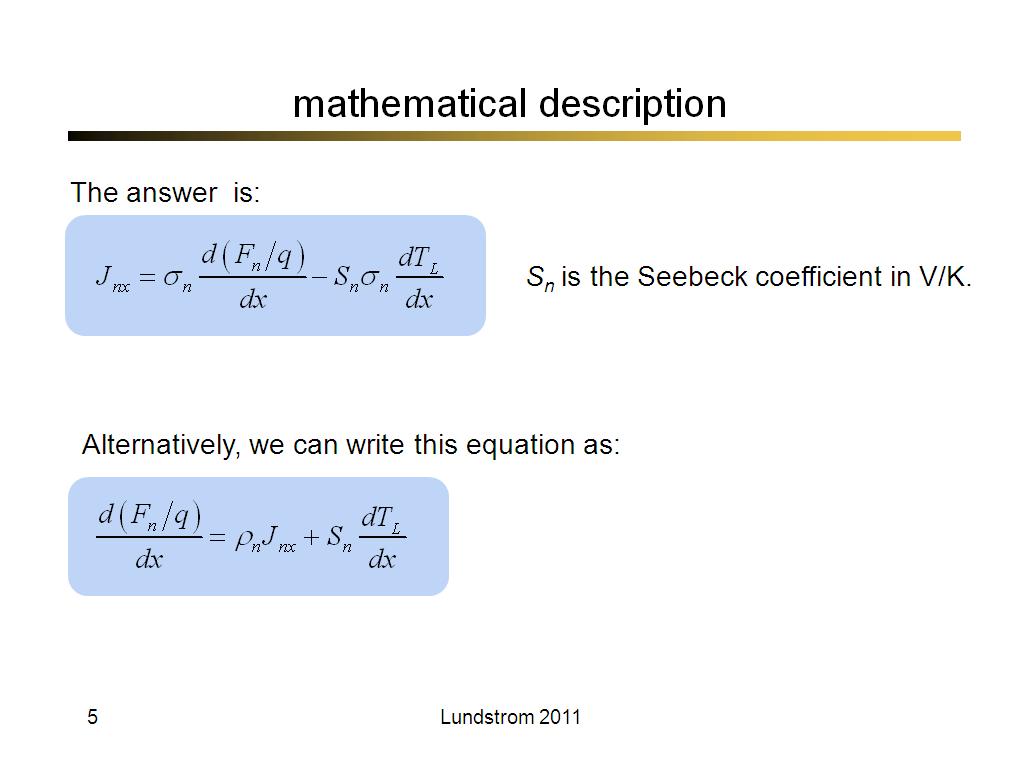 5. mathematical description
185.86666666666667
00:00/00:00
5. mathematical description
185.86666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
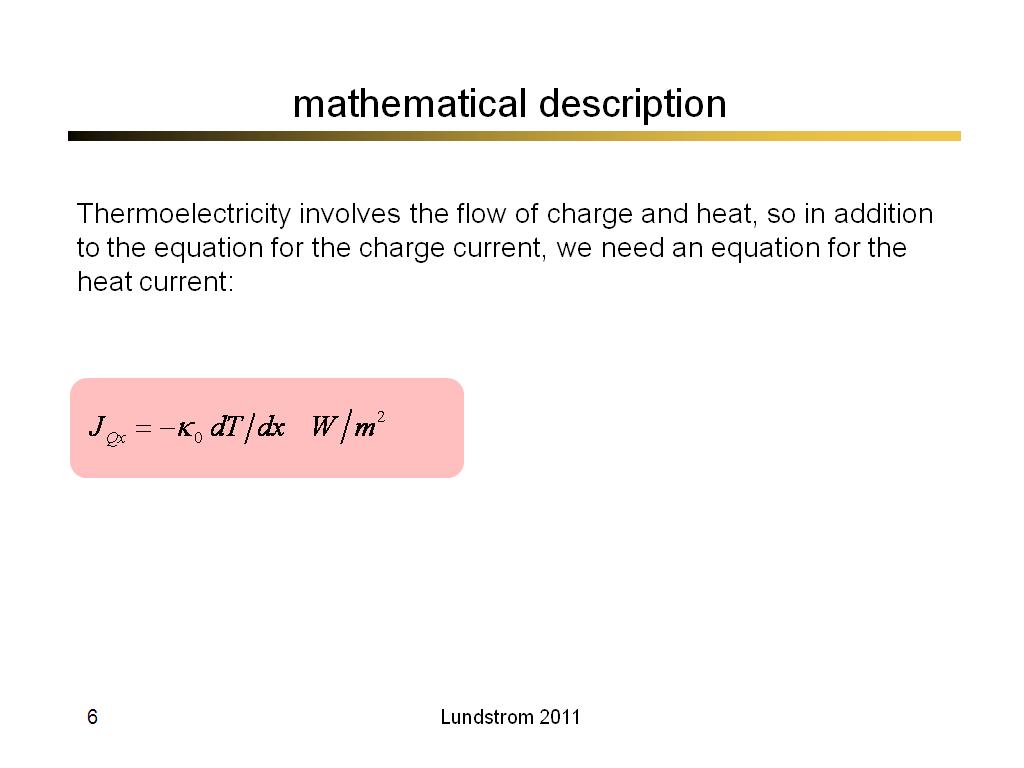
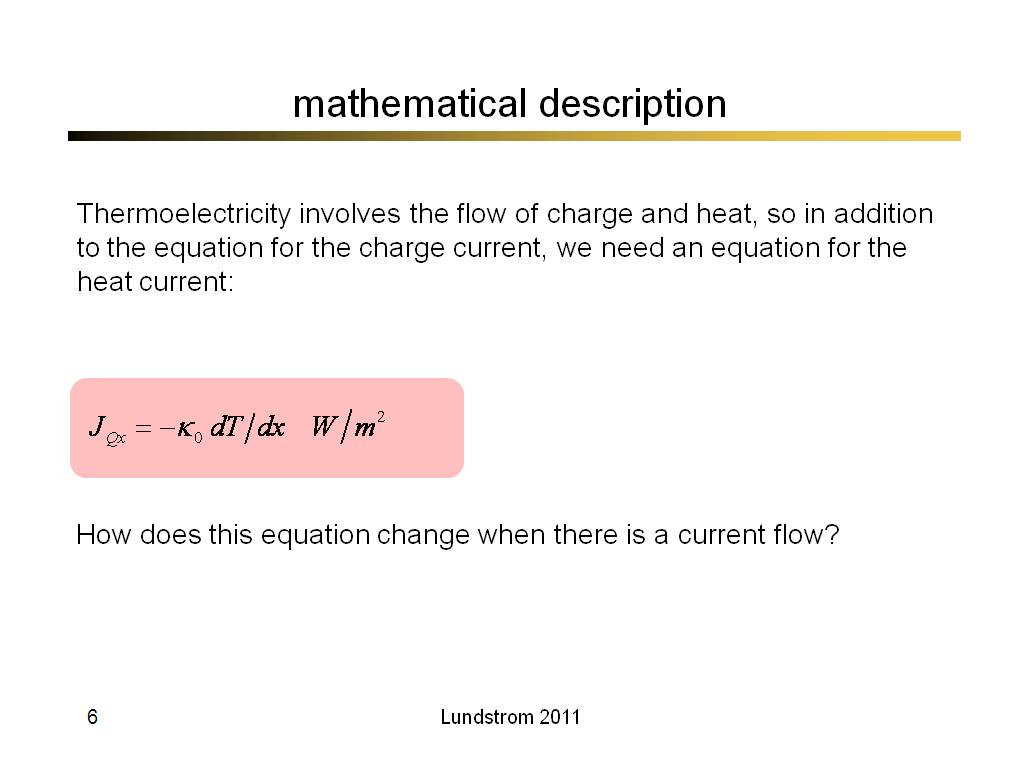 6. mathematical description
223.3
00:00/00:00
6. mathematical description
223.3
00:00/00:00 -
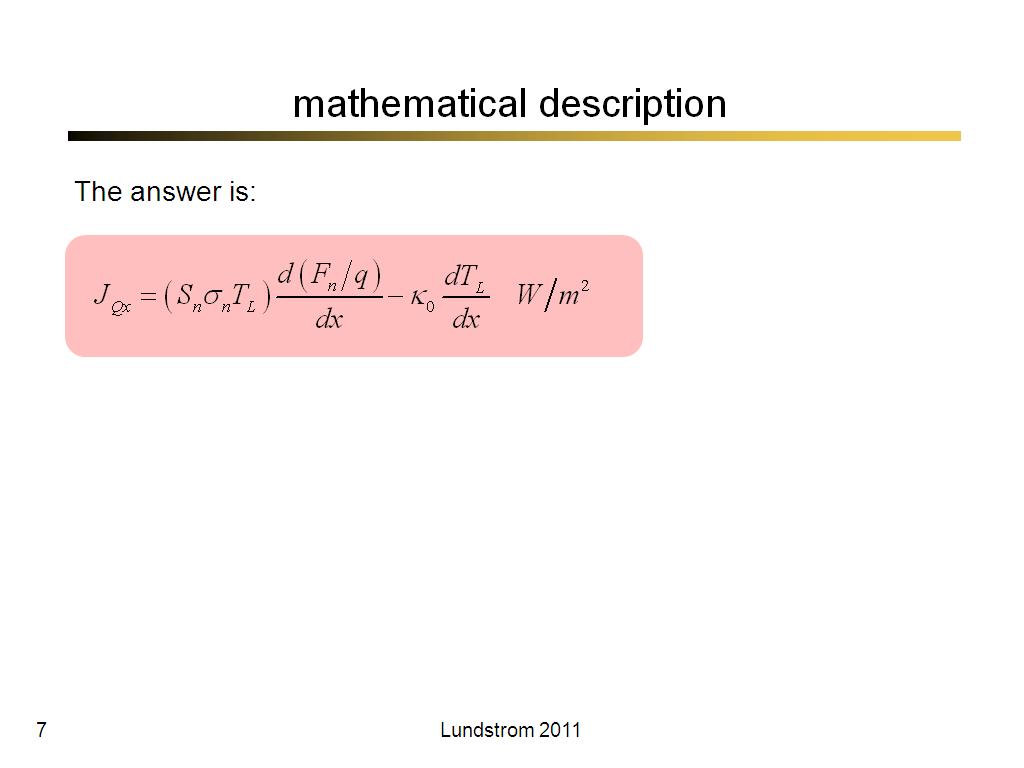
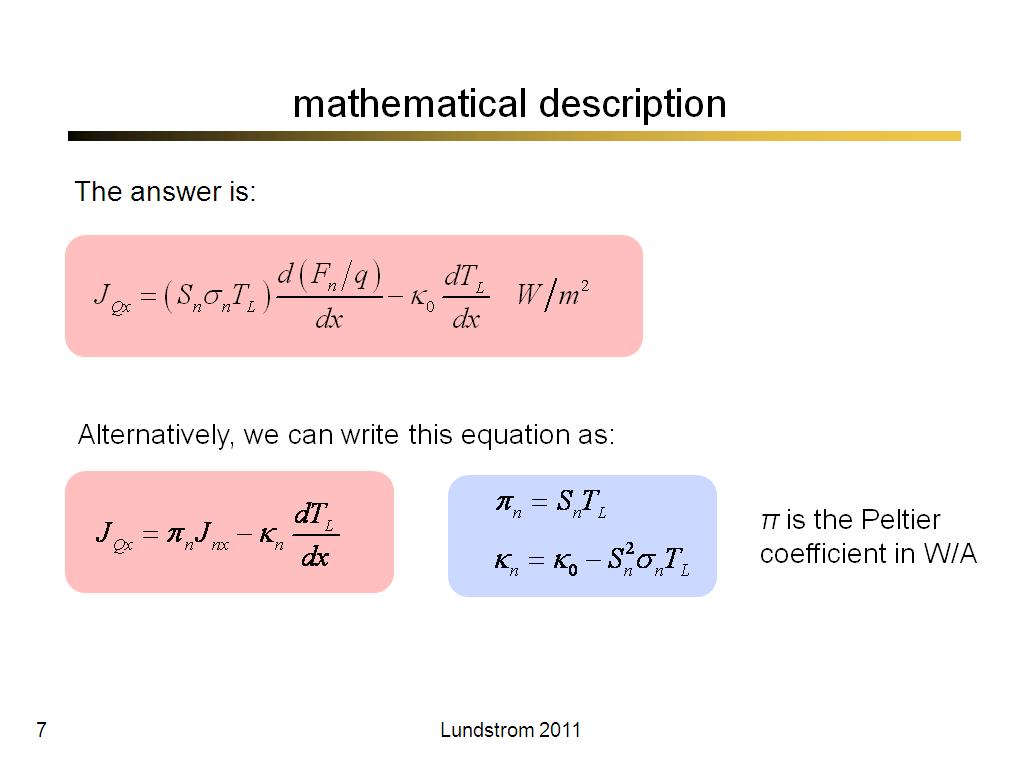
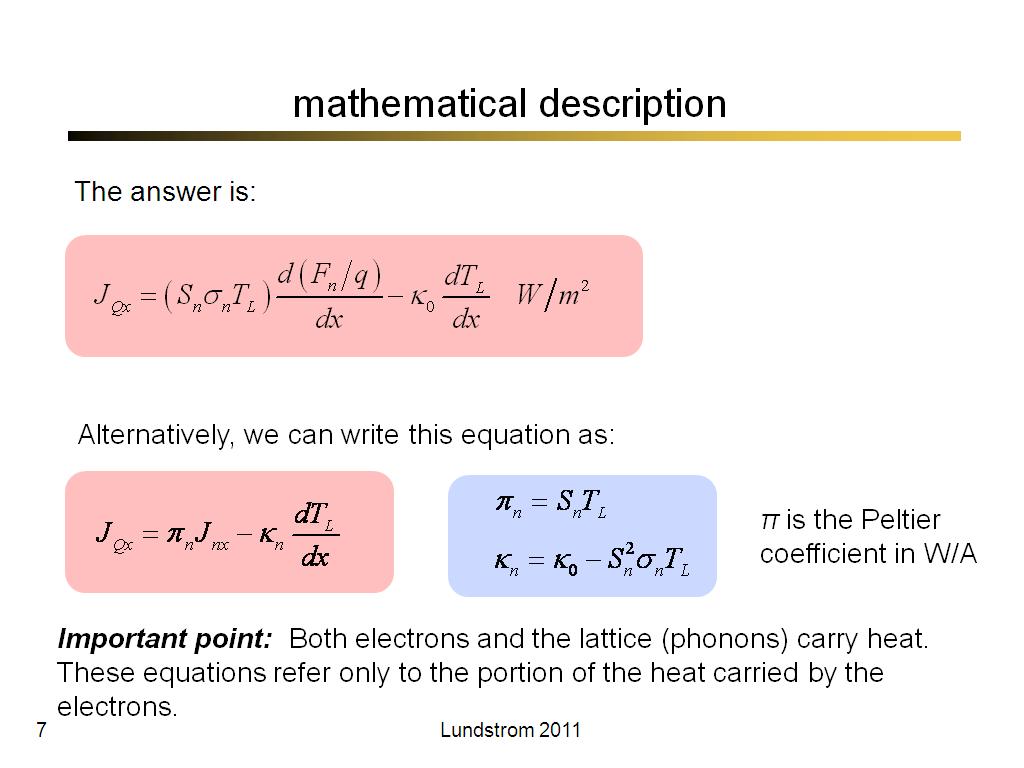 7. mathematical description
311.06666666666666
00:00/00:00
7. mathematical description
311.06666666666666
00:00/00:00 -
 8. in this lecture…
455.83333333333331
00:00/00:00
8. in this lecture…
455.83333333333331
00:00/00:00 -
 9. outline
465.53333333333336
00:00/00:00
9. outline
465.53333333333336
00:00/00:00 -
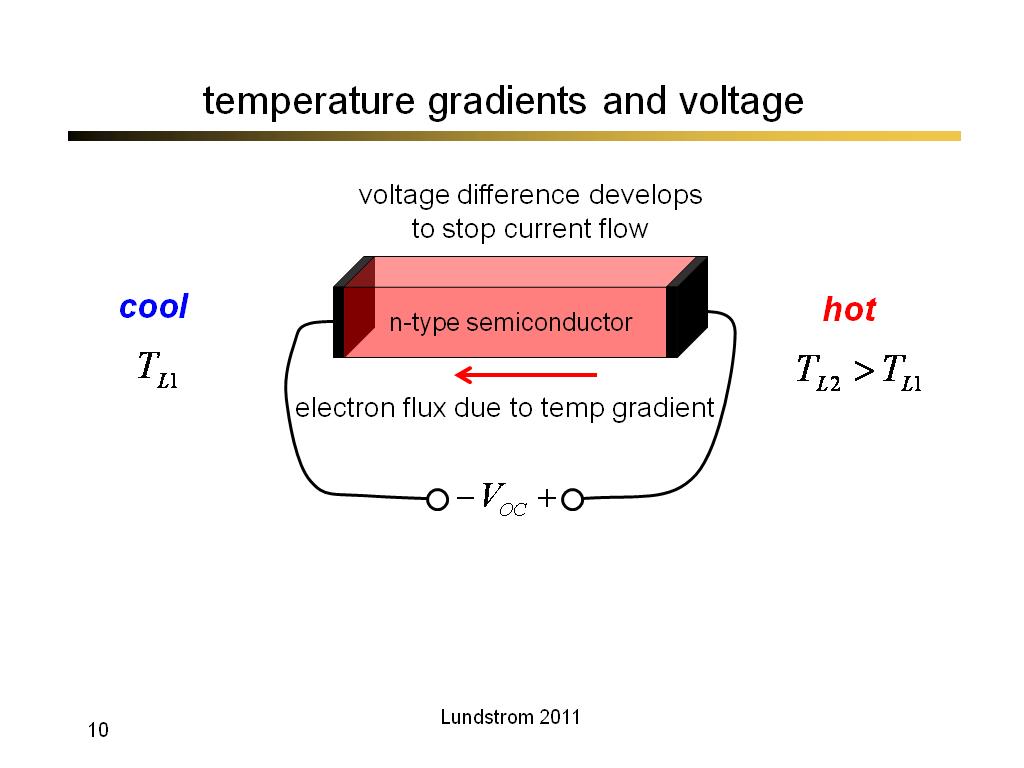
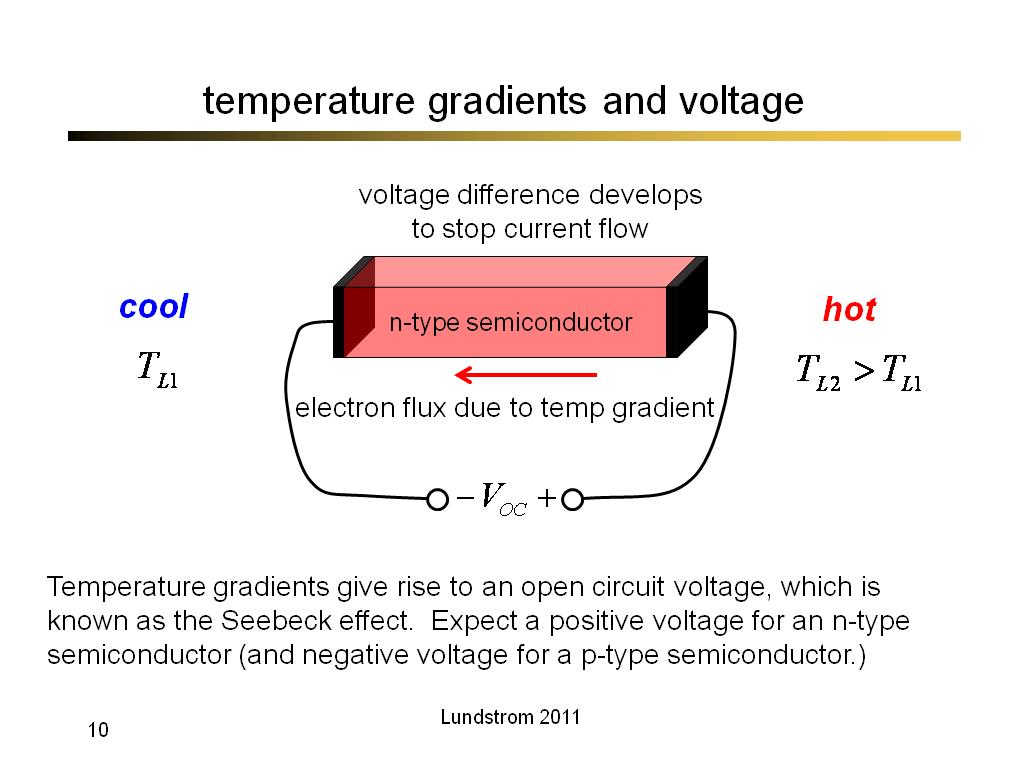 10. temperature gradients and volt…
478.83333333333331
00:00/00:00
10. temperature gradients and volt…
478.83333333333331
00:00/00:00 -
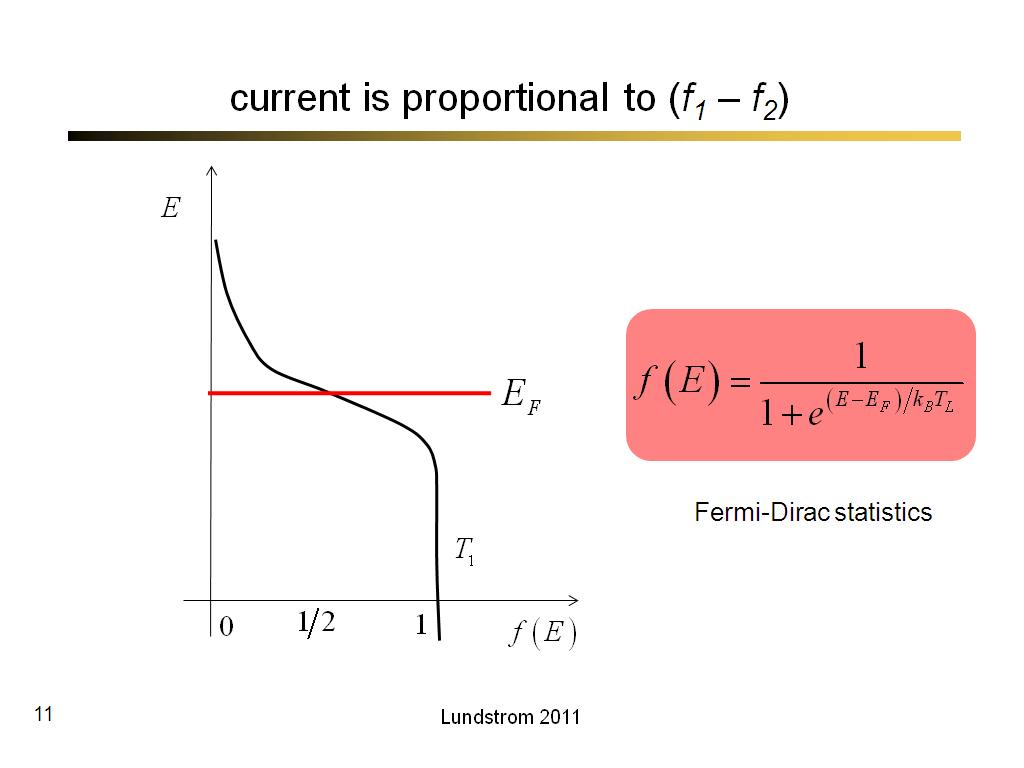
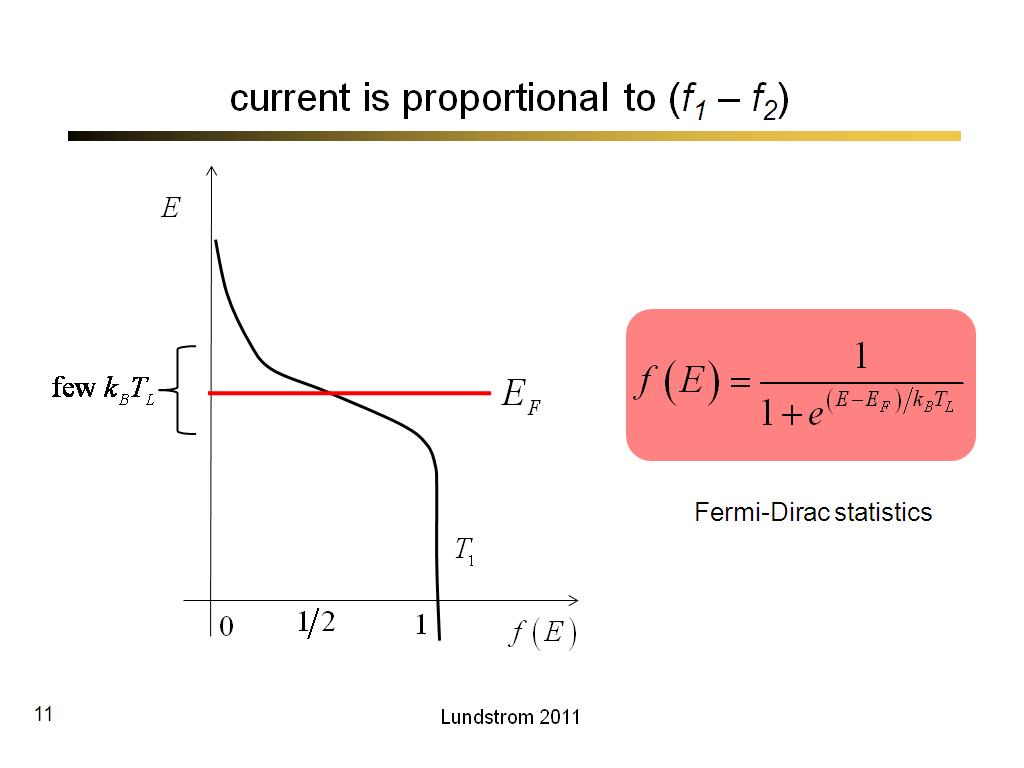
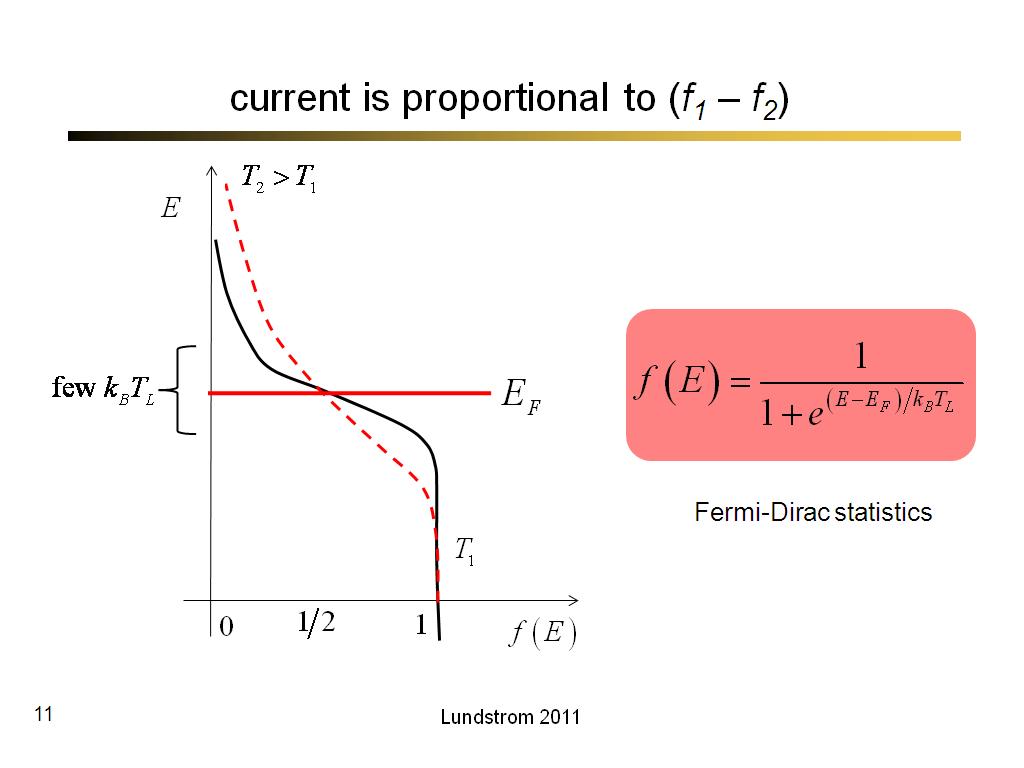
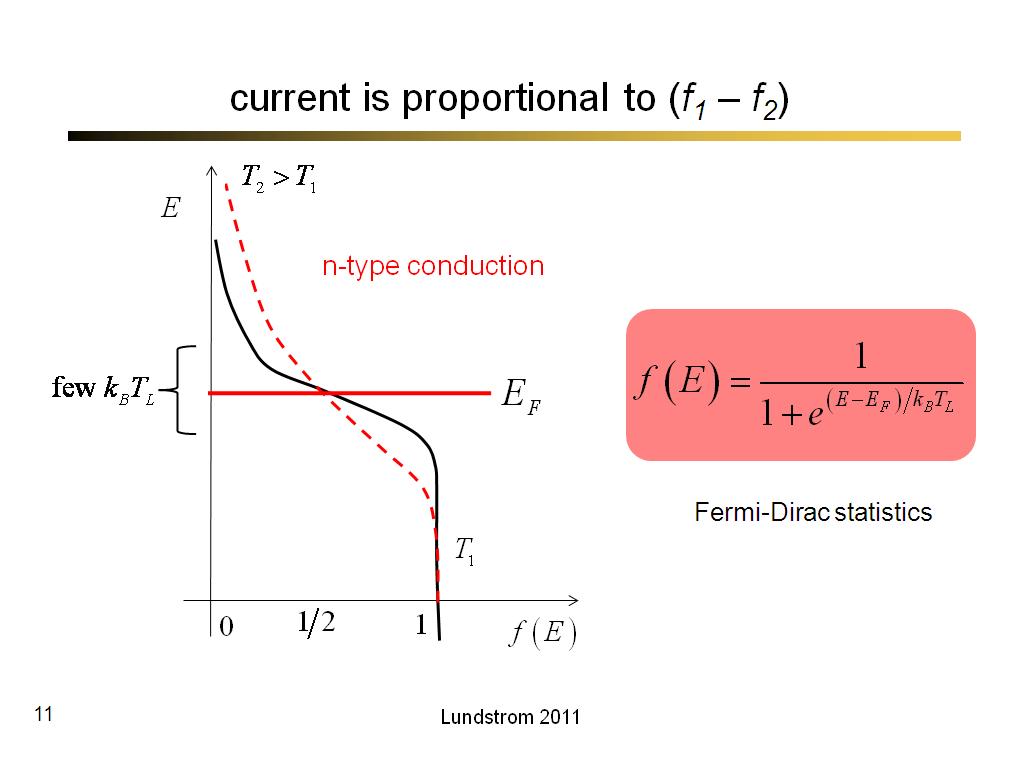
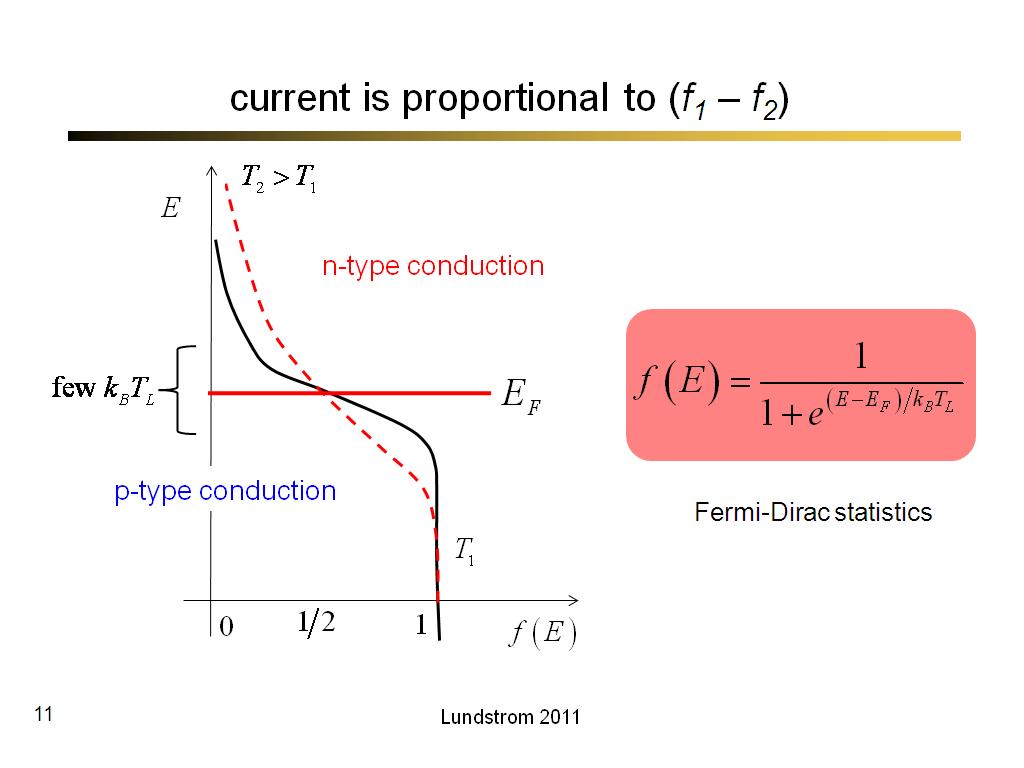 11. current is proportional to (f1…
582.63333333333333
00:00/00:00
11. current is proportional to (f1…
582.63333333333333
00:00/00:00 -
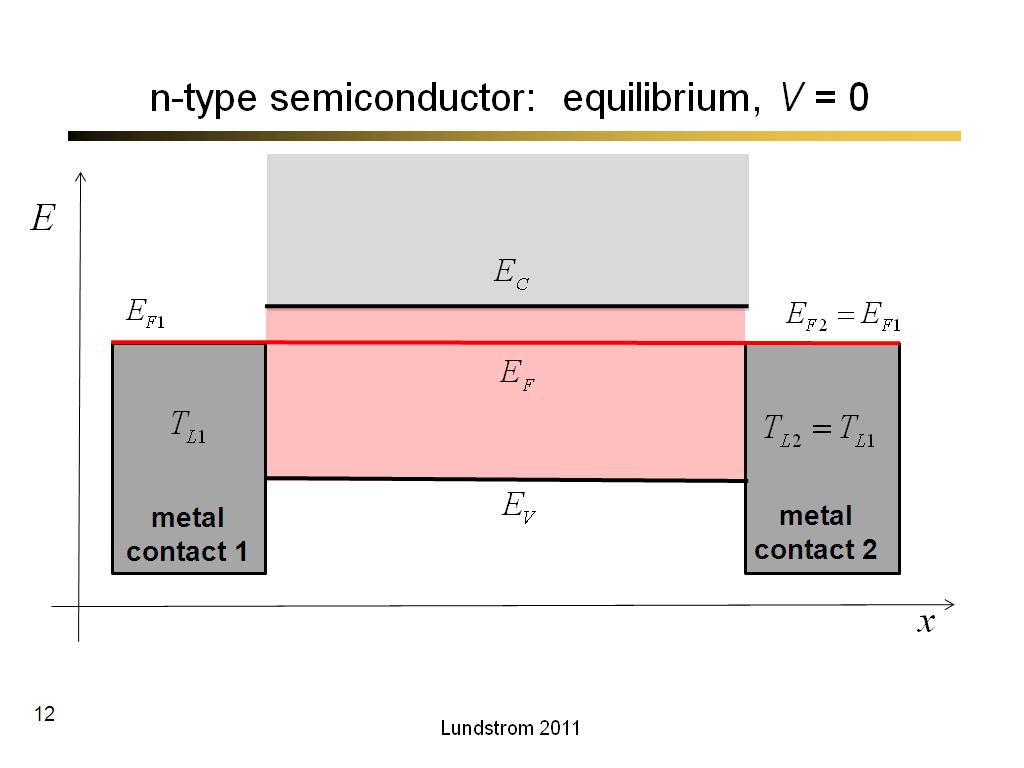
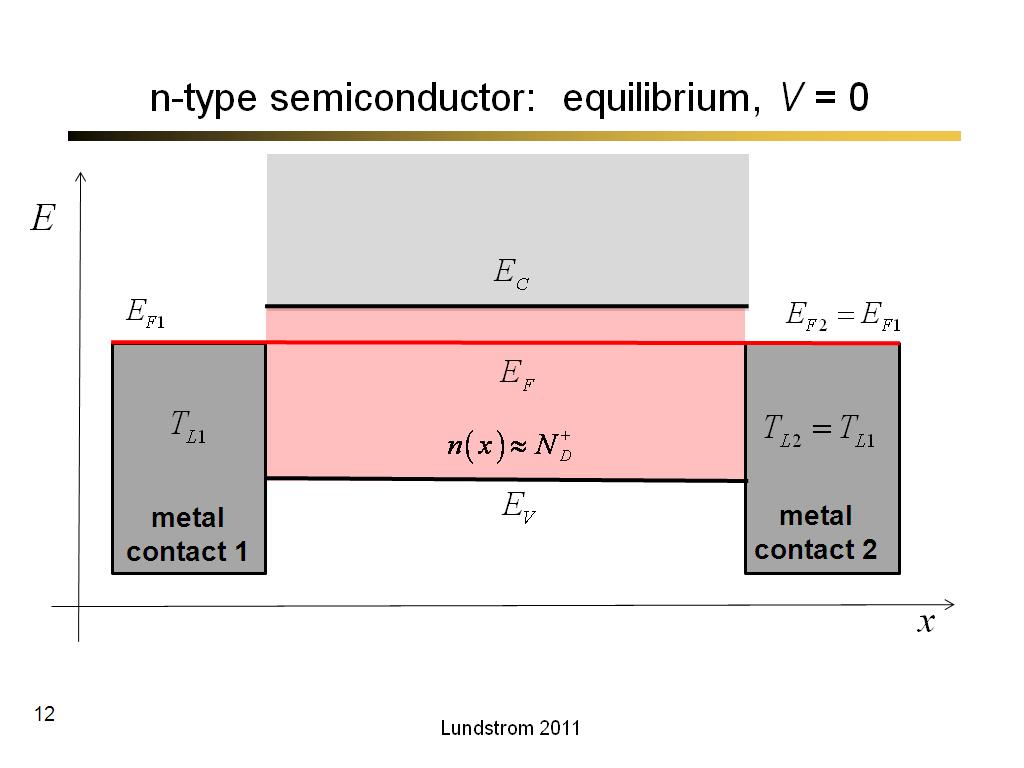
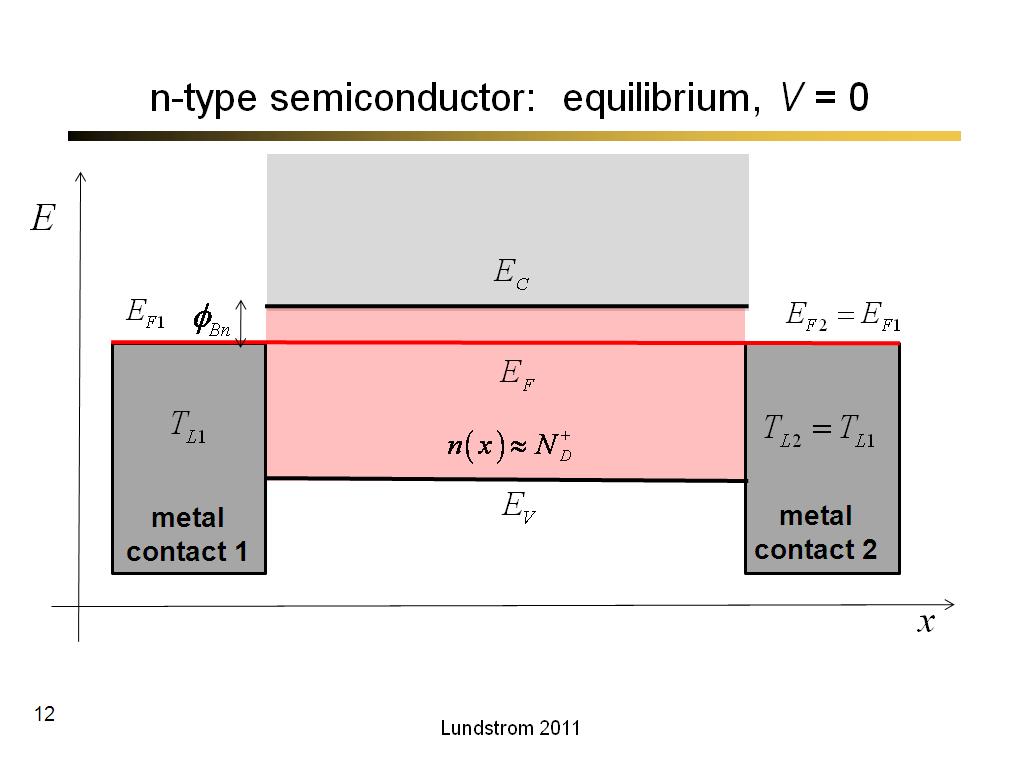
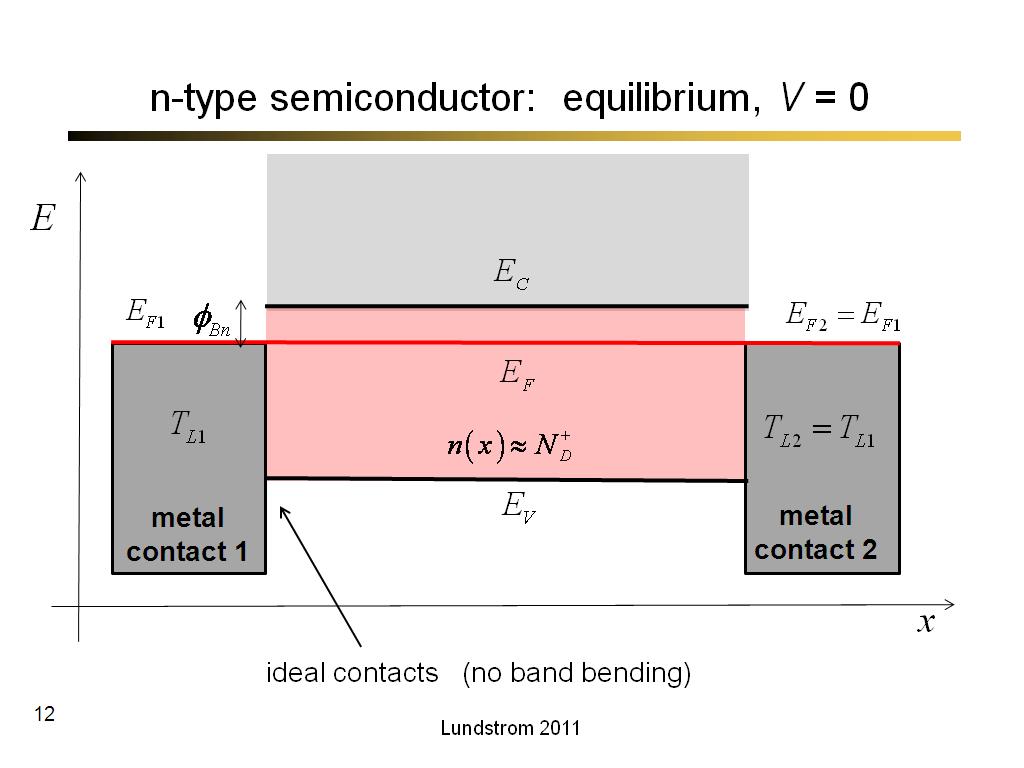 12. n-type semiconductor: equilib…
662.7
00:00/00:00
12. n-type semiconductor: equilib…
662.7
00:00/00:00 -
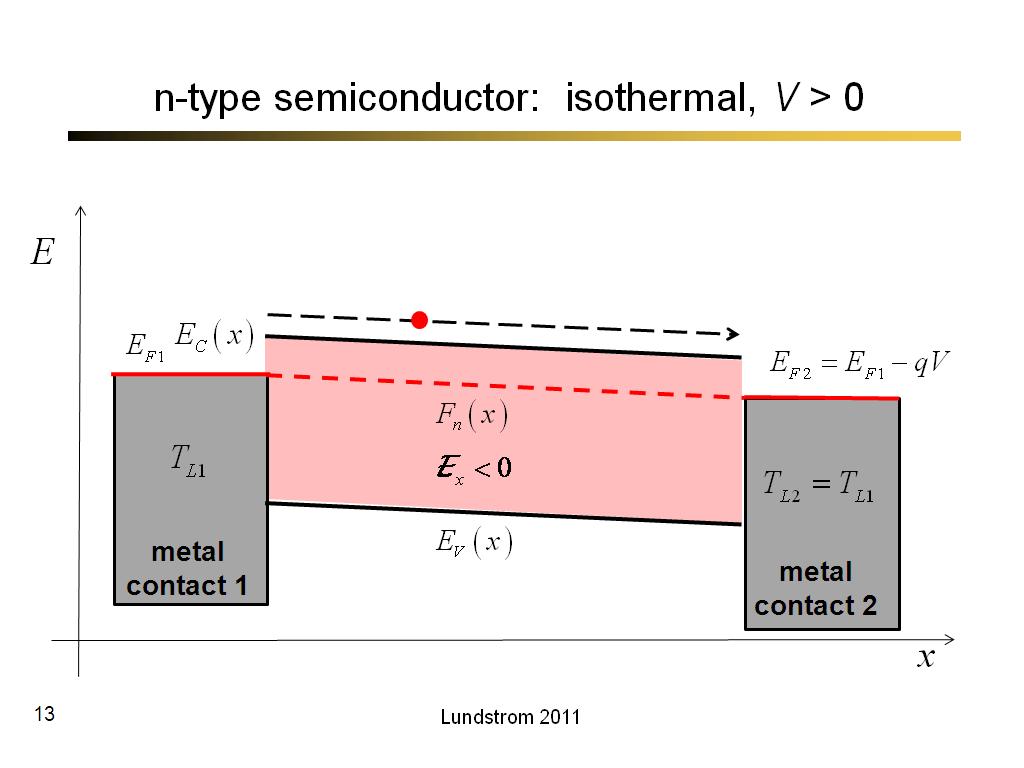
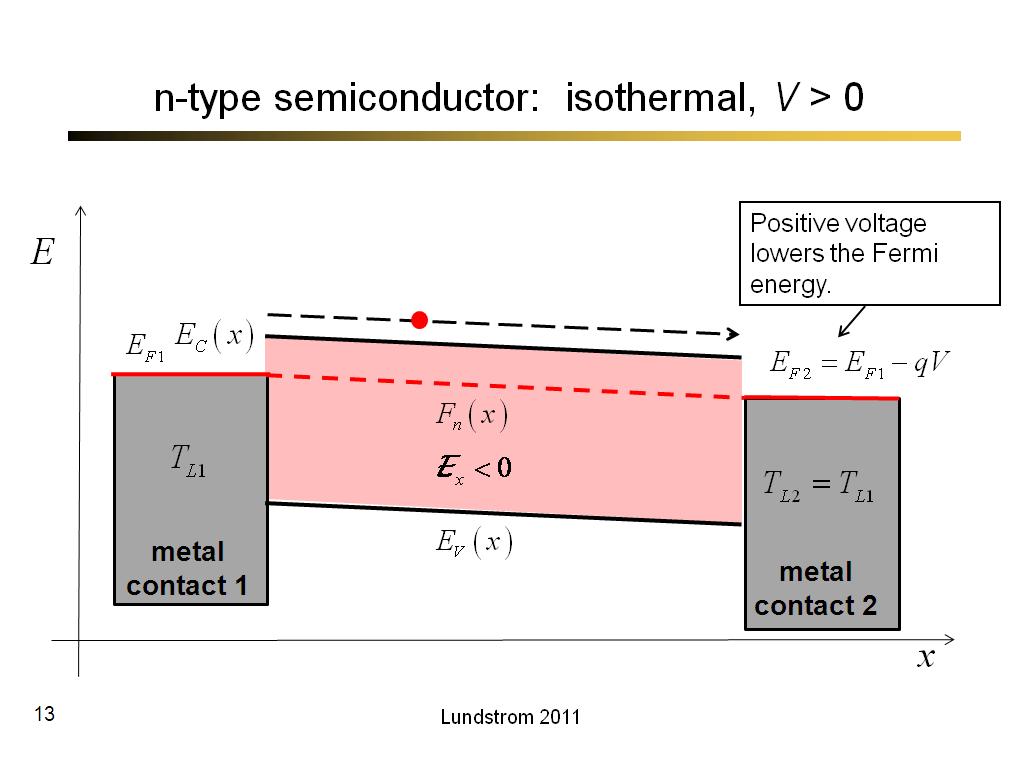
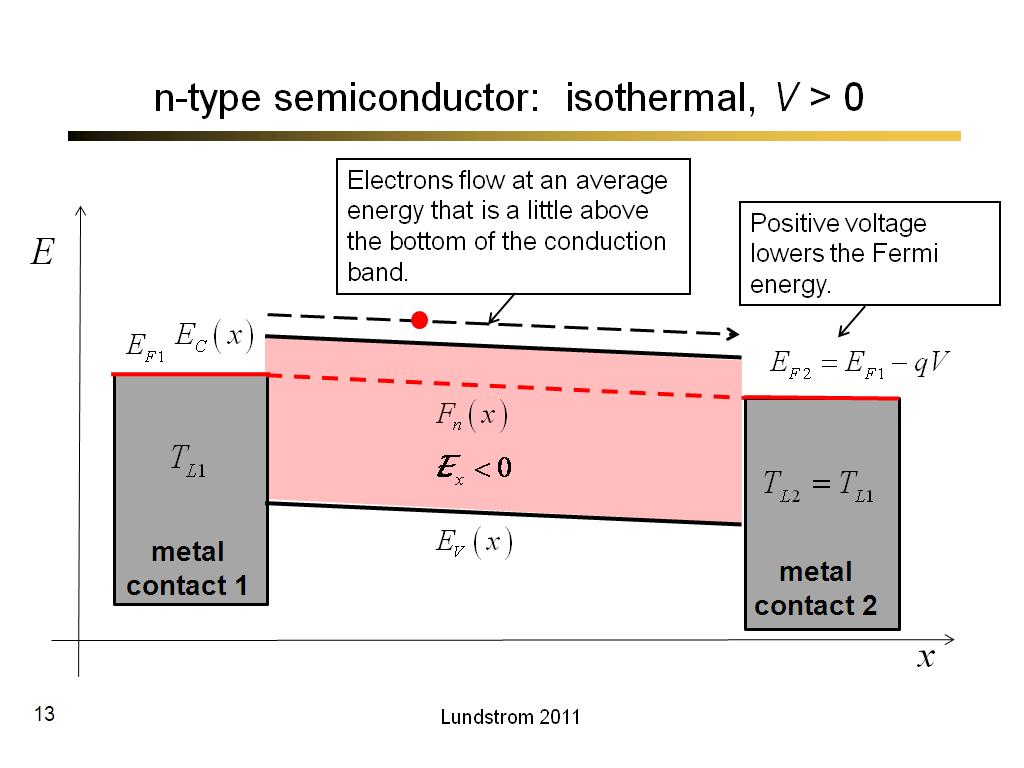
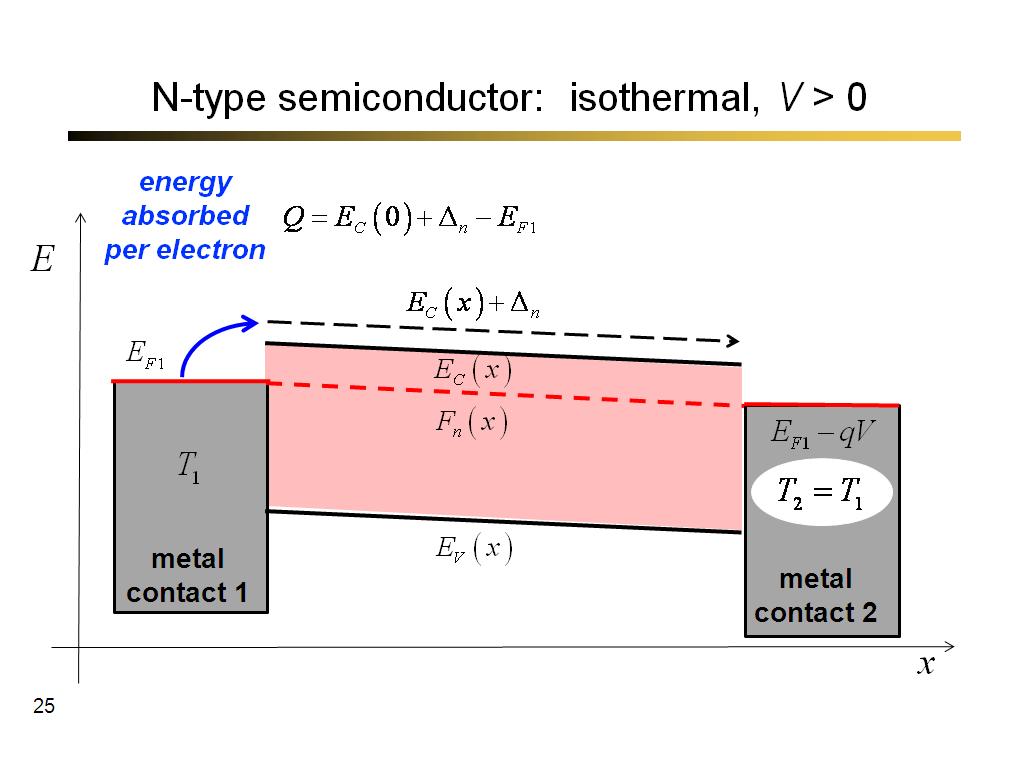
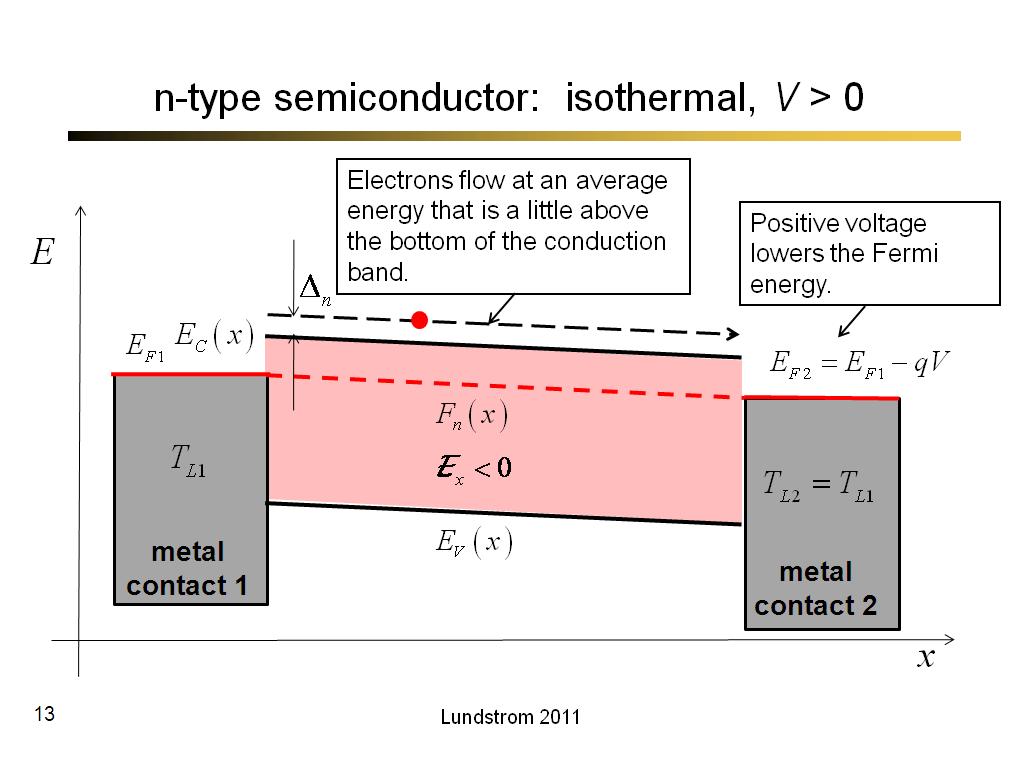 13. n-type semiconductor: isother…
747.26666666666665
00:00/00:00
13. n-type semiconductor: isother…
747.26666666666665
00:00/00:00 -
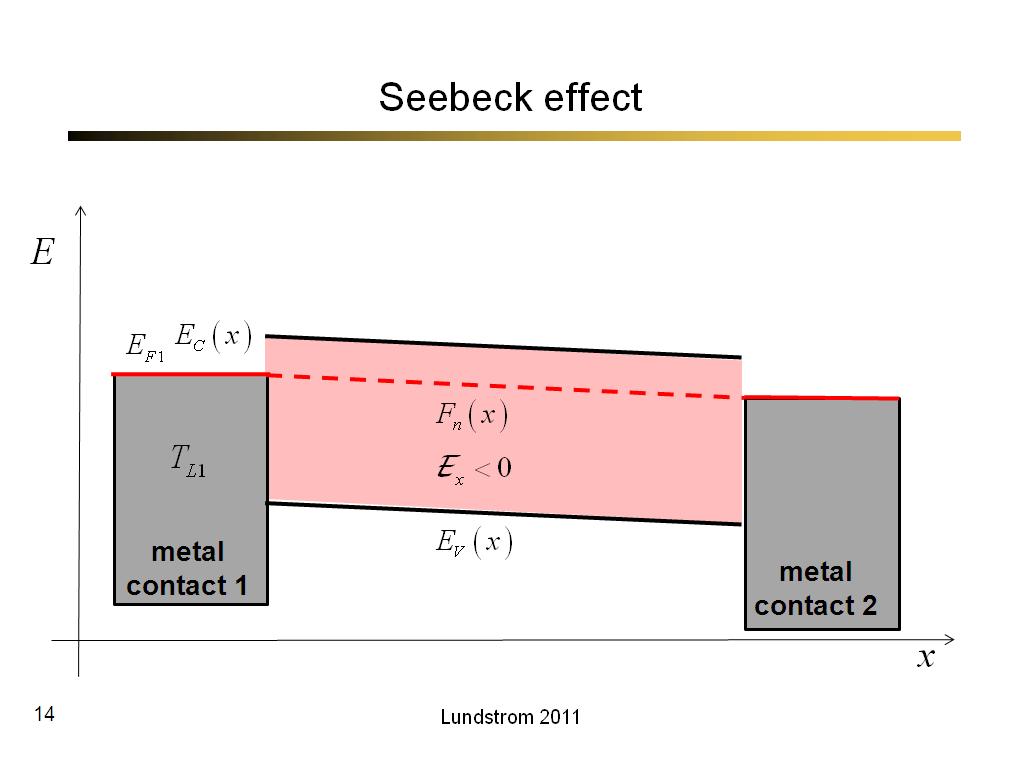
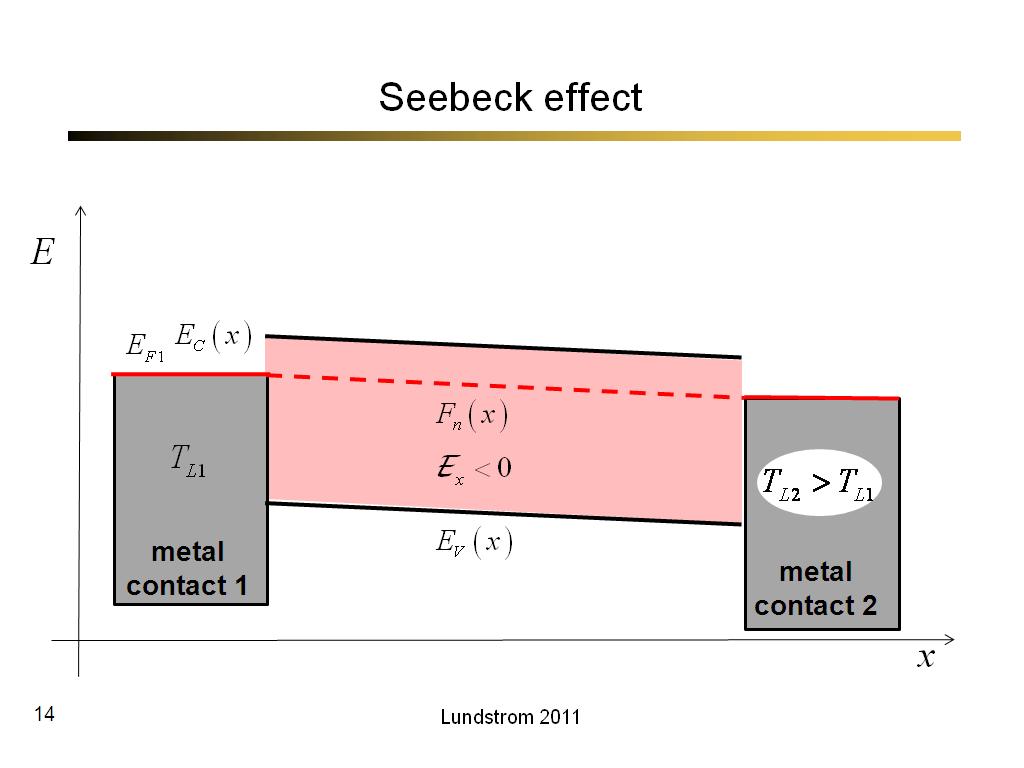
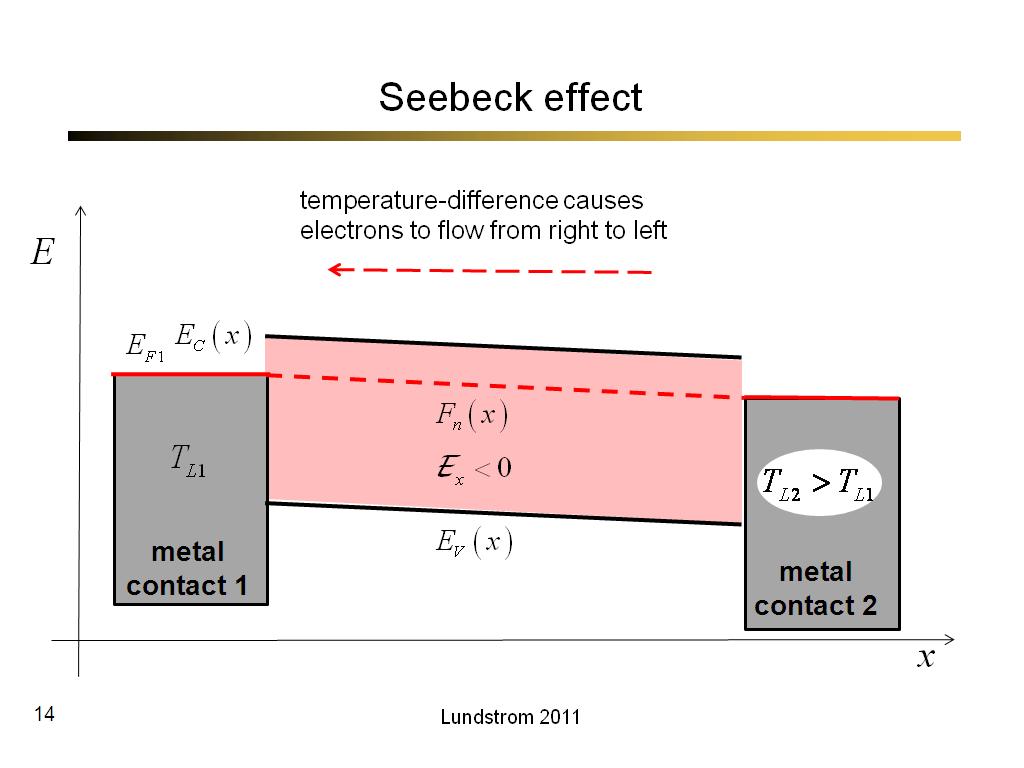
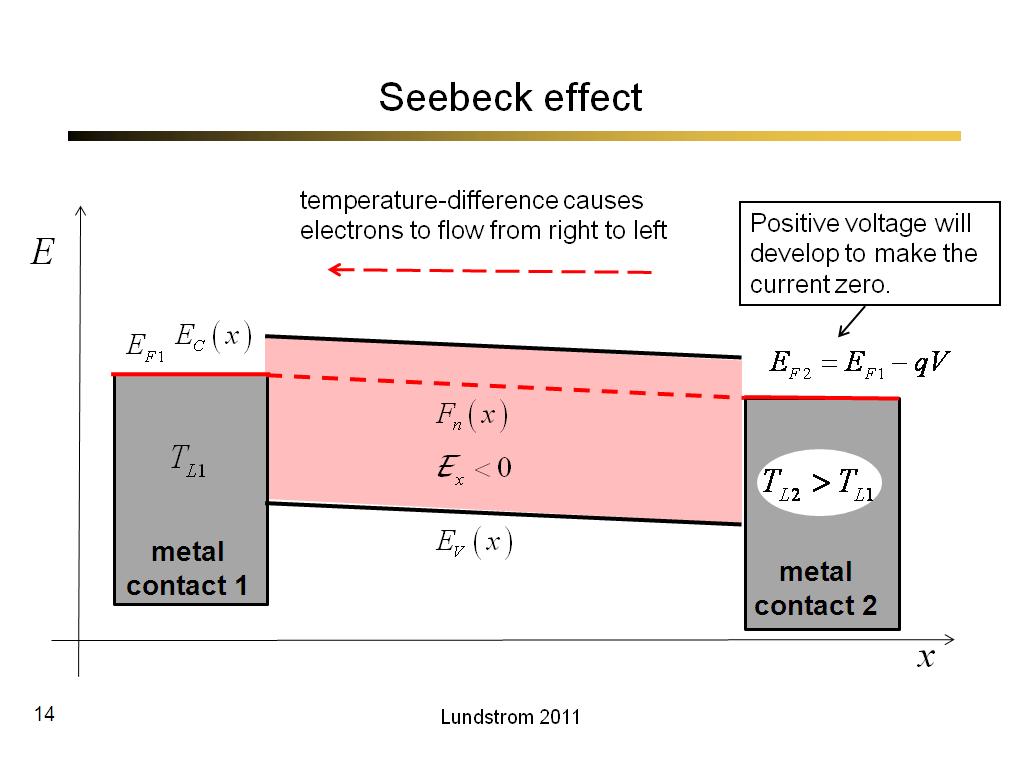 14. Seebeck effect
828.4666666666667
00:00/00:00
14. Seebeck effect
828.4666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
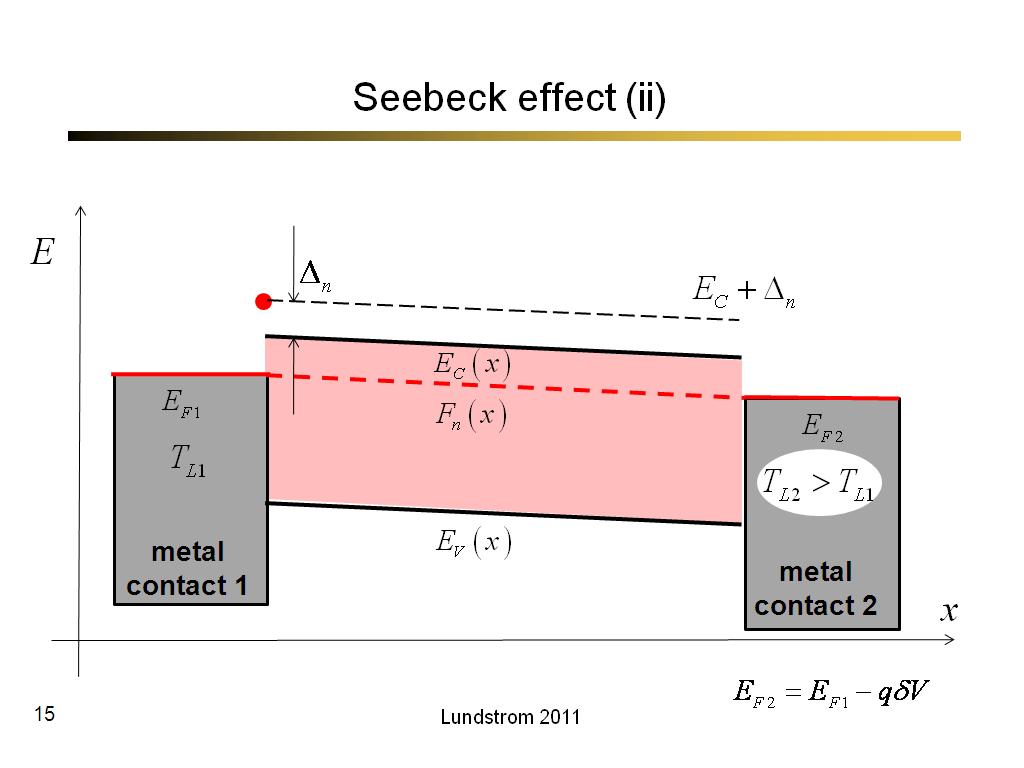
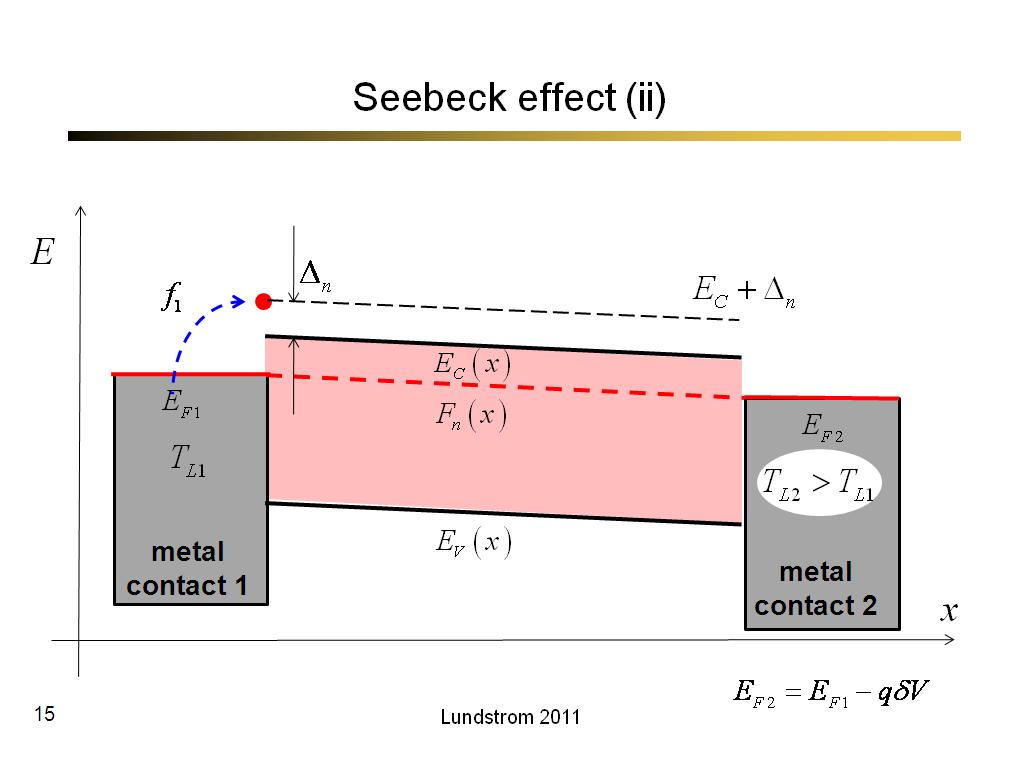
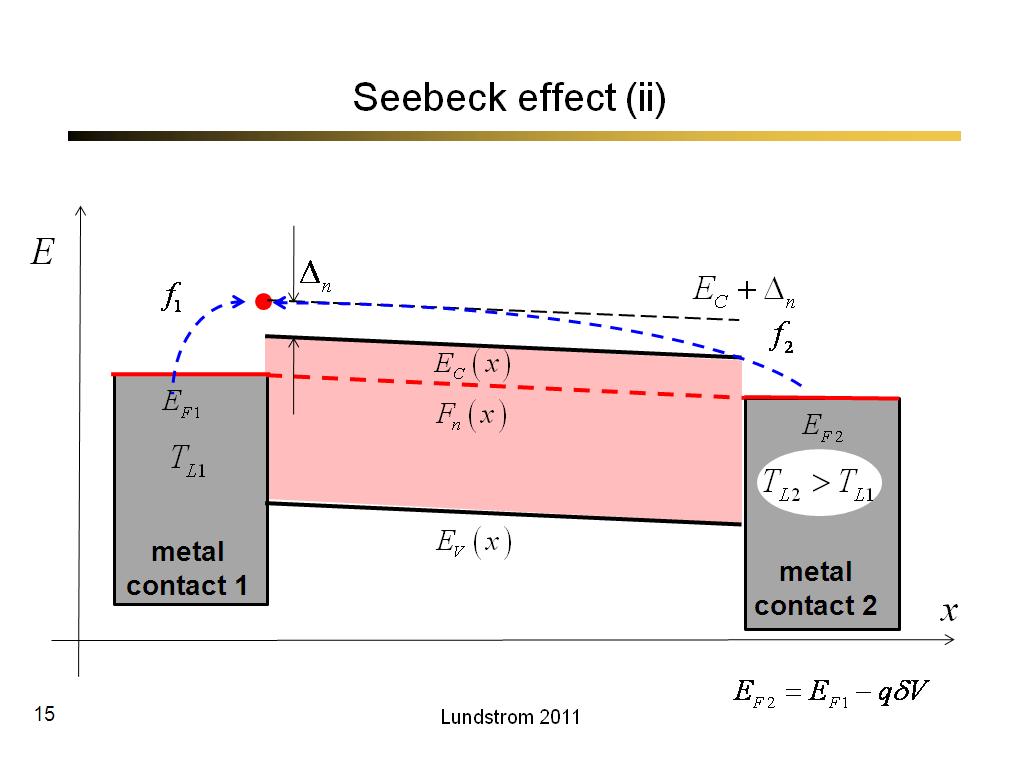
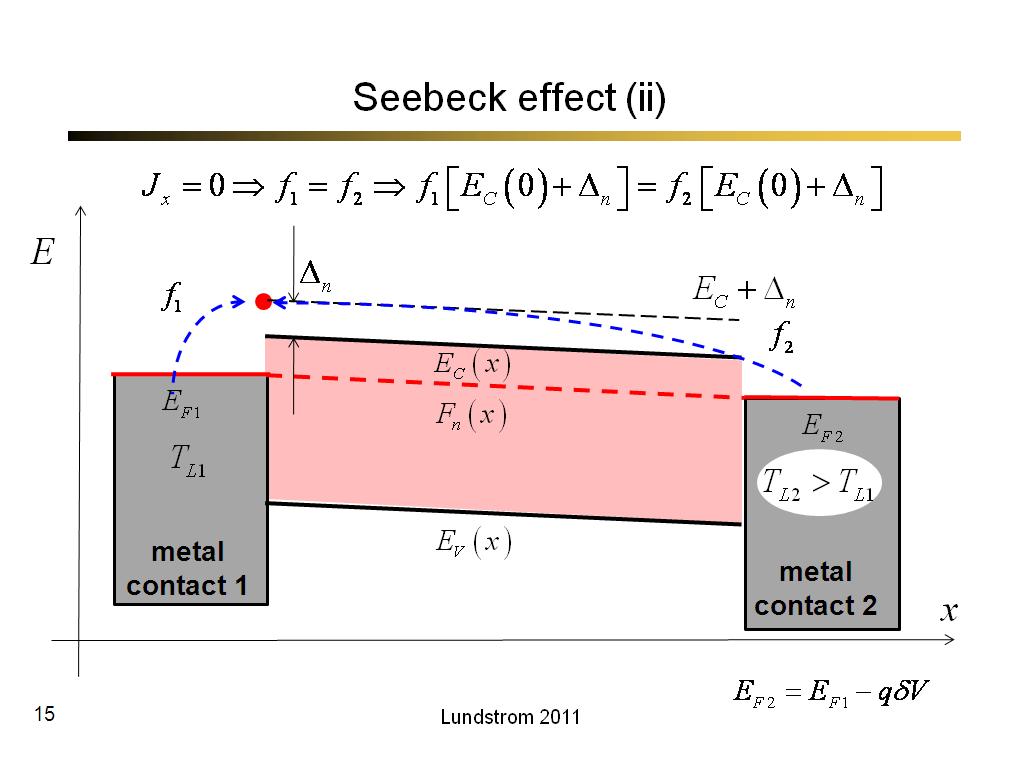
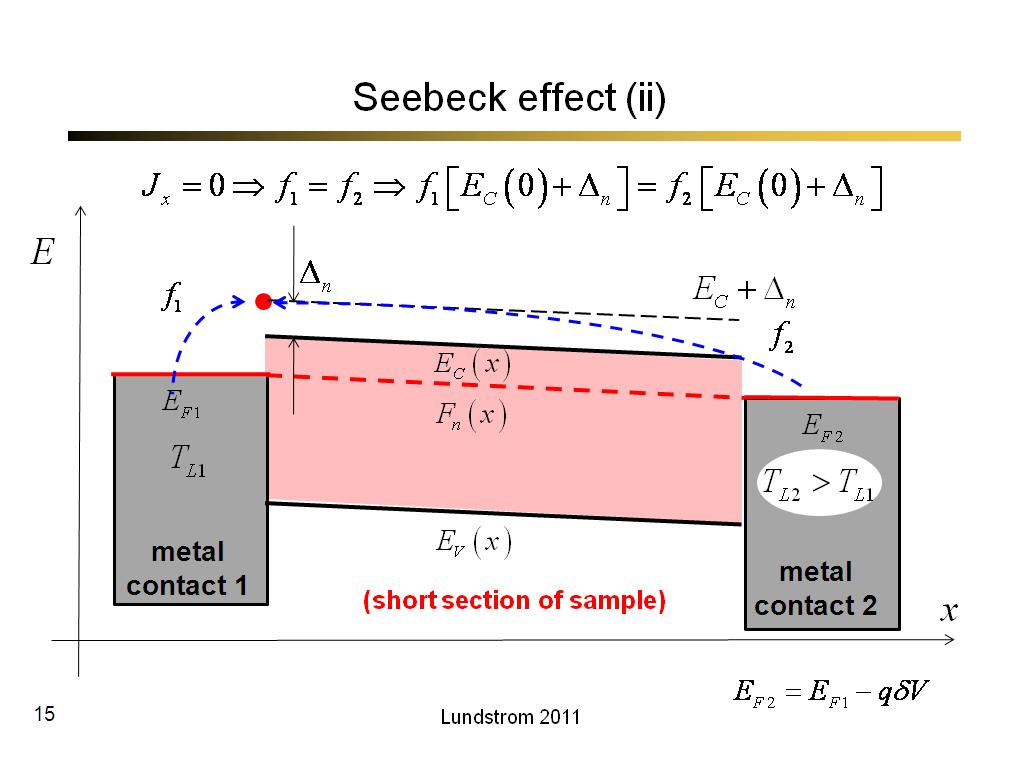 15. Seebeck effect (ii)
866.7
00:00/00:00
15. Seebeck effect (ii)
866.7
00:00/00:00 -
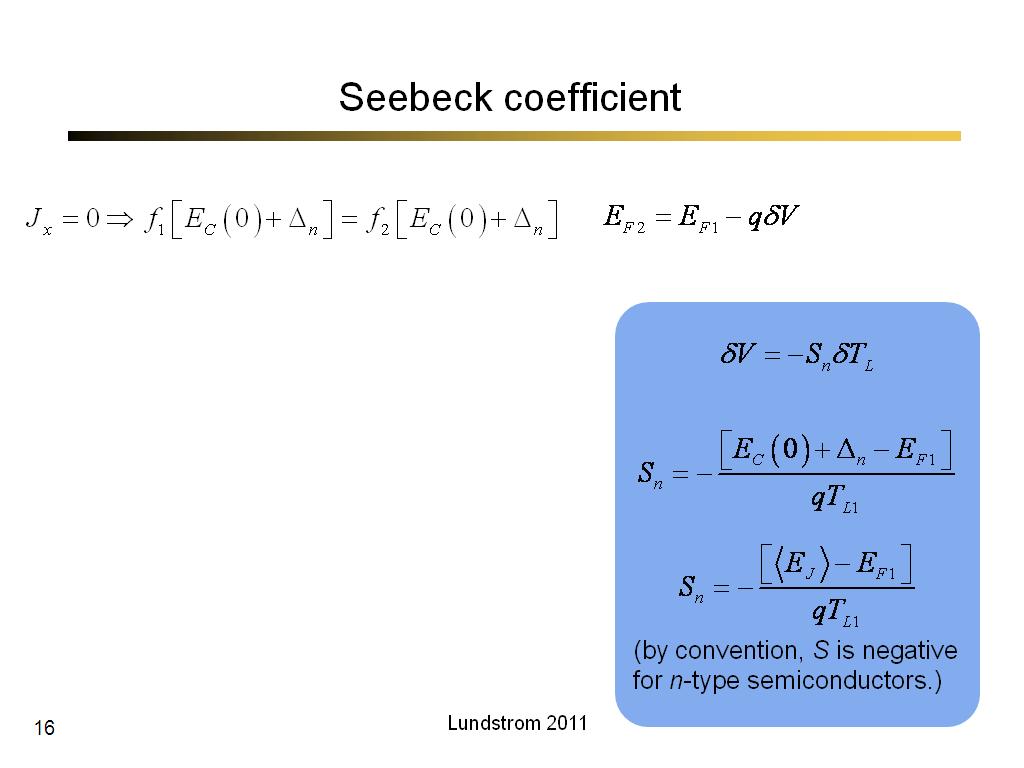
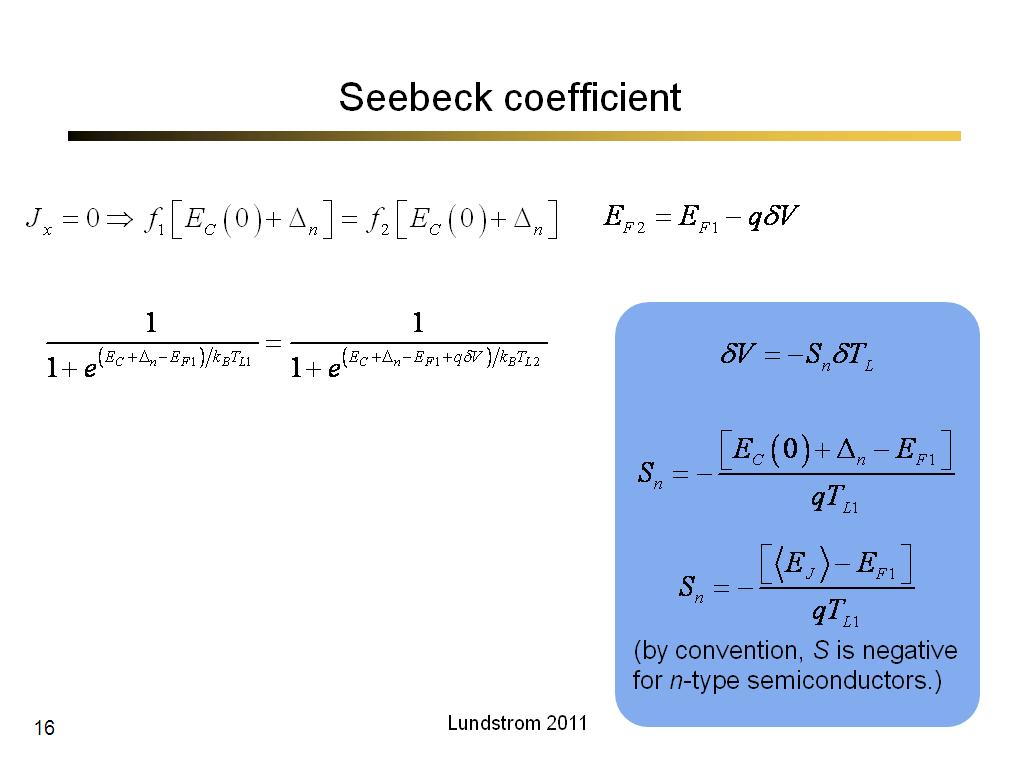
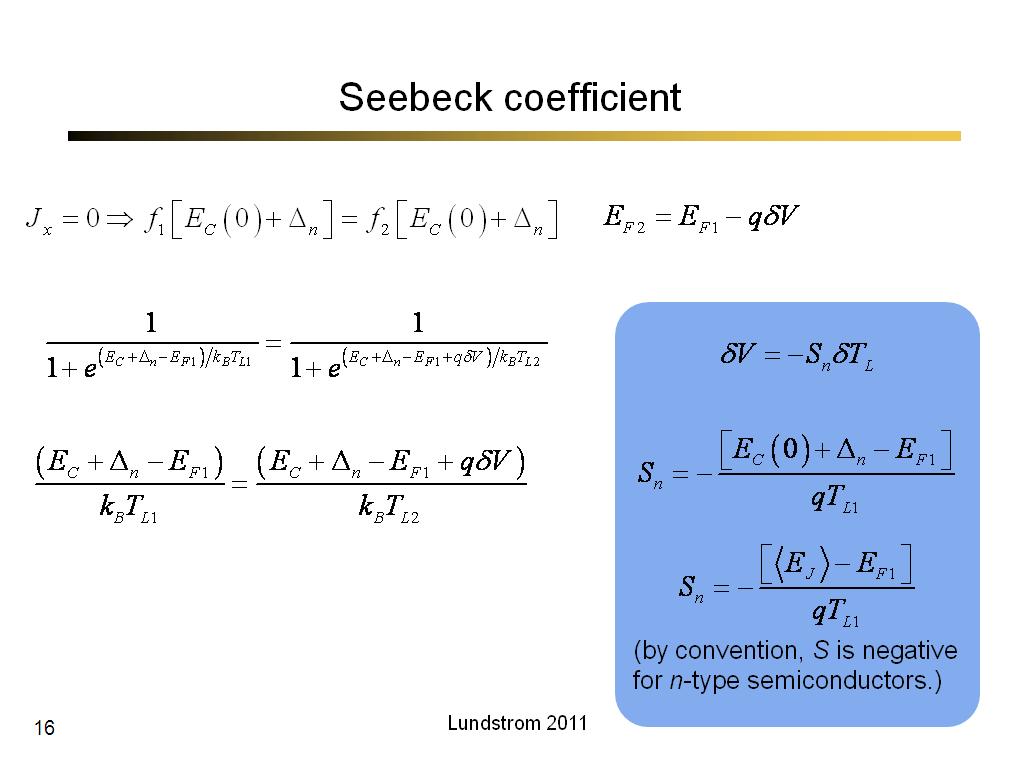
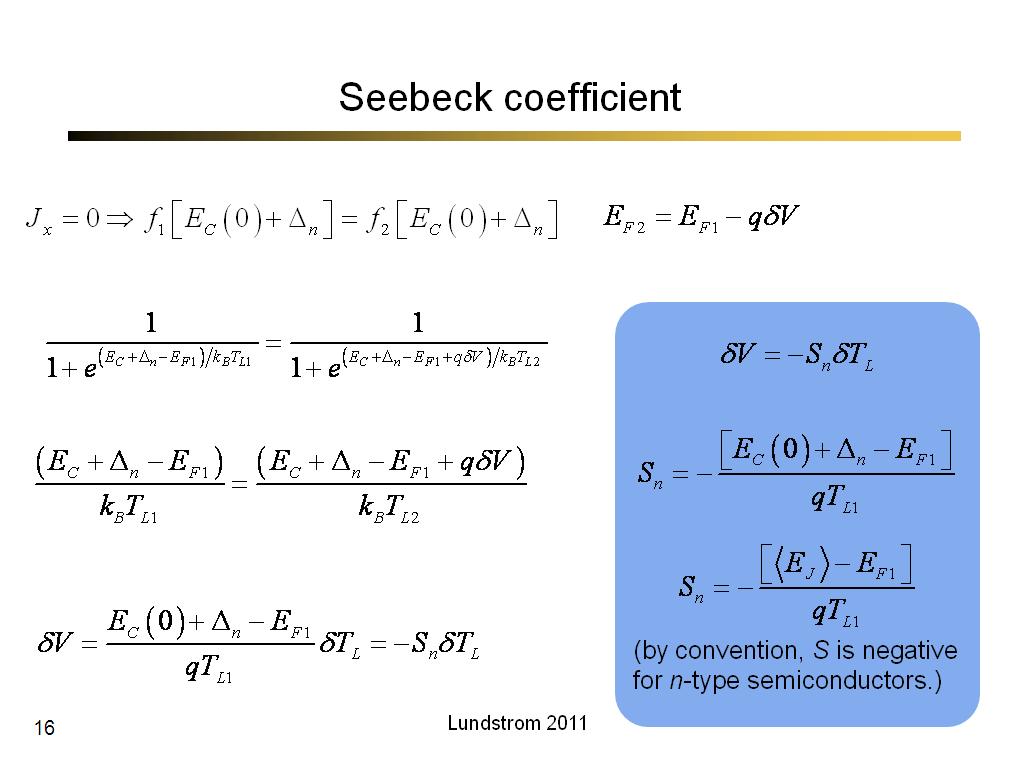 16. Seebeck coefficient
984.5
00:00/00:00
16. Seebeck coefficient
984.5
00:00/00:00 -
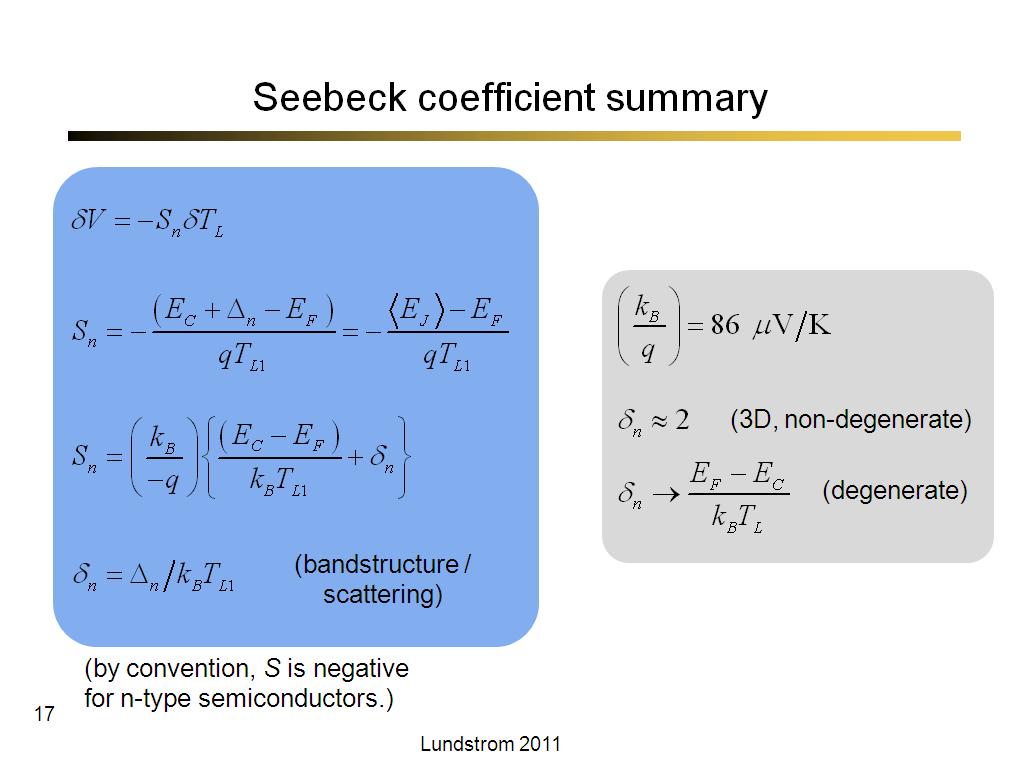 17. Seebeck coefficient summary
1068.7333333333334
00:00/00:00
17. Seebeck coefficient summary
1068.7333333333334
00:00/00:00 -
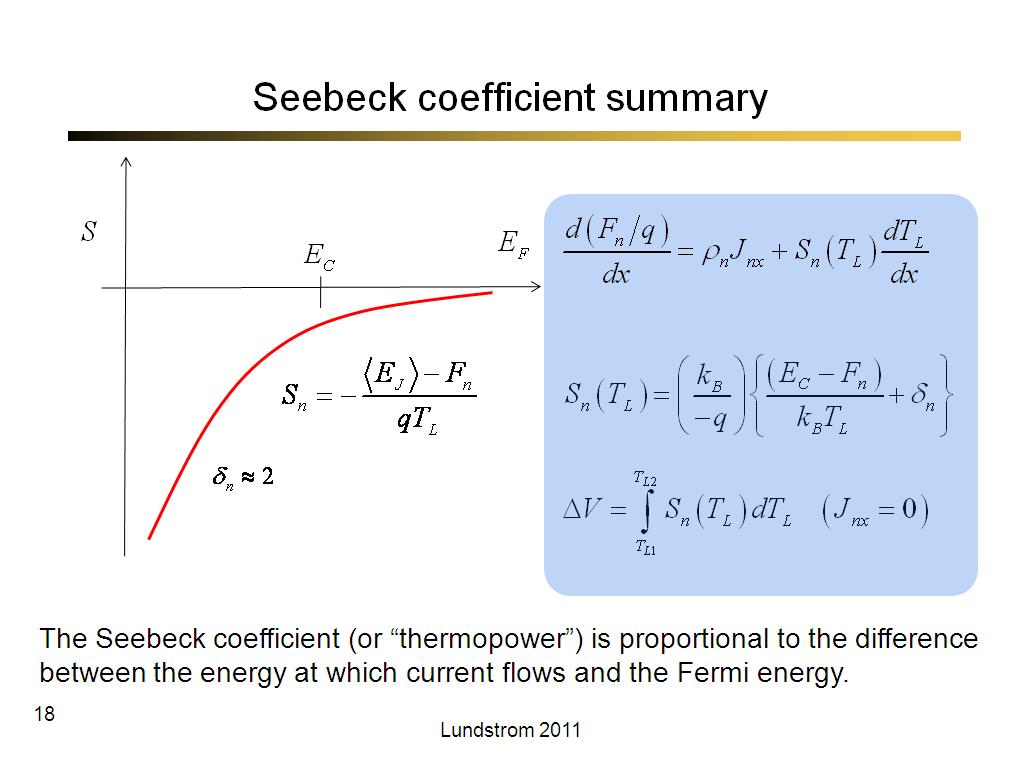
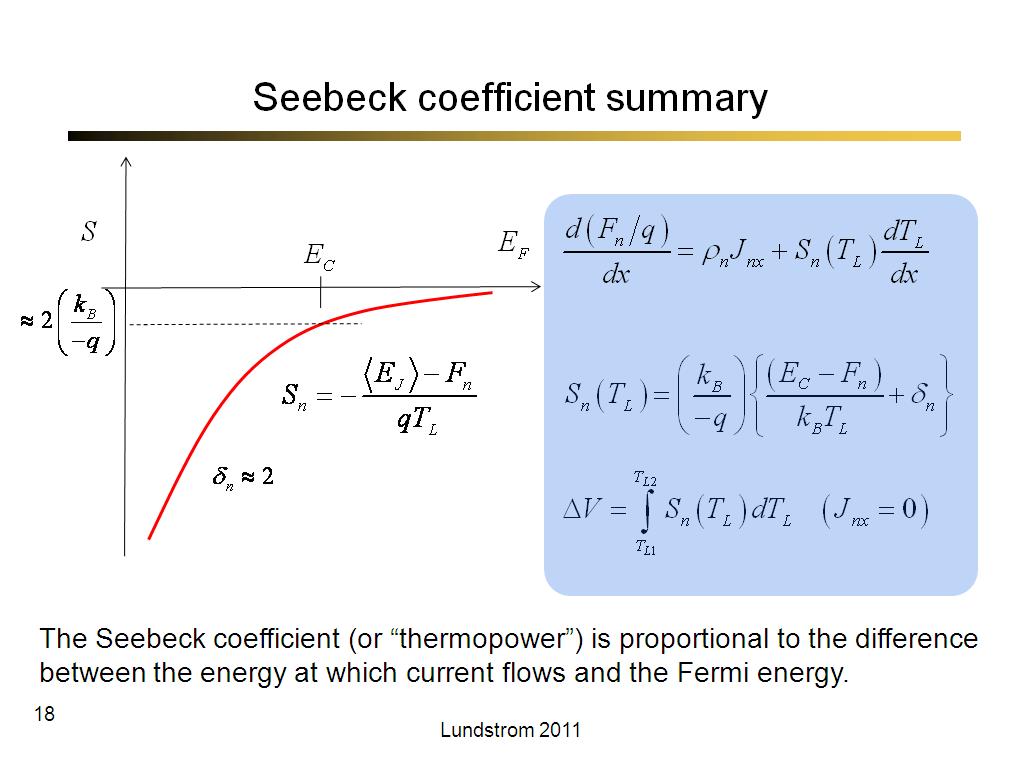
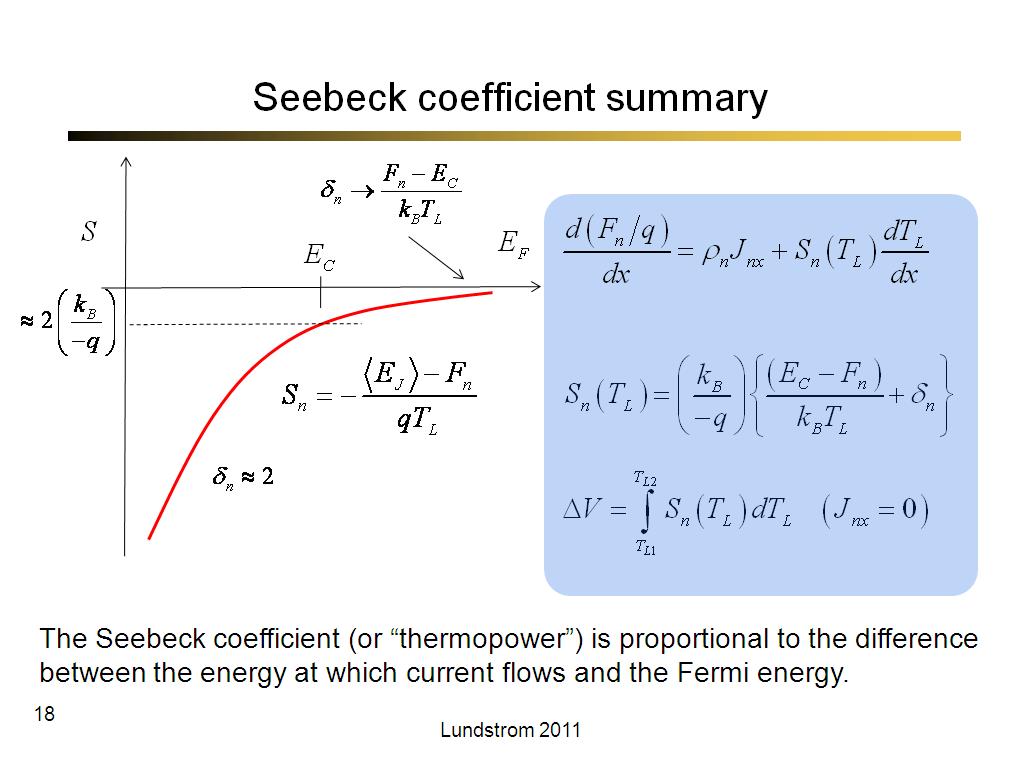 18. Seebeck coefficient summary
1163.5
00:00/00:00
18. Seebeck coefficient summary
1163.5
00:00/00:00 -
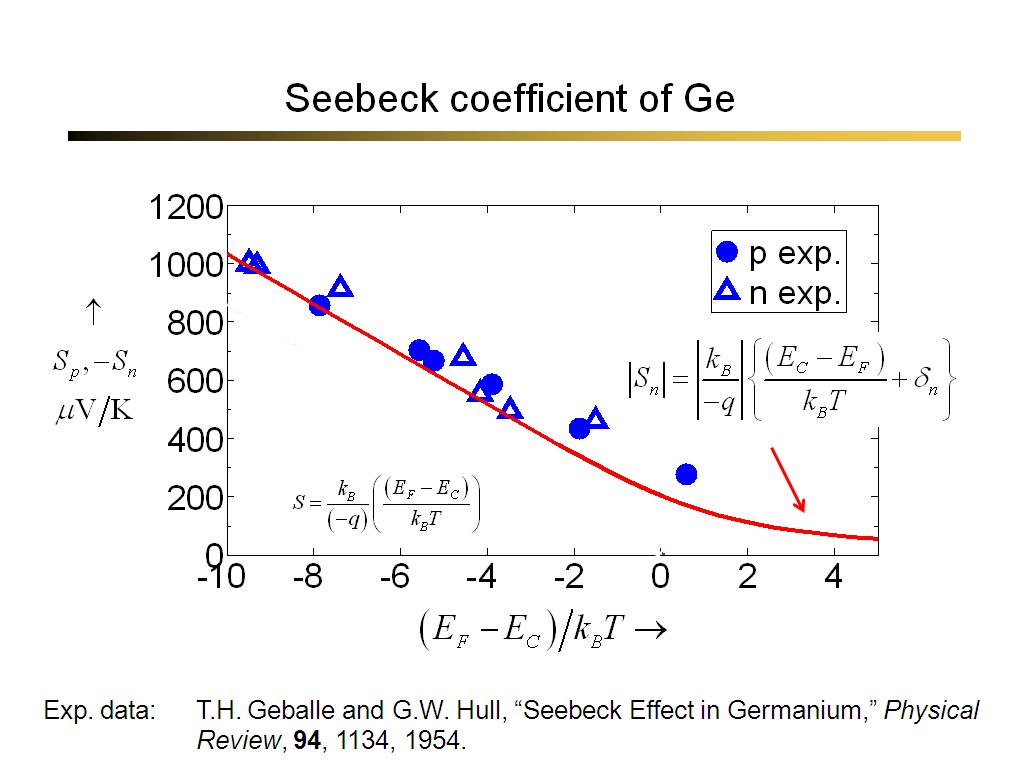 19. Seebeck coefficient of Ge
1276.9
00:00/00:00
19. Seebeck coefficient of Ge
1276.9
00:00/00:00 -
 20. outline
1320.7333333333334
00:00/00:00
20. outline
1320.7333333333334
00:00/00:00 -
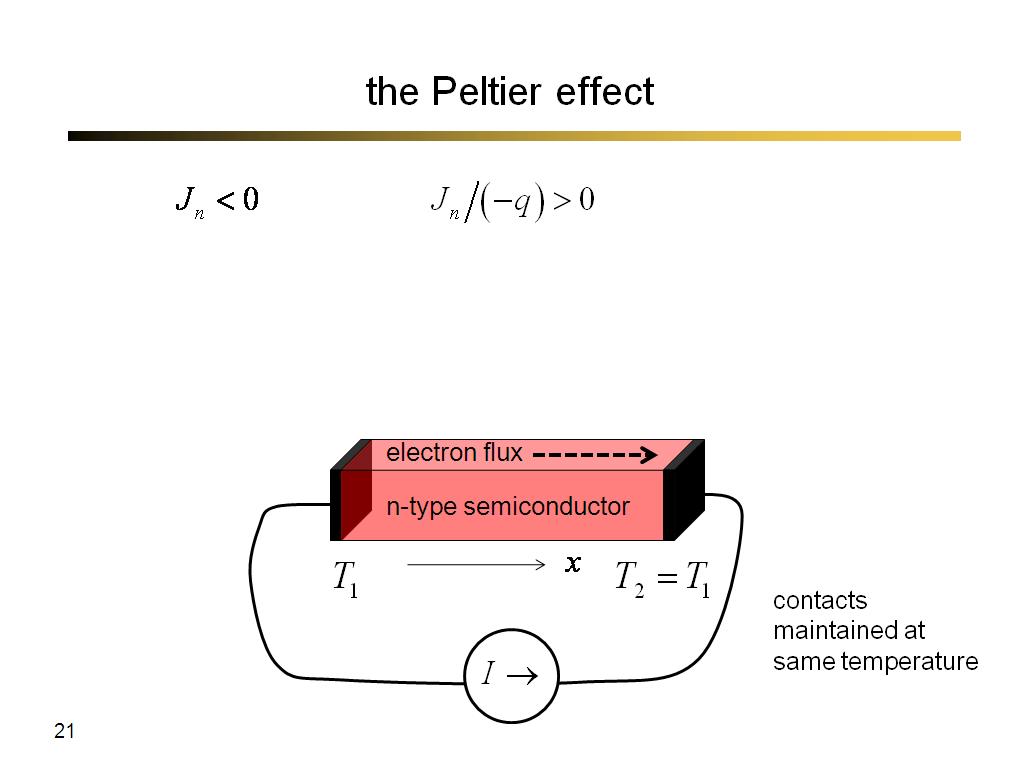
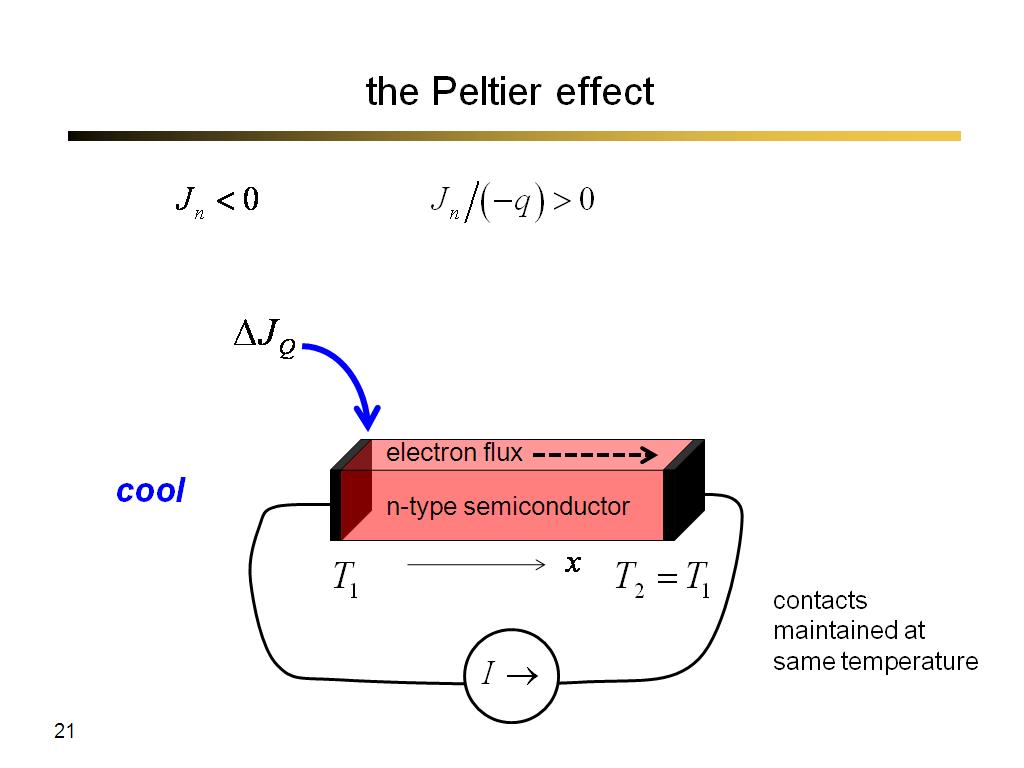
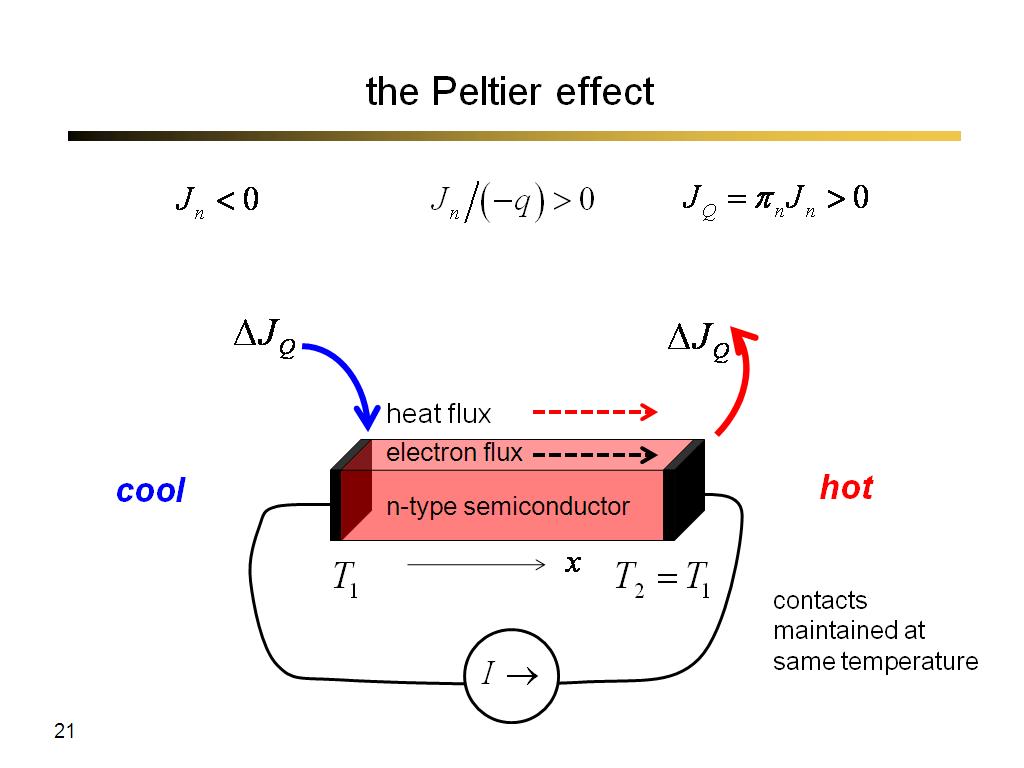 21. the Peltier effect
1339.9333333333334
00:00/00:00
21. the Peltier effect
1339.9333333333334
00:00/00:00 -
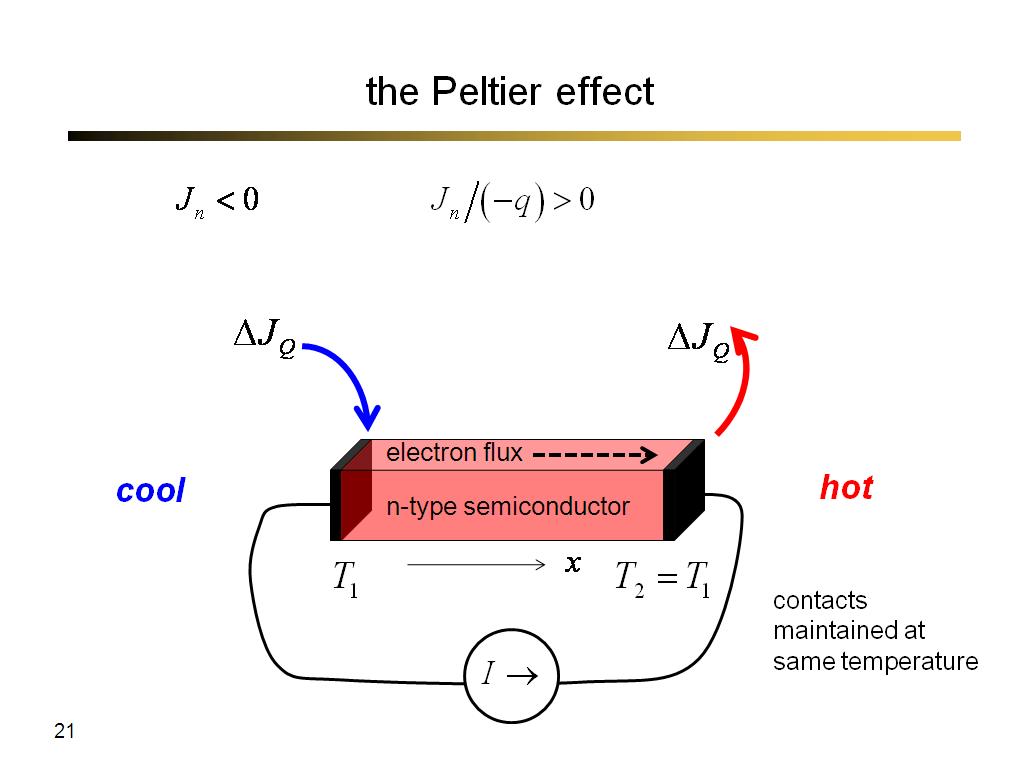
 22. understanding the Peltier effe…
1425.6666666666667
00:00/00:00
22. understanding the Peltier effe…
1425.6666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
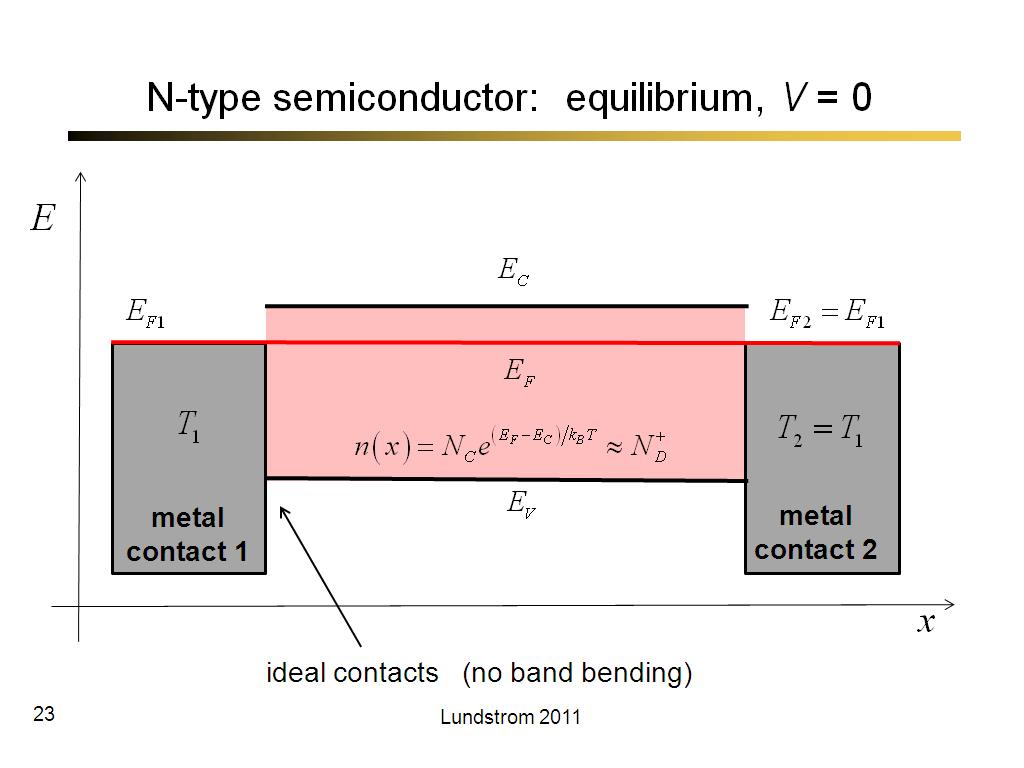 23. N-type semiconductor: equilib…
1465.2666666666667
00:00/00:00
23. N-type semiconductor: equilib…
1465.2666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
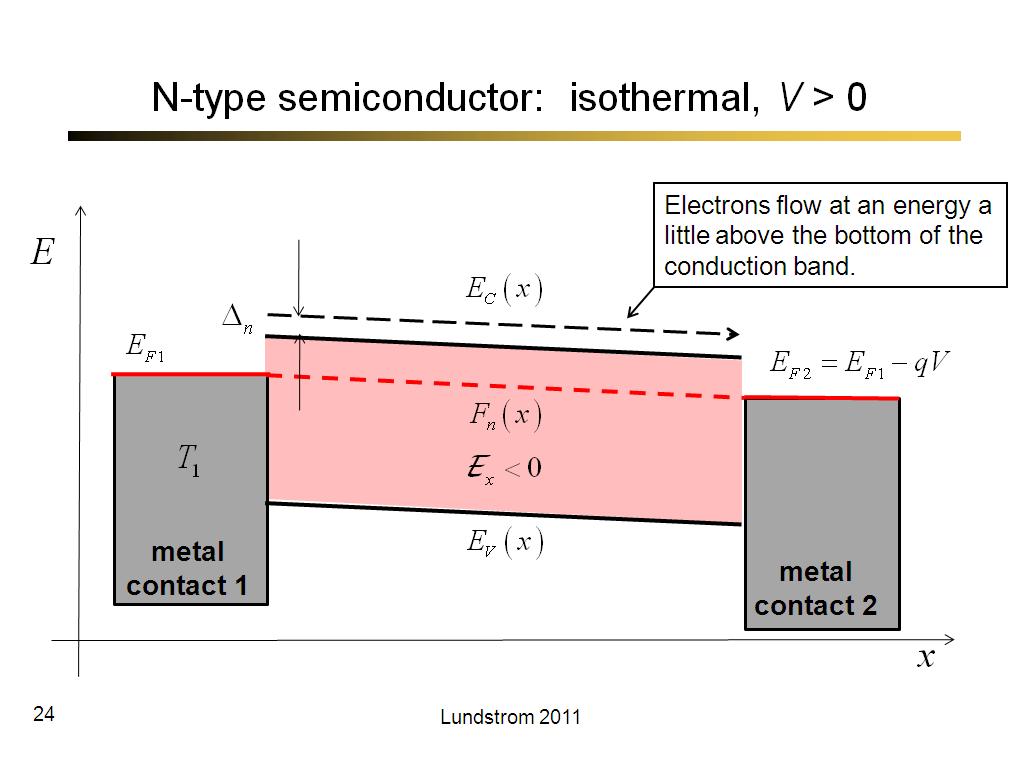
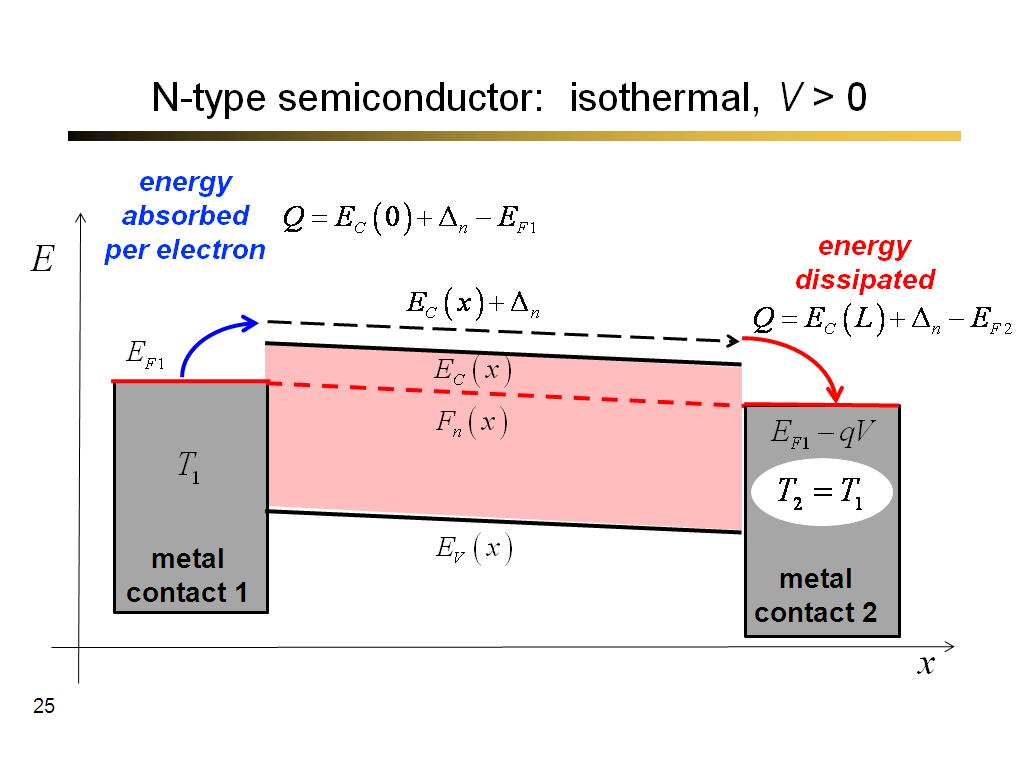
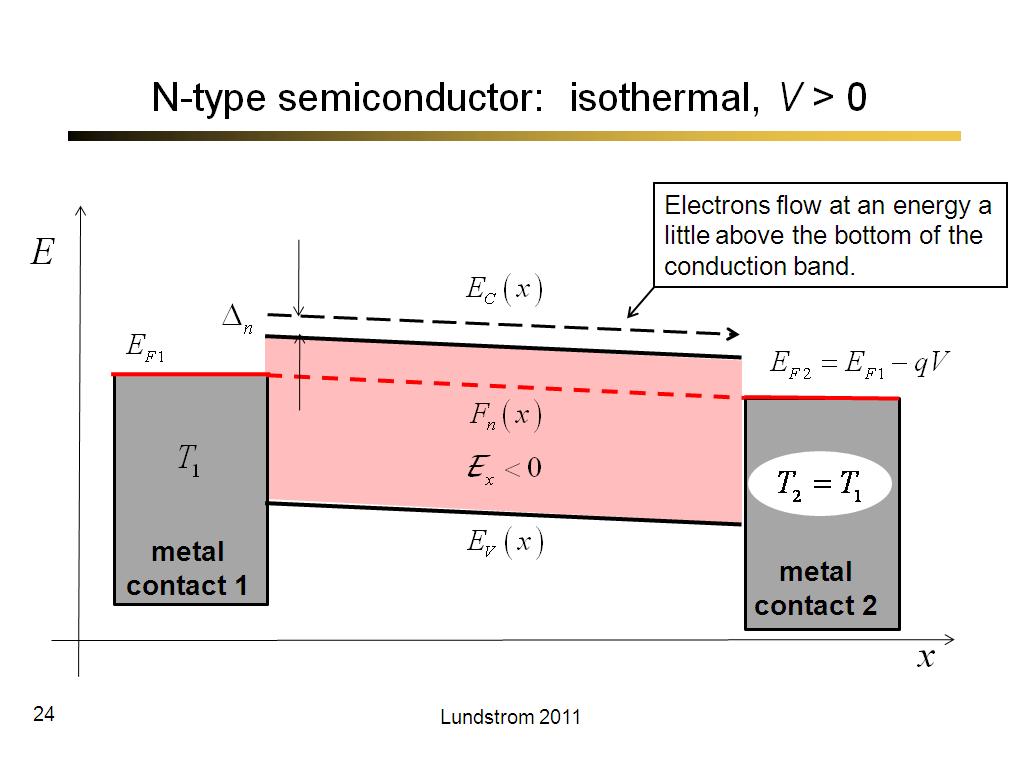 24. N-type semiconductor: isother…
1485.5333333333333
00:00/00:00
24. N-type semiconductor: isother…
1485.5333333333333
00:00/00:00 -
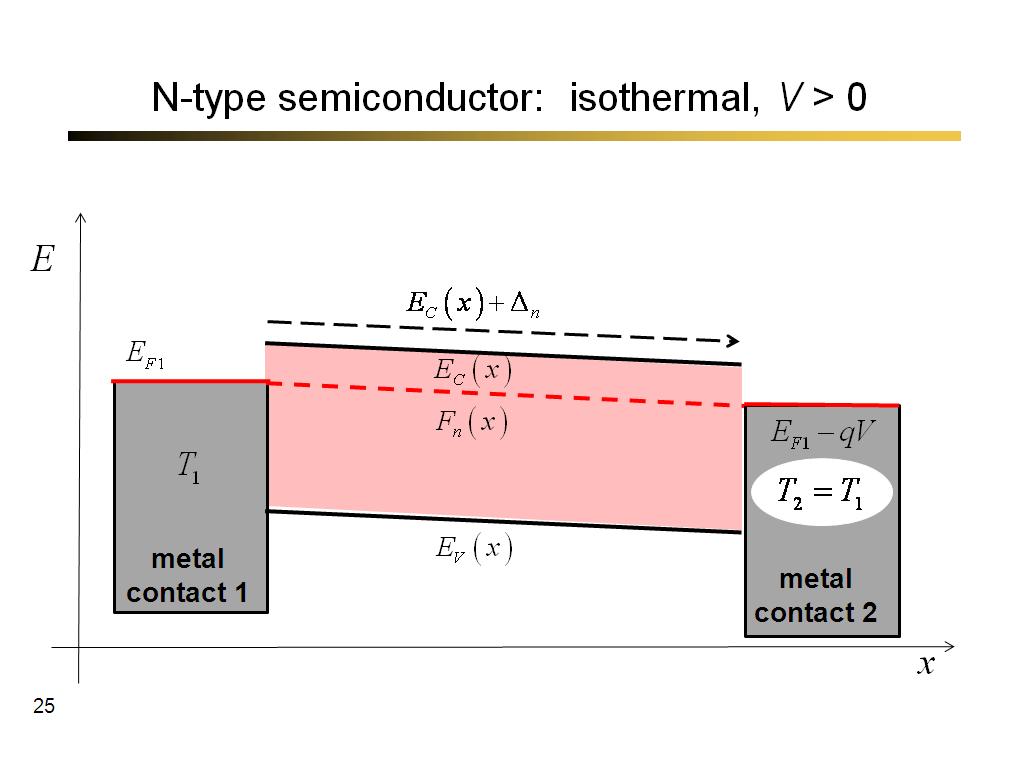
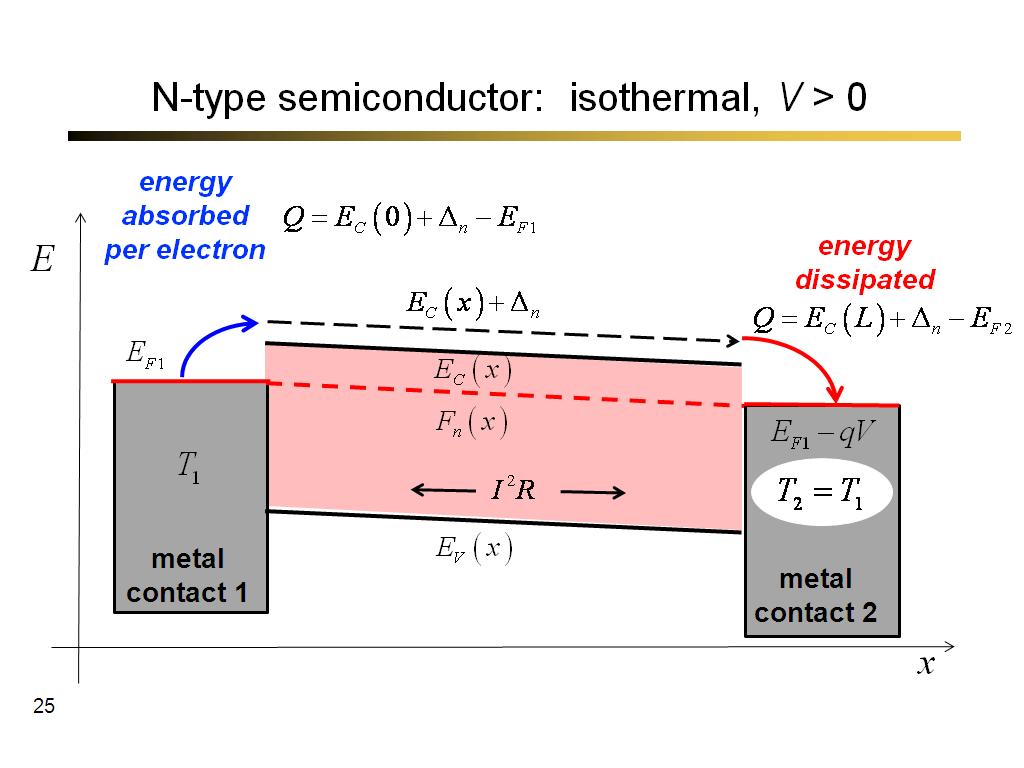
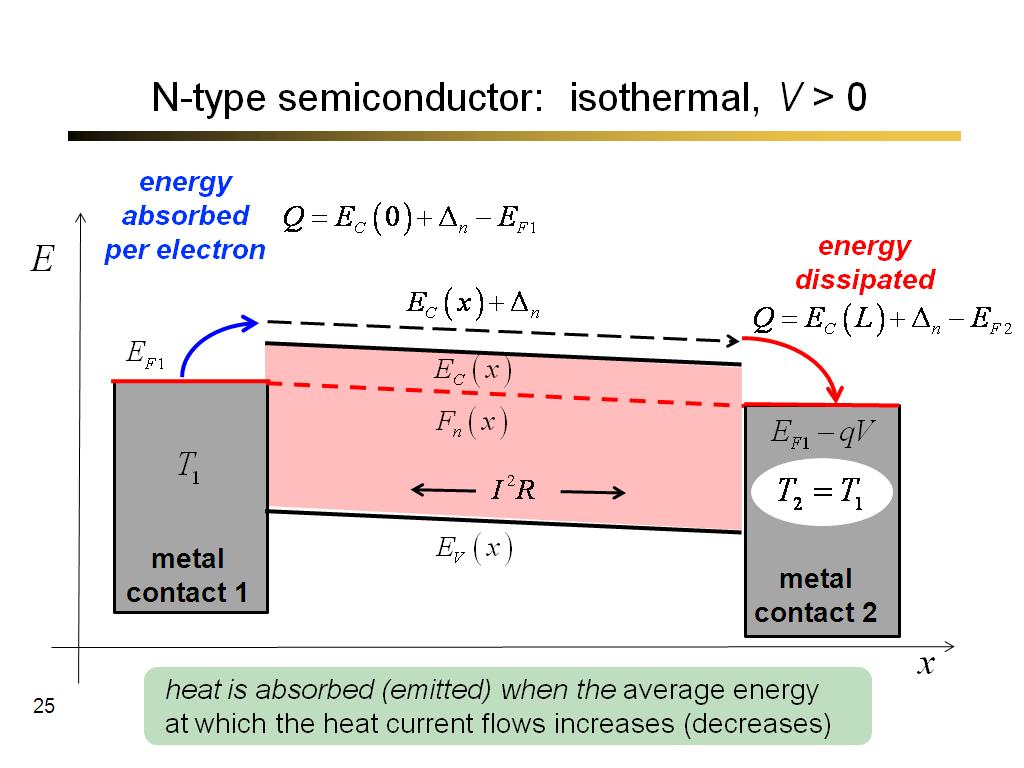 25. N-type semiconductor: isother…
1516.2666666666667
00:00/00:00
25. N-type semiconductor: isother…
1516.2666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
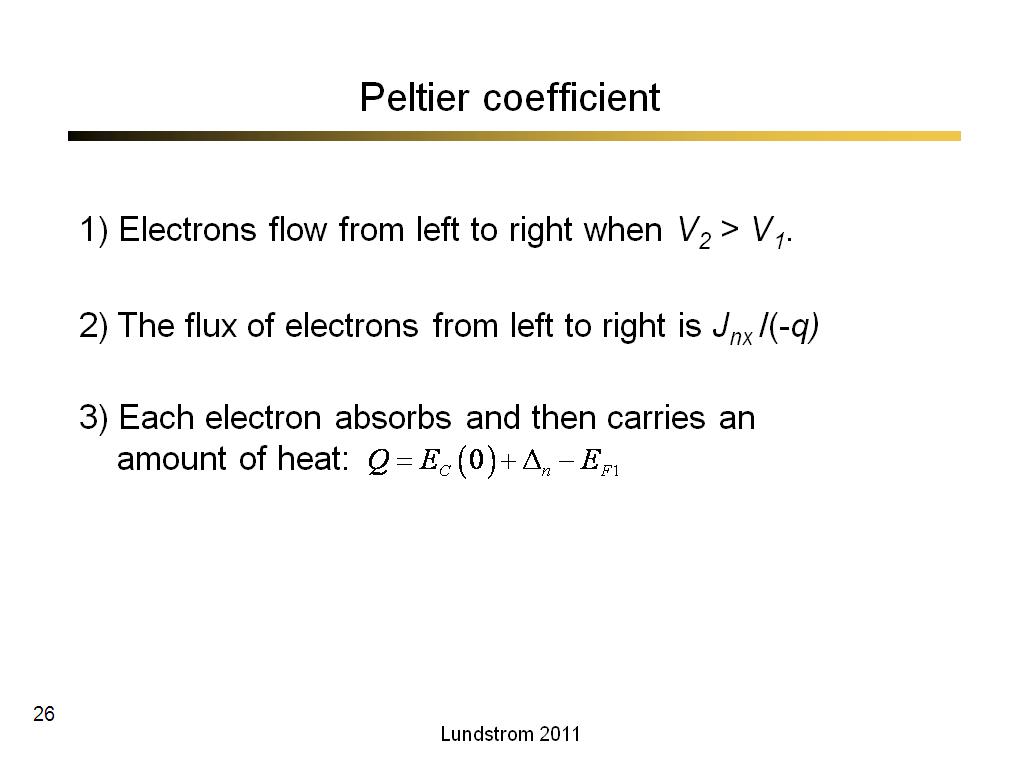
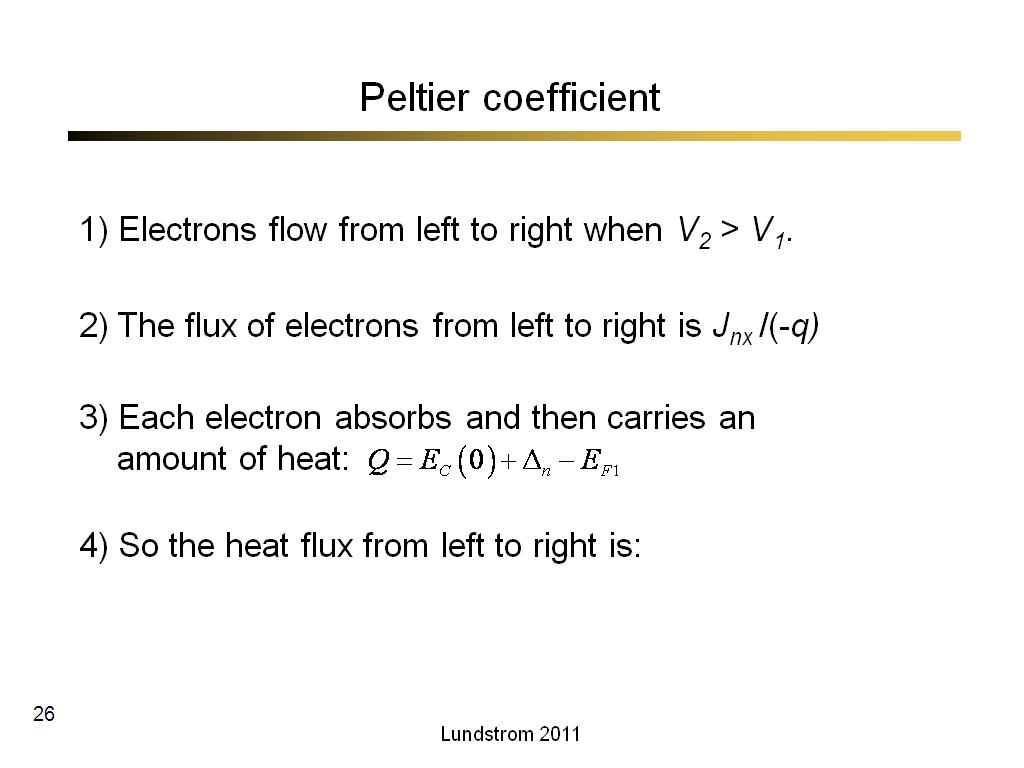
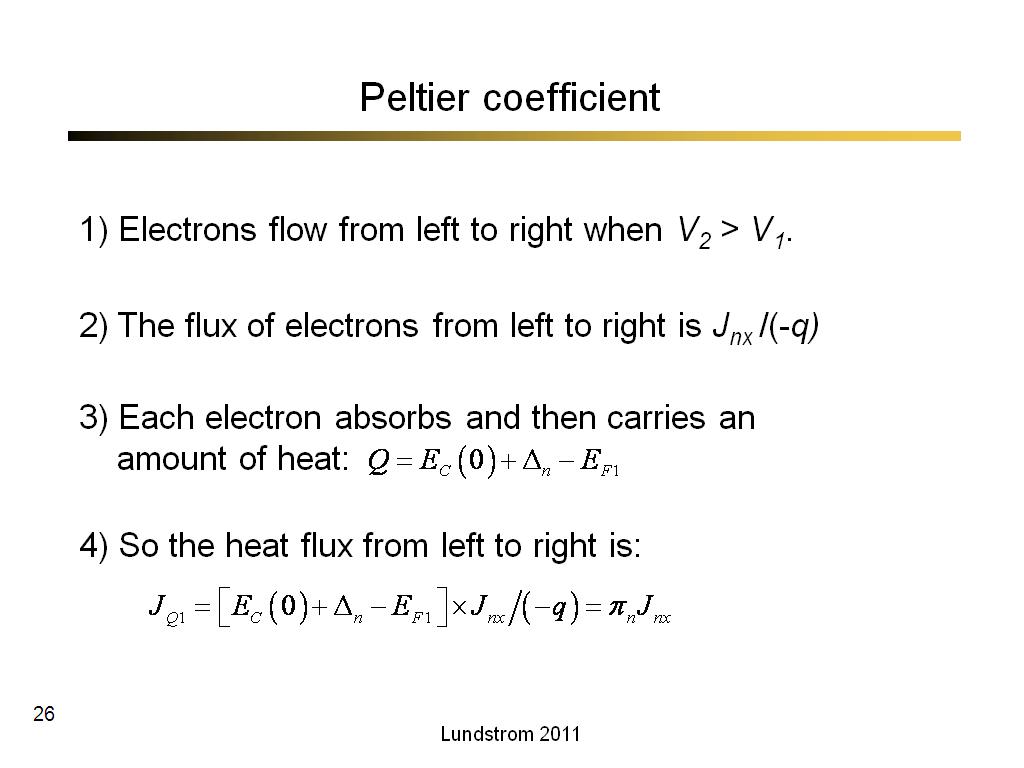
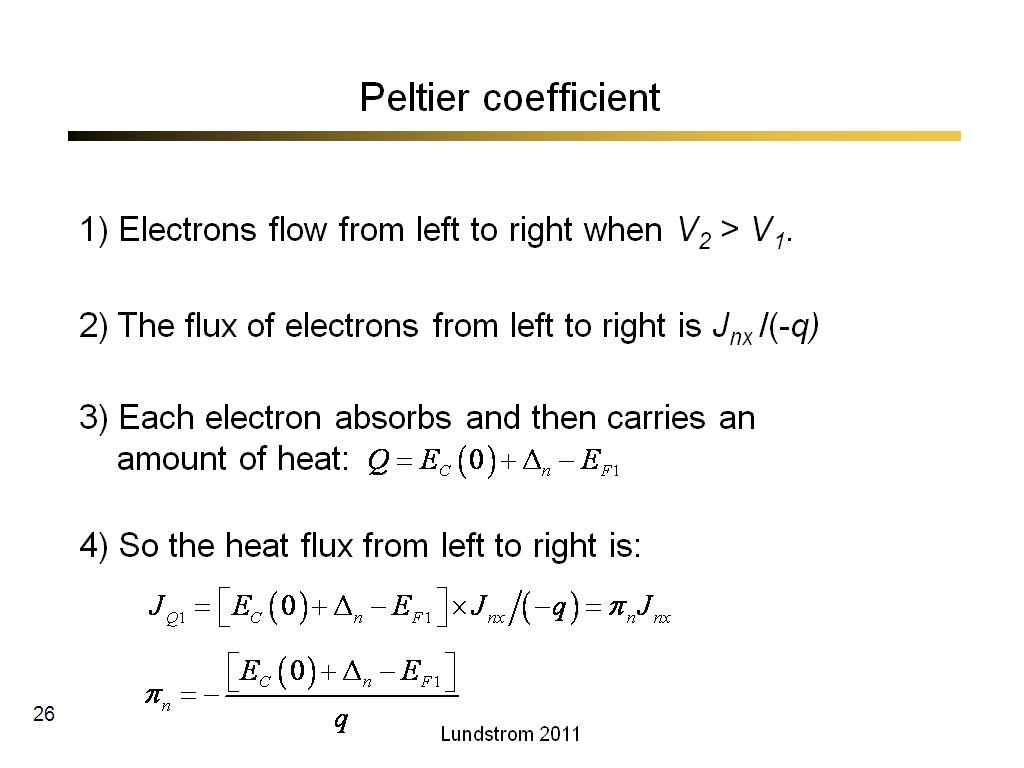
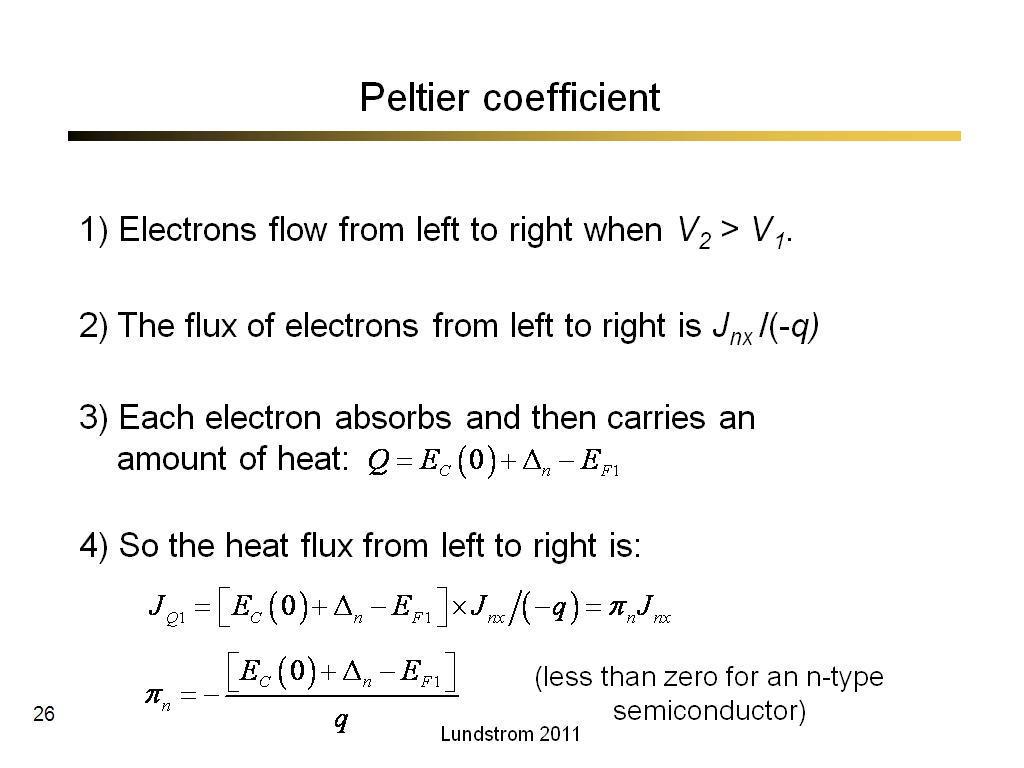 26. Peltier coefficient
1677.1333333333334
00:00/00:00
26. Peltier coefficient
1677.1333333333334
00:00/00:00 -
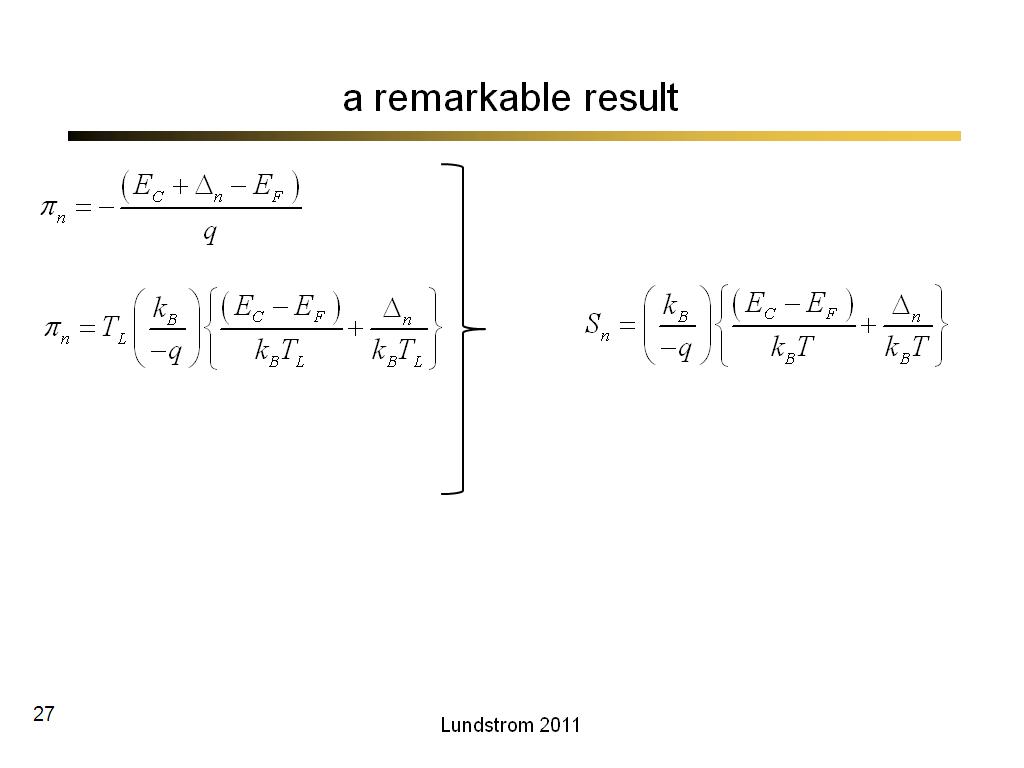
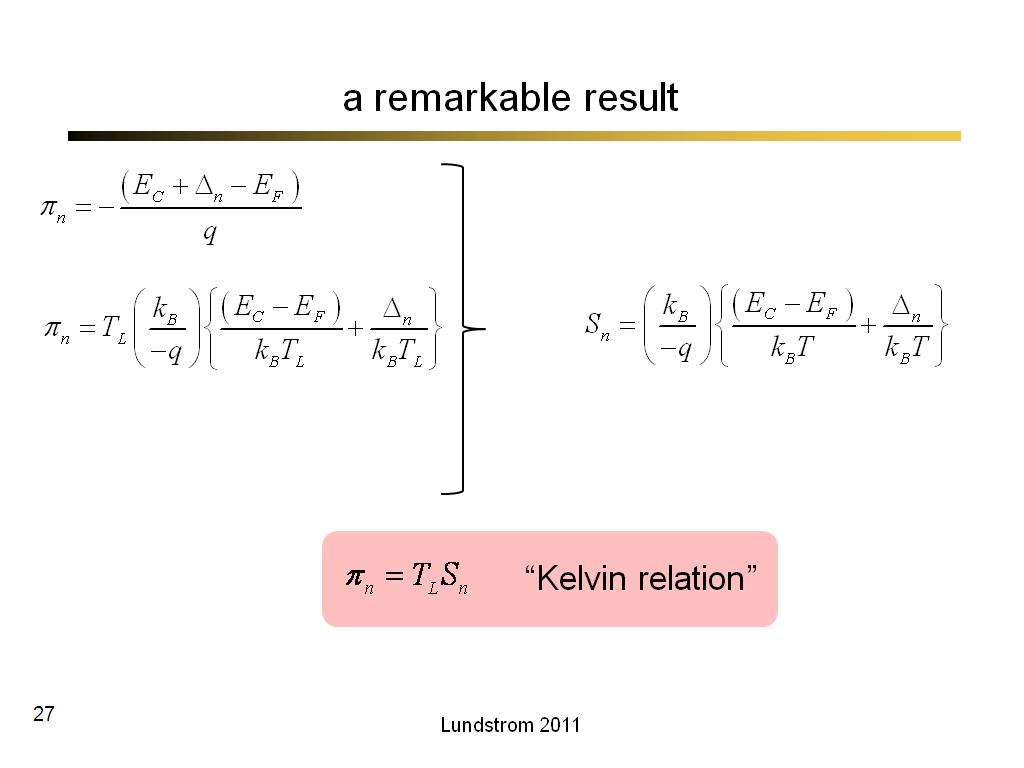
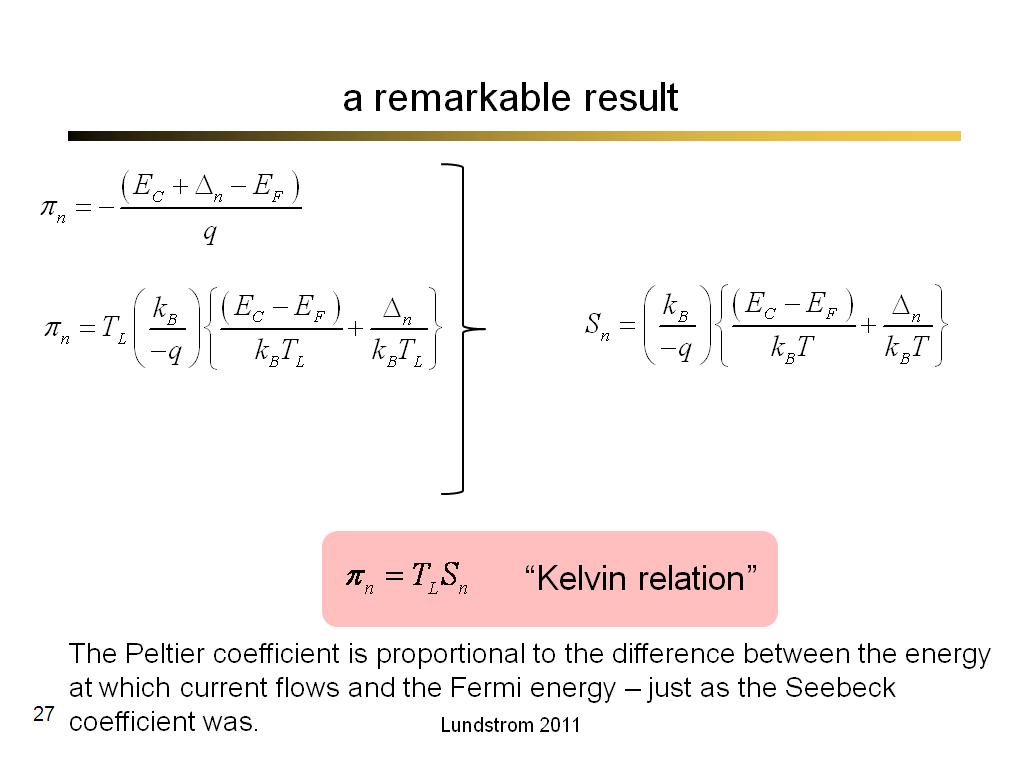 27. a remarkable result
1725
00:00/00:00
27. a remarkable result
1725
00:00/00:00 -
 28. outline
1785.4333333333334
00:00/00:00
28. outline
1785.4333333333334
00:00/00:00 -
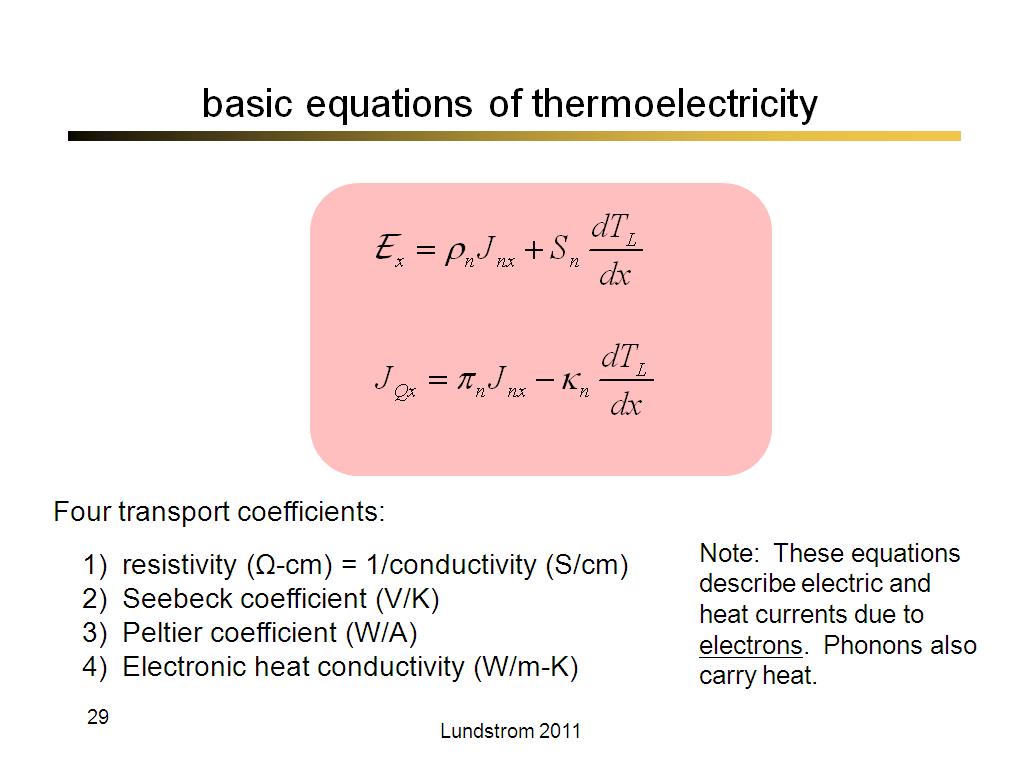 29. basic equations of thermoelect…
1790.7666666666667
00:00/00:00
29. basic equations of thermoelect…
1790.7666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
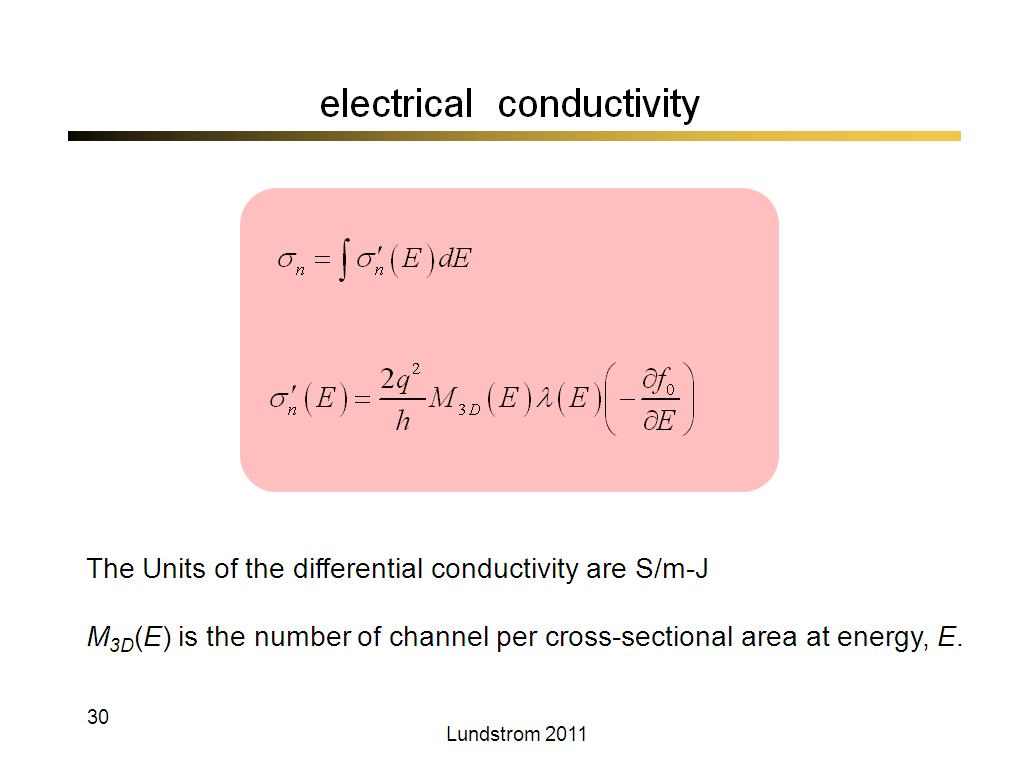 30. electrical conductivity
1877.9666666666667
00:00/00:00
30. electrical conductivity
1877.9666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
 31. Seebeck coefficient
1906.1333333333334
00:00/00:00
31. Seebeck coefficient
1906.1333333333334
00:00/00:00 -
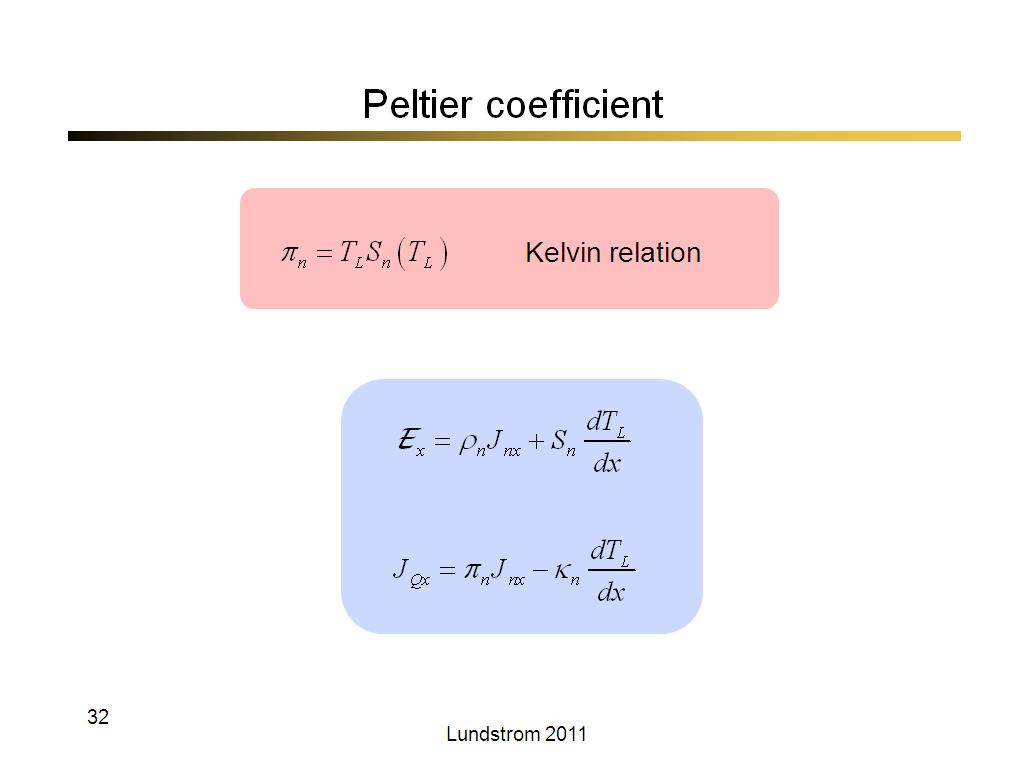
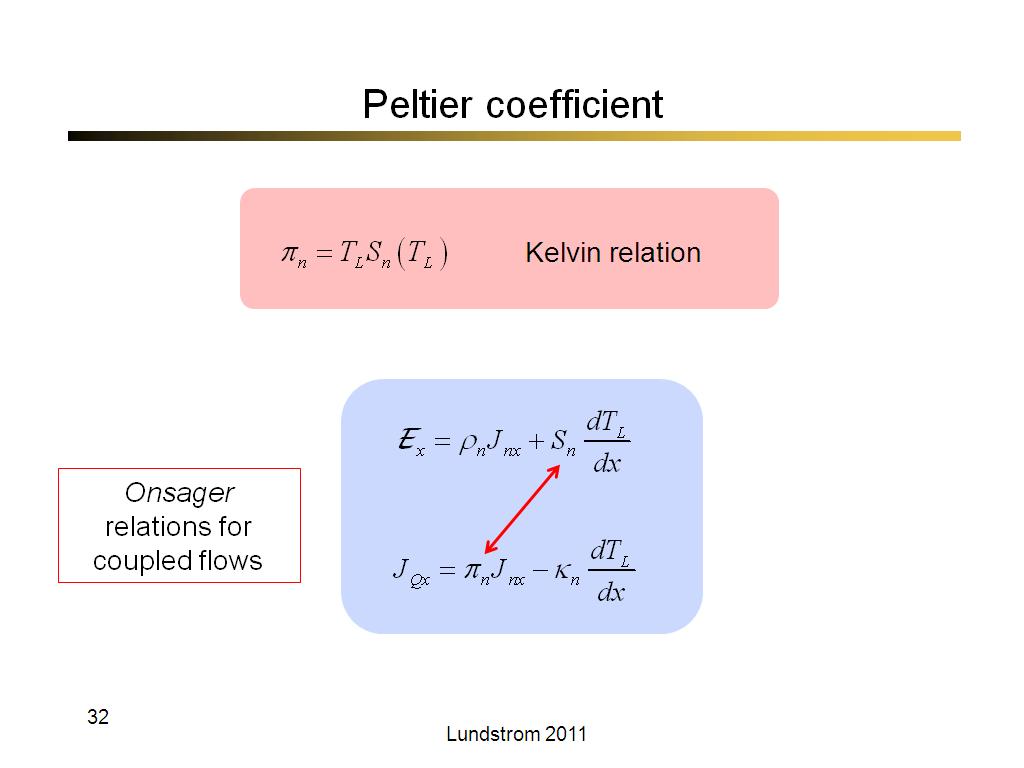 32. Peltier coefficient
1980.4666666666667
00:00/00:00
32. Peltier coefficient
1980.4666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
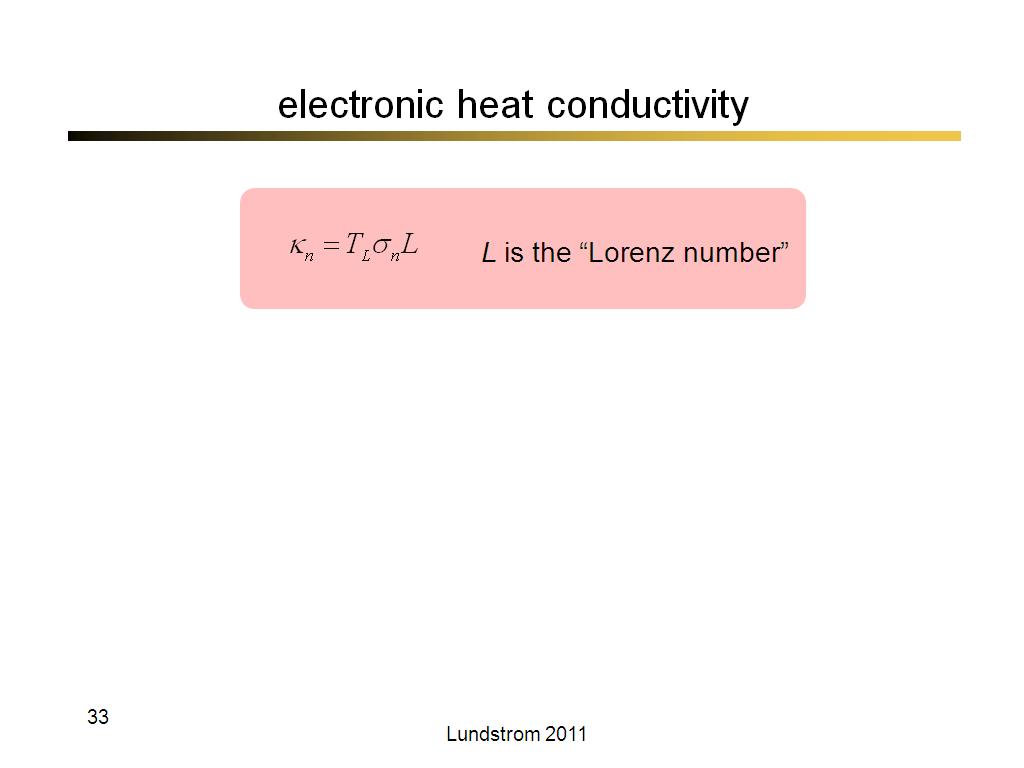
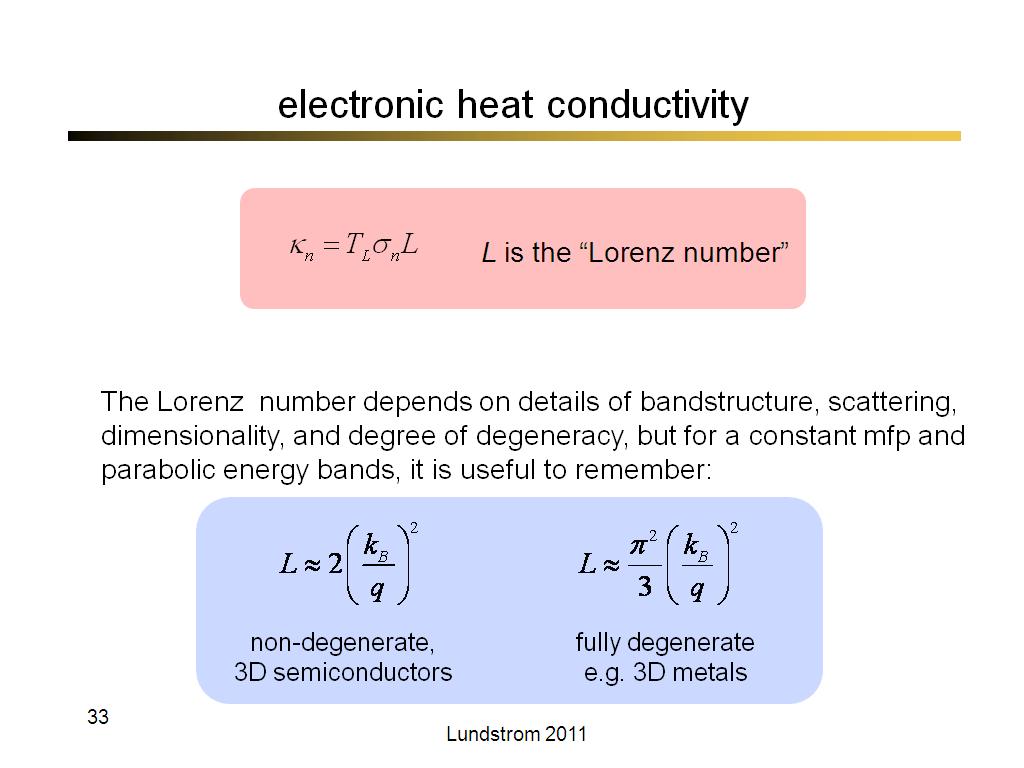 33. electronic heat conductivity
2049.7666666666669
00:00/00:00
33. electronic heat conductivity
2049.7666666666669
00:00/00:00 -
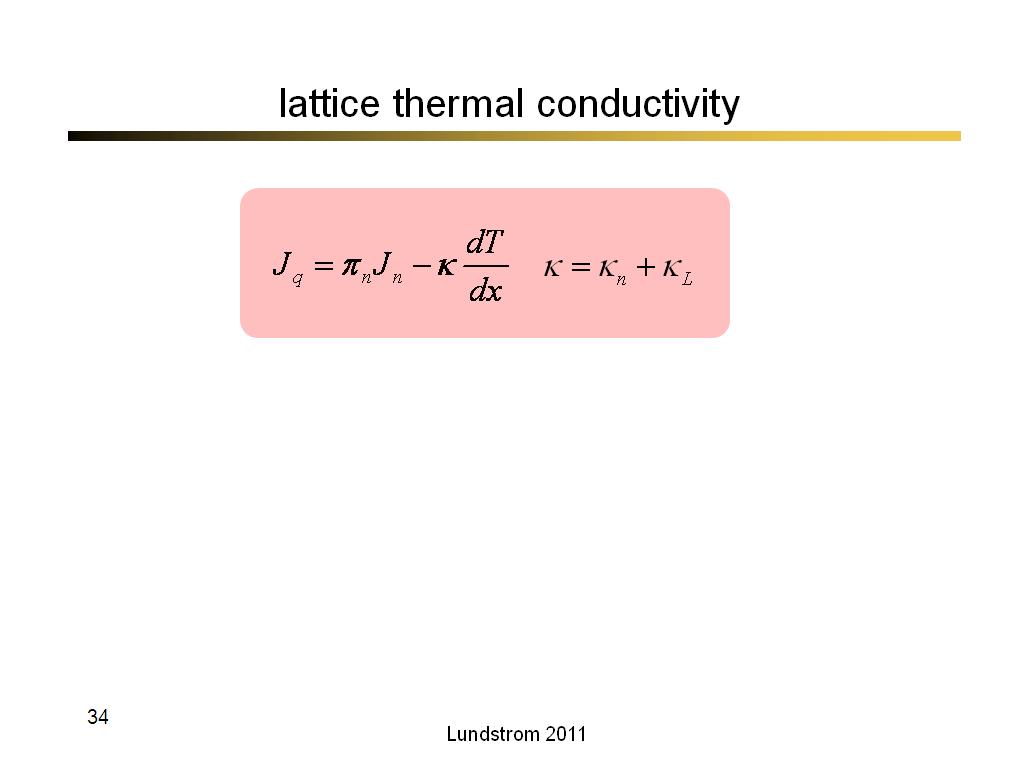
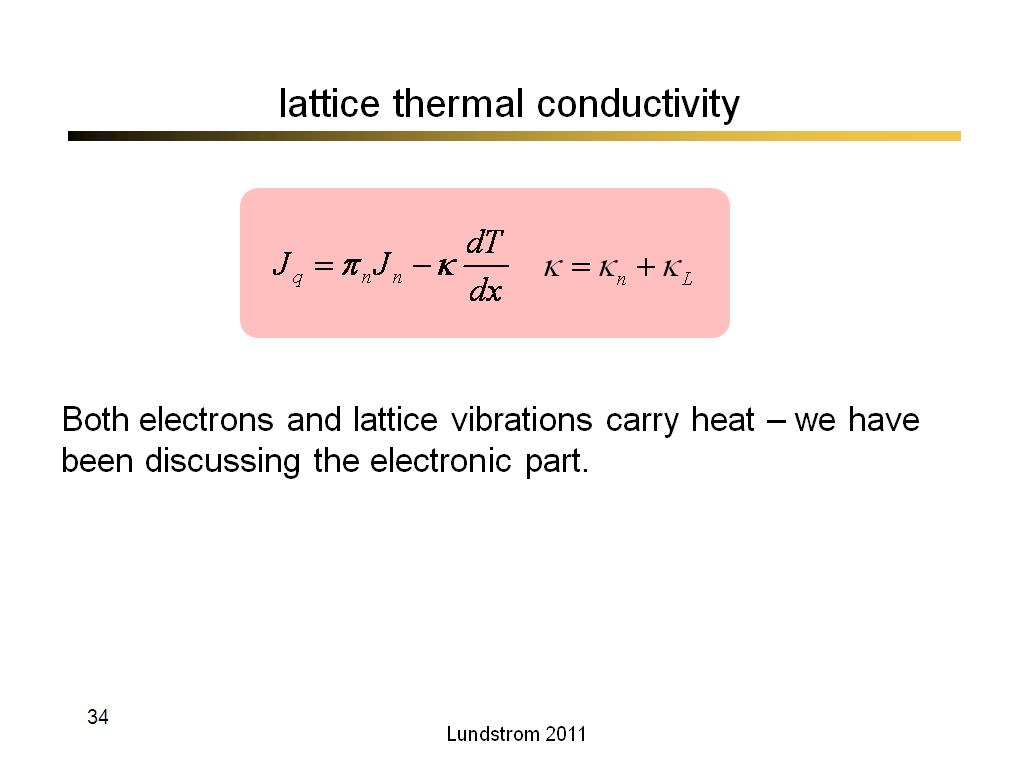
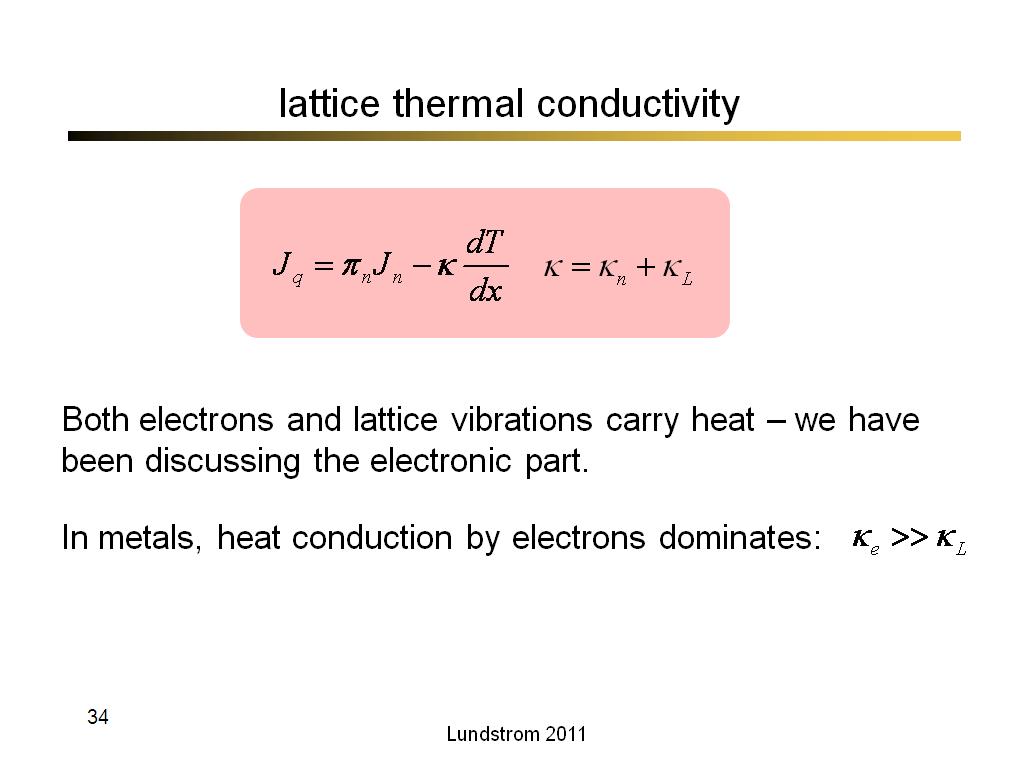
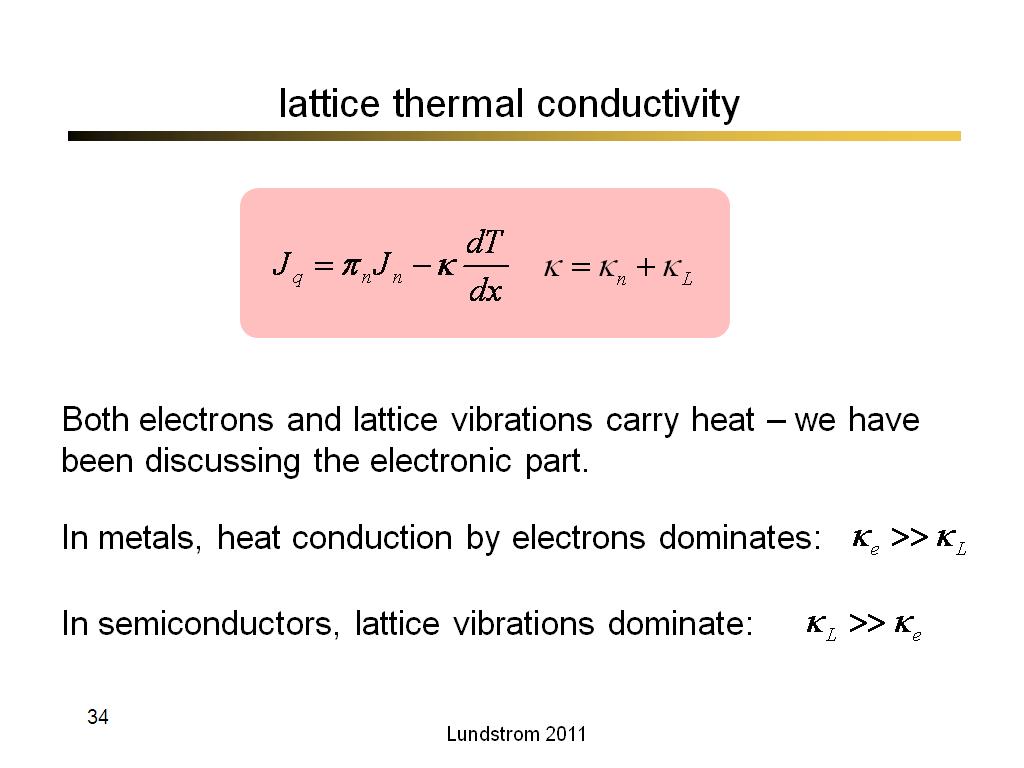 34. lattice thermal conductivity
2184.9
00:00/00:00
34. lattice thermal conductivity
2184.9
00:00/00:00 -
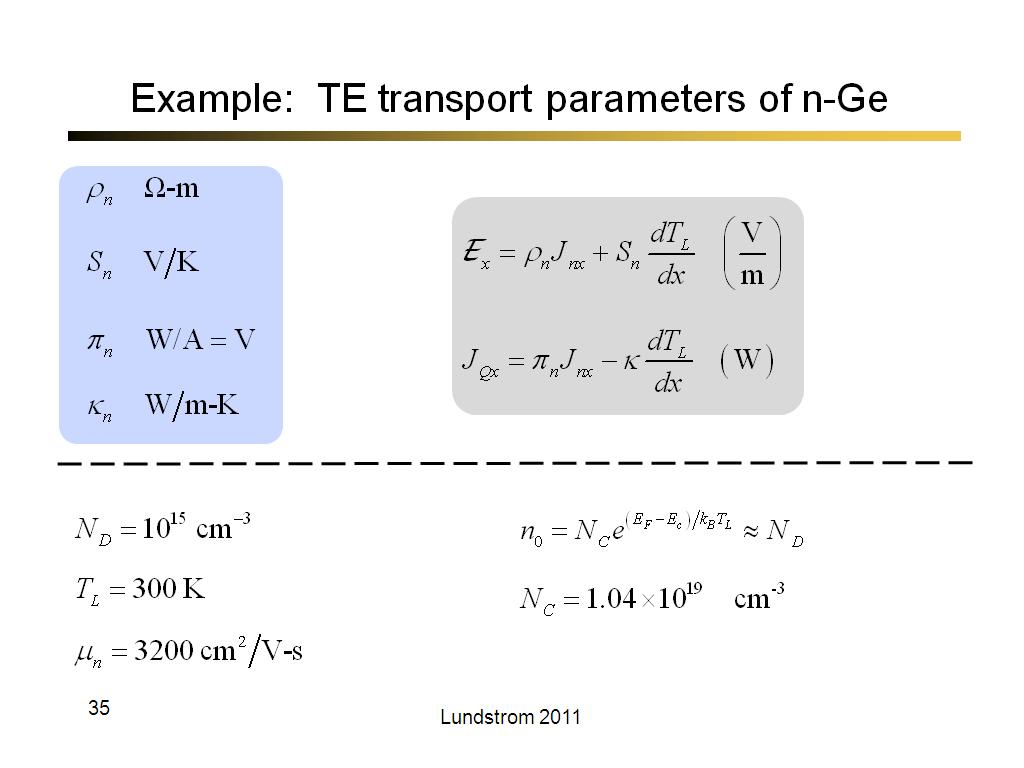 35. Example: TE transport paramet…
2217.3666666666668
00:00/00:00
35. Example: TE transport paramet…
2217.3666666666668
00:00/00:00 -
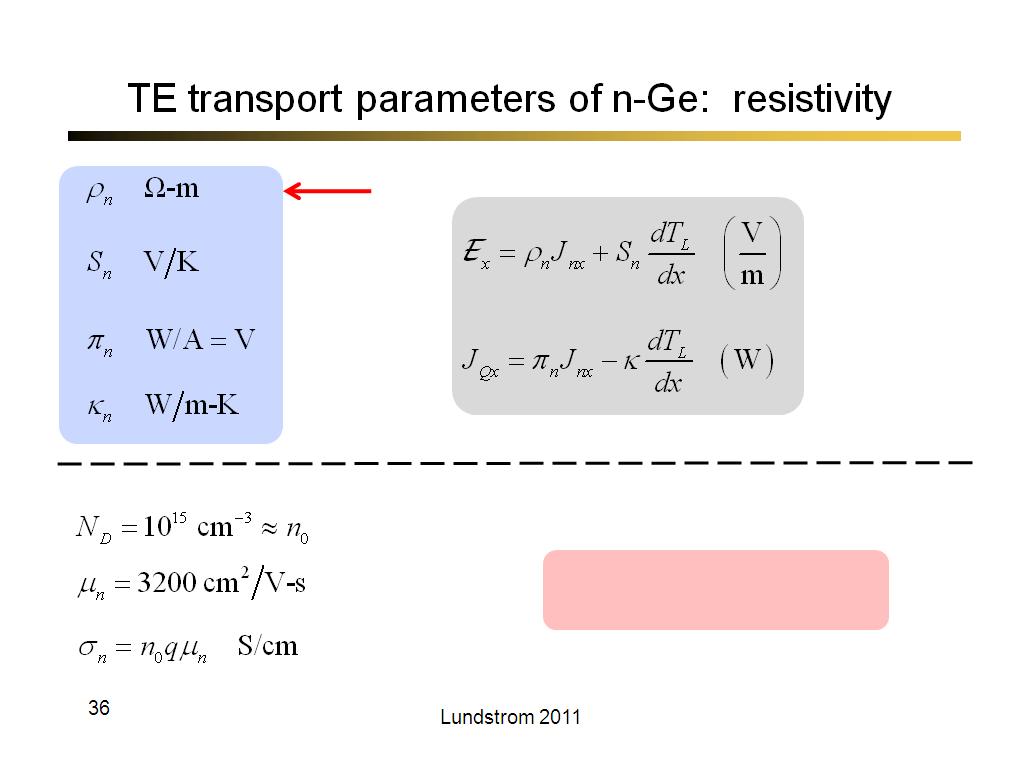
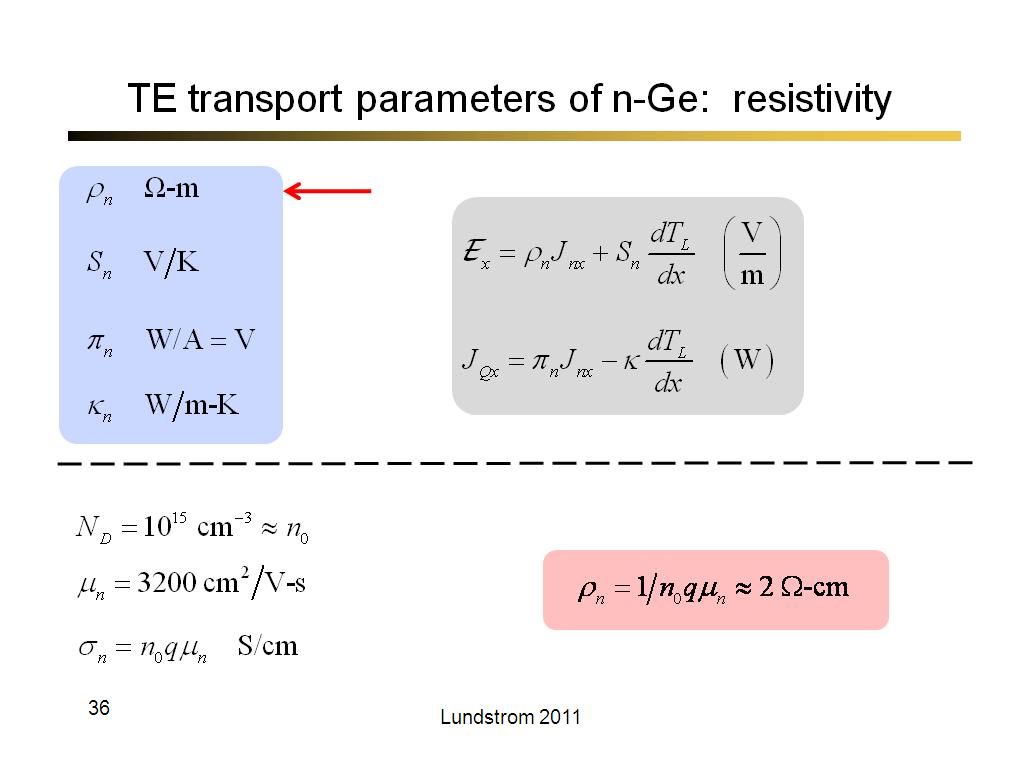 36. TE transport parameters of n-G…
2268.7333333333331
00:00/00:00
36. TE transport parameters of n-G…
2268.7333333333331
00:00/00:00 -
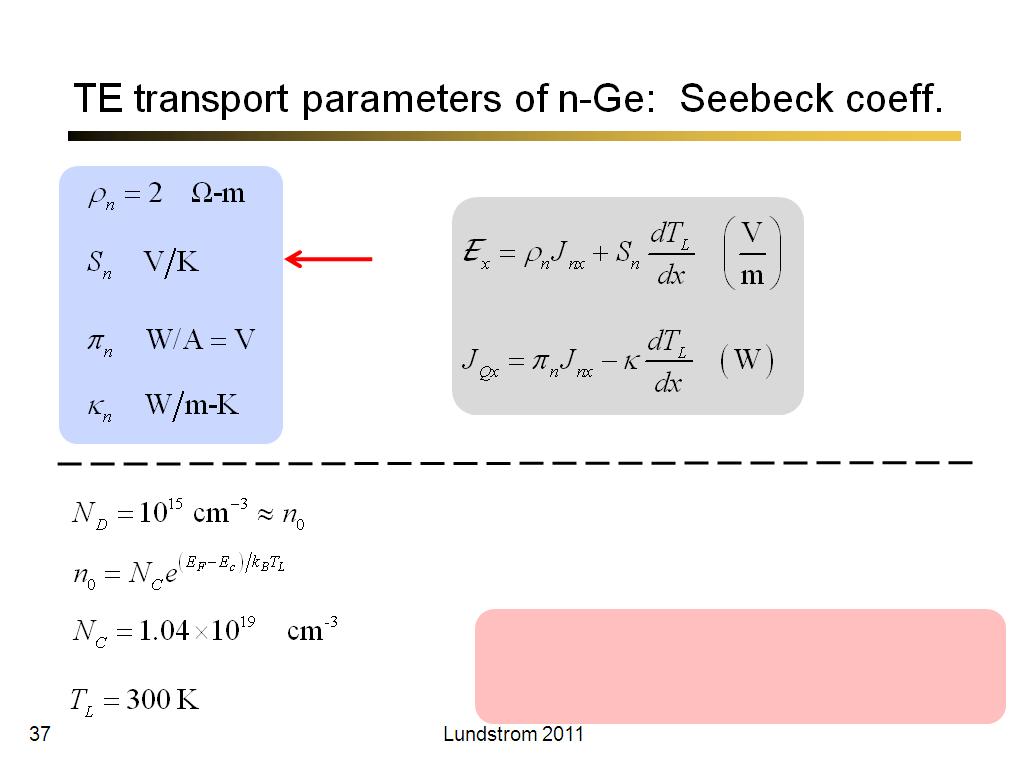
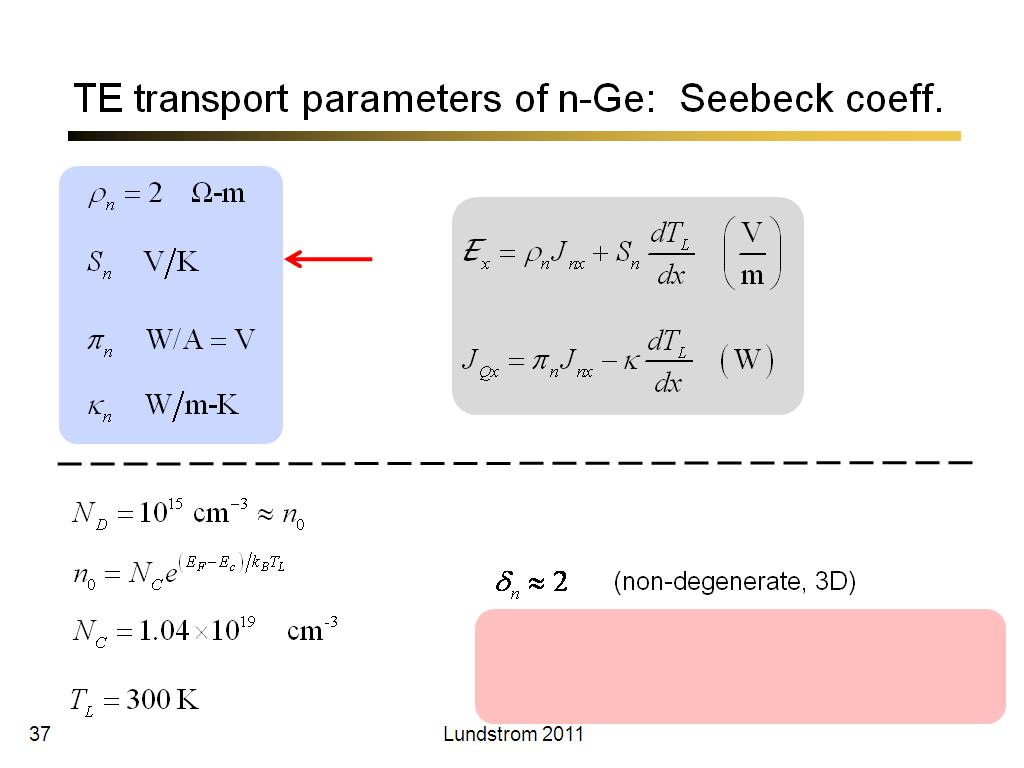
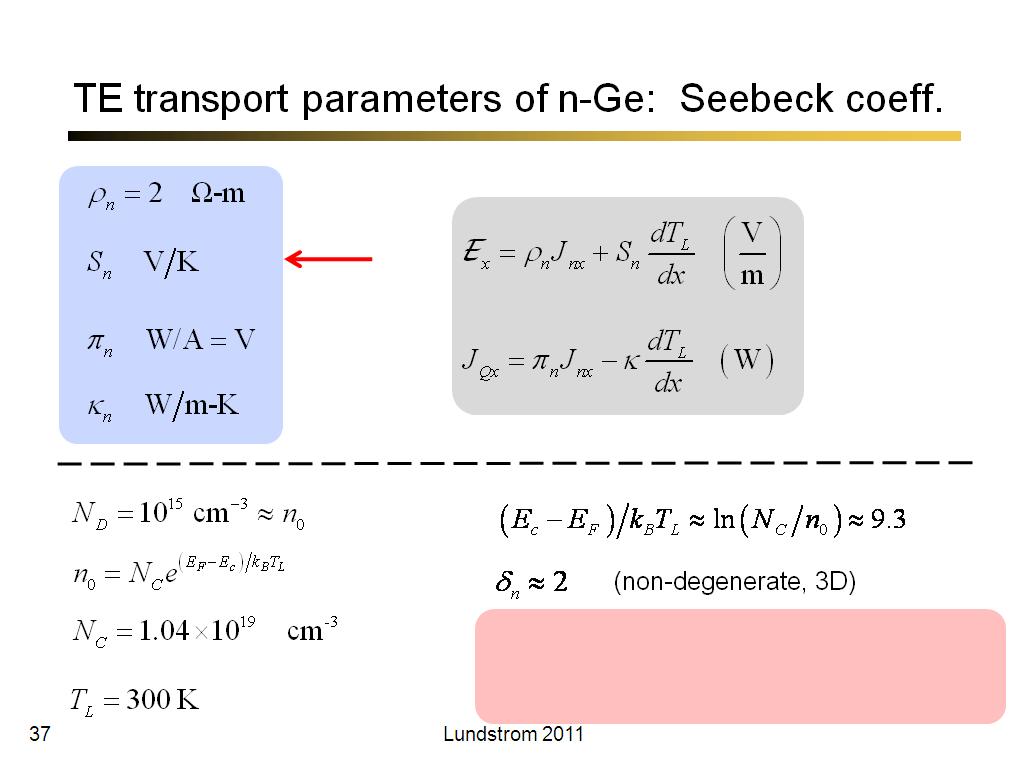
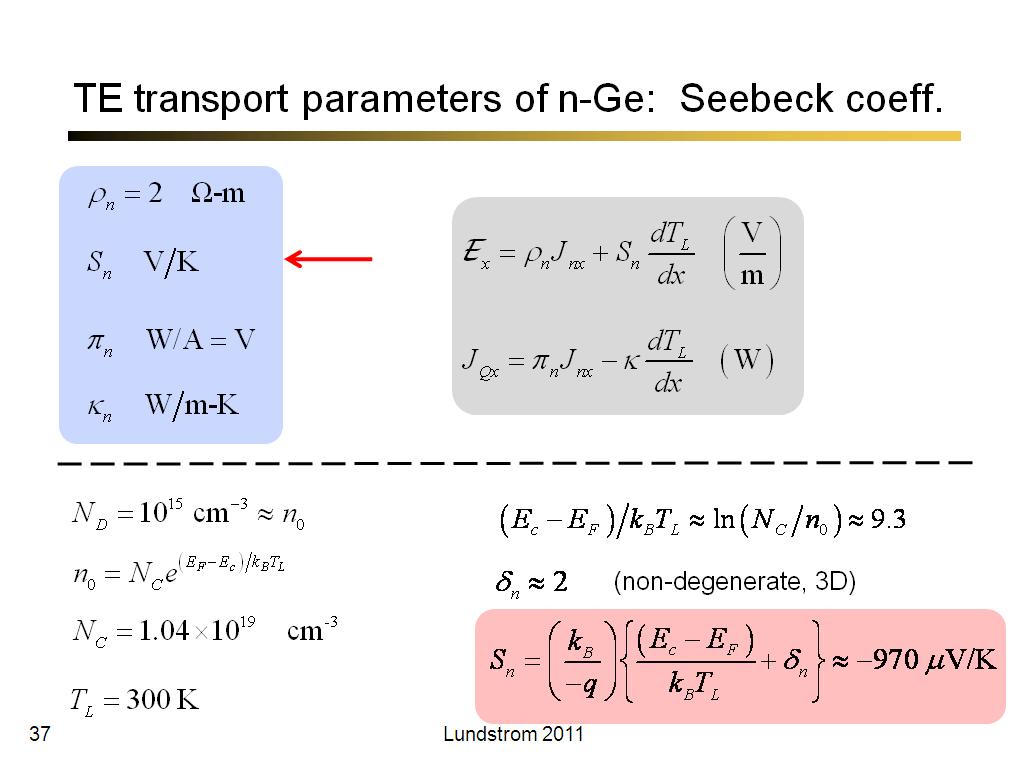 37. TE transport parameters of n-G…
2286.8333333333335
00:00/00:00
37. TE transport parameters of n-G…
2286.8333333333335
00:00/00:00 -
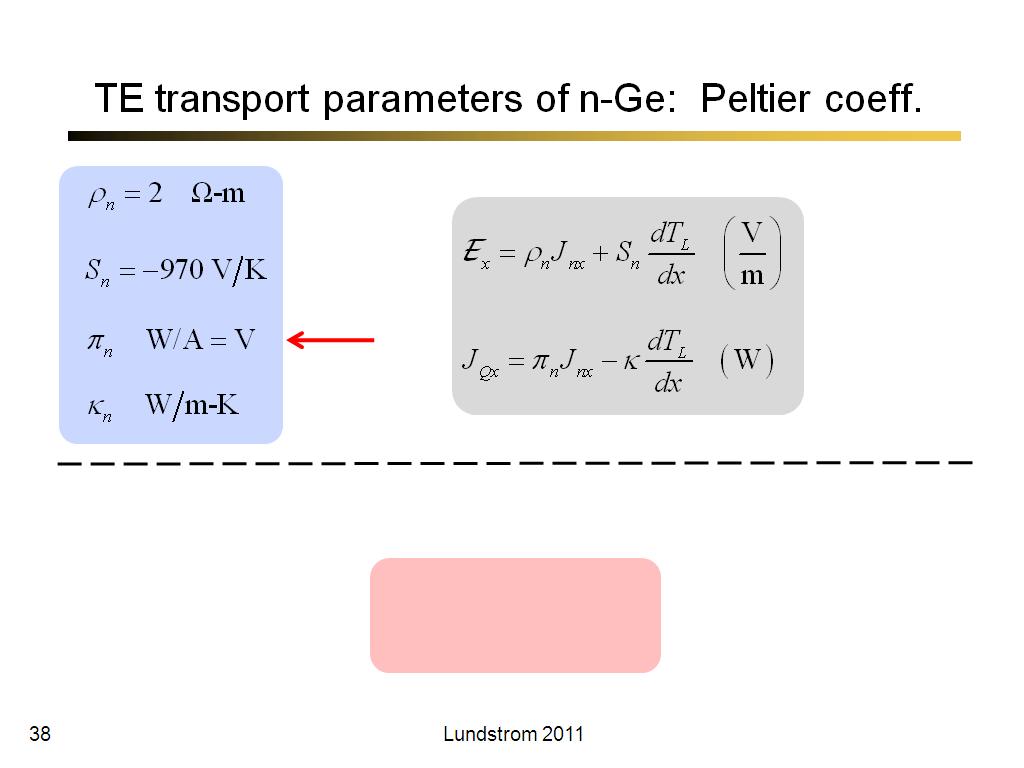
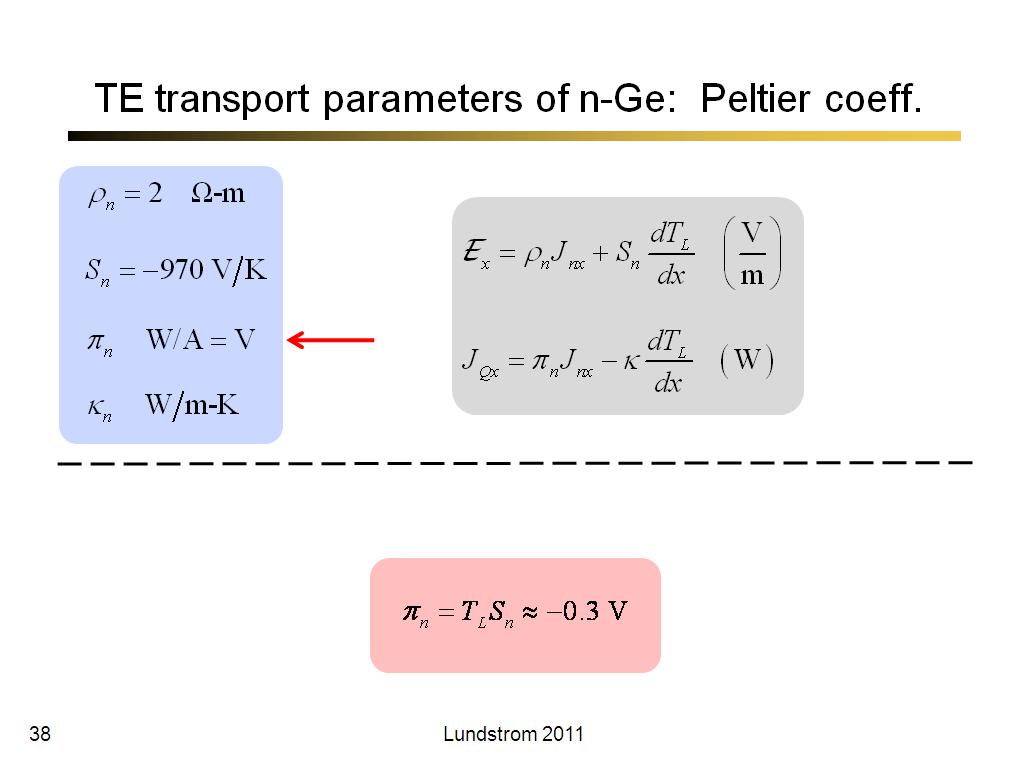 38. TE transport parameters of n-G…
2329.5333333333333
00:00/00:00
38. TE transport parameters of n-G…
2329.5333333333333
00:00/00:00 -
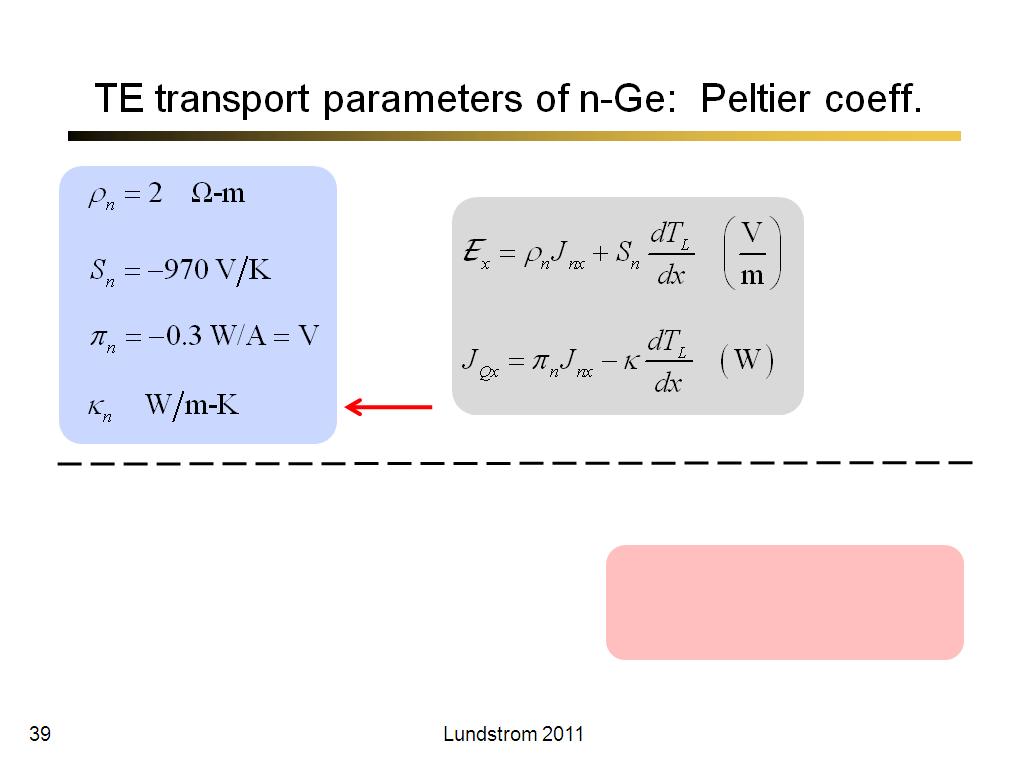
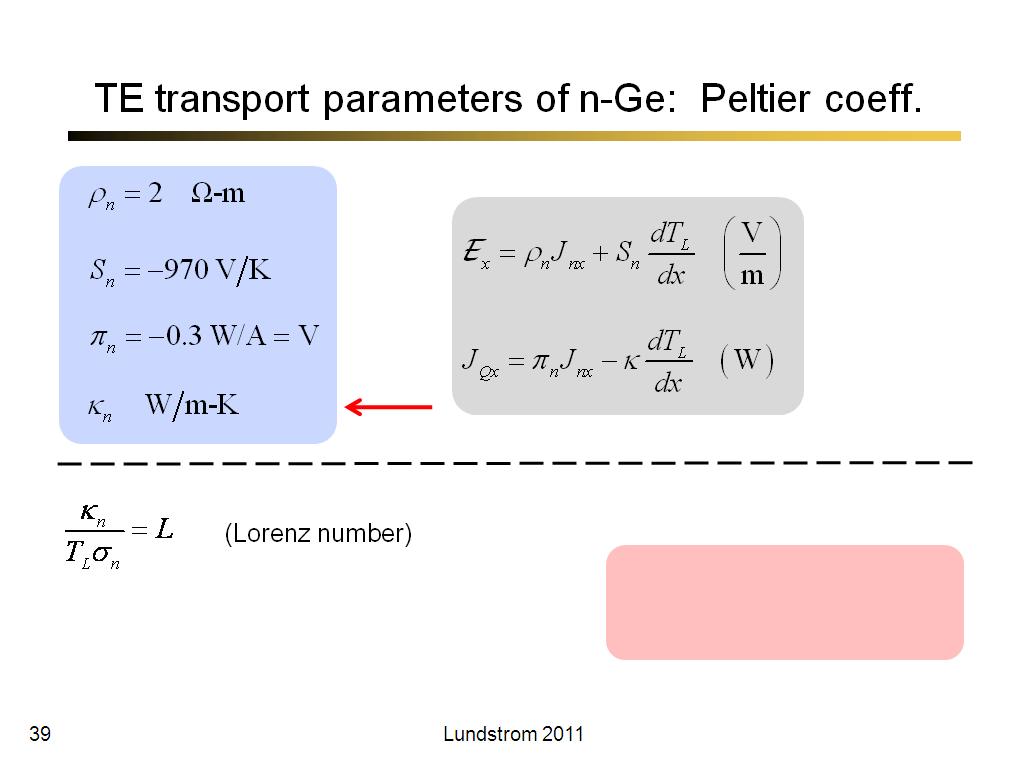
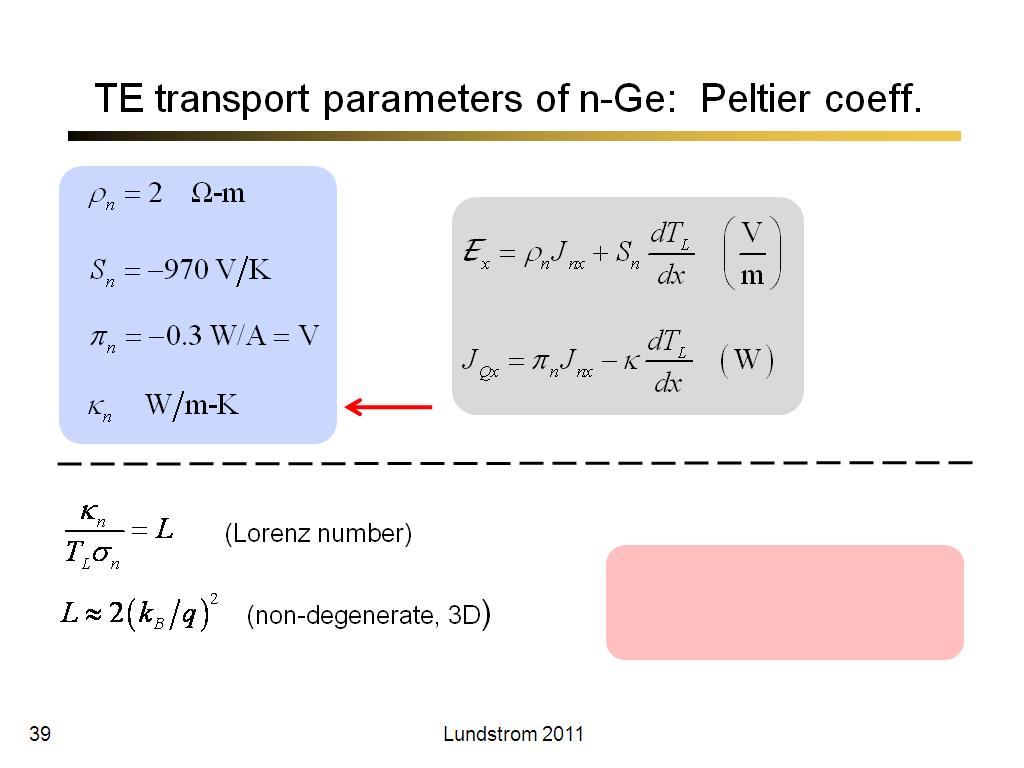
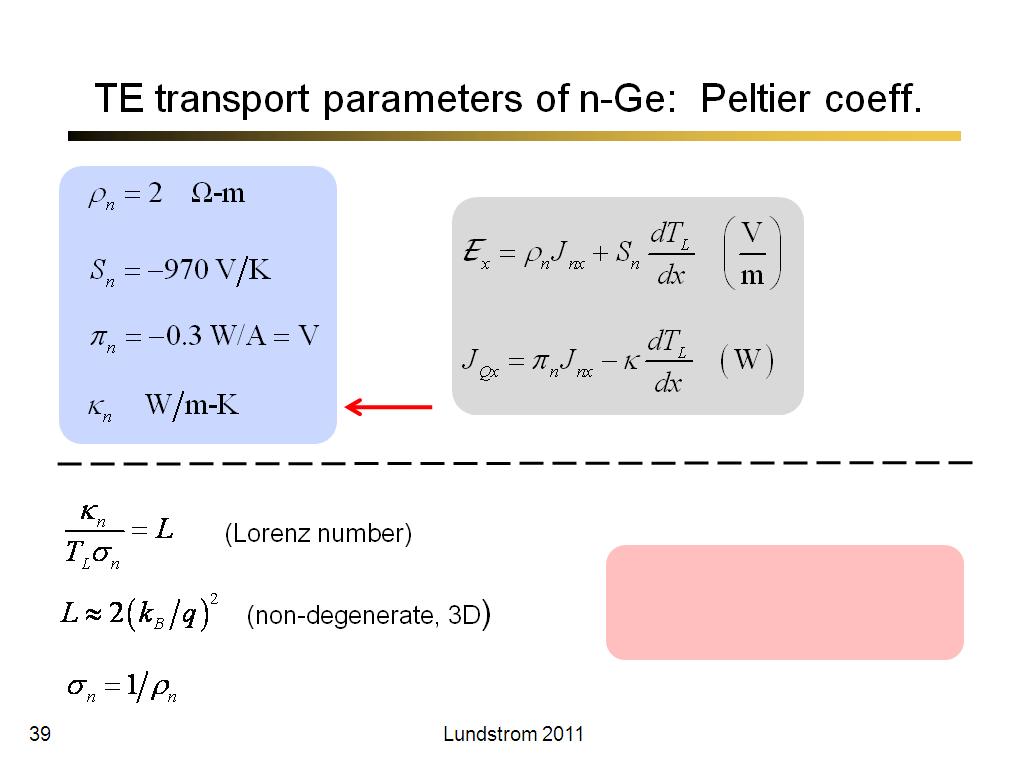
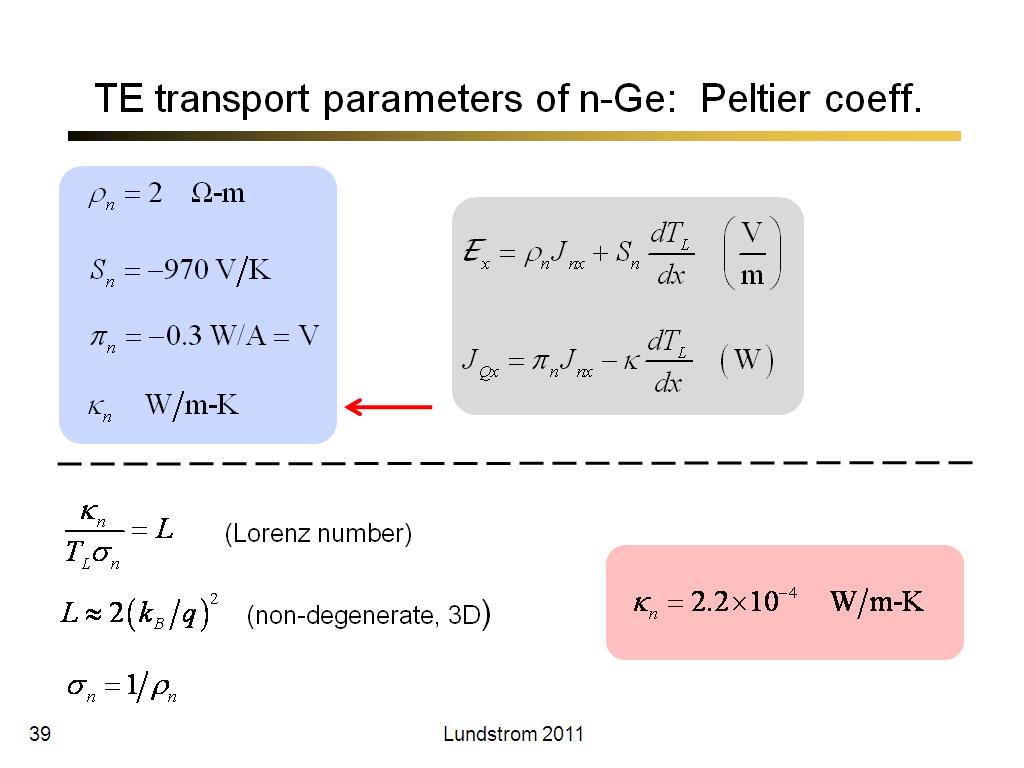 39. TE transport parameters of n-G…
2339.1666666666665
00:00/00:00
39. TE transport parameters of n-G…
2339.1666666666665
00:00/00:00 -
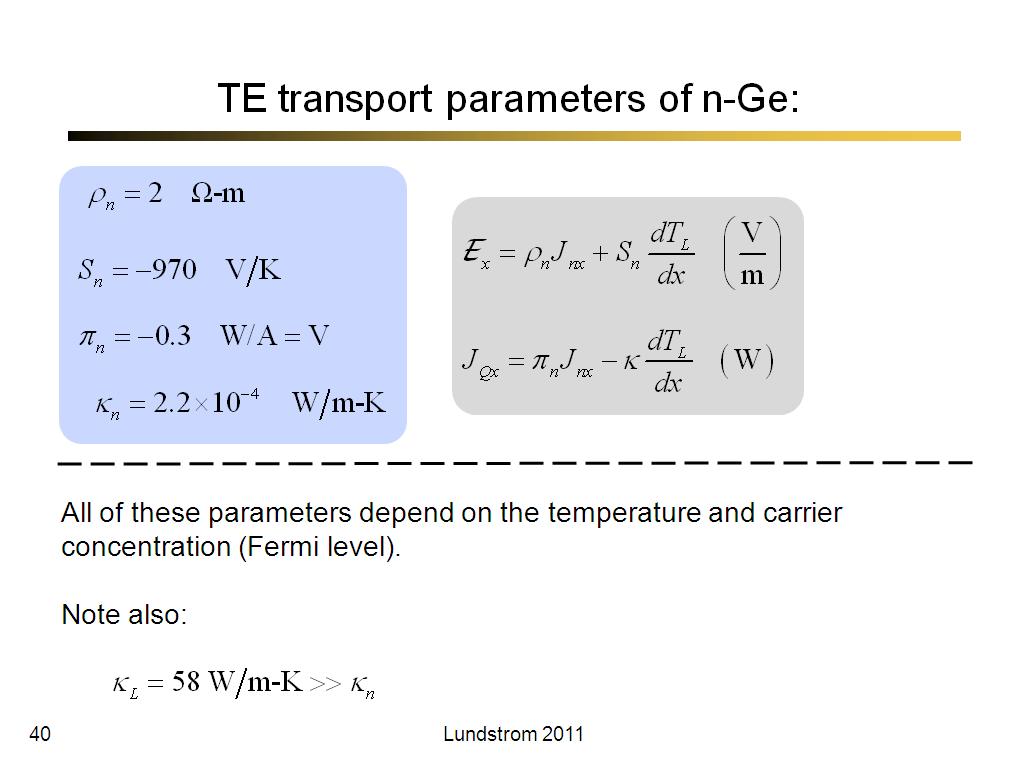 40. TE transport parameters of n-G…
2368
00:00/00:00
40. TE transport parameters of n-G…
2368
00:00/00:00 -
 41. outline
2404.3666666666668
00:00/00:00
41. outline
2404.3666666666668
00:00/00:00 -
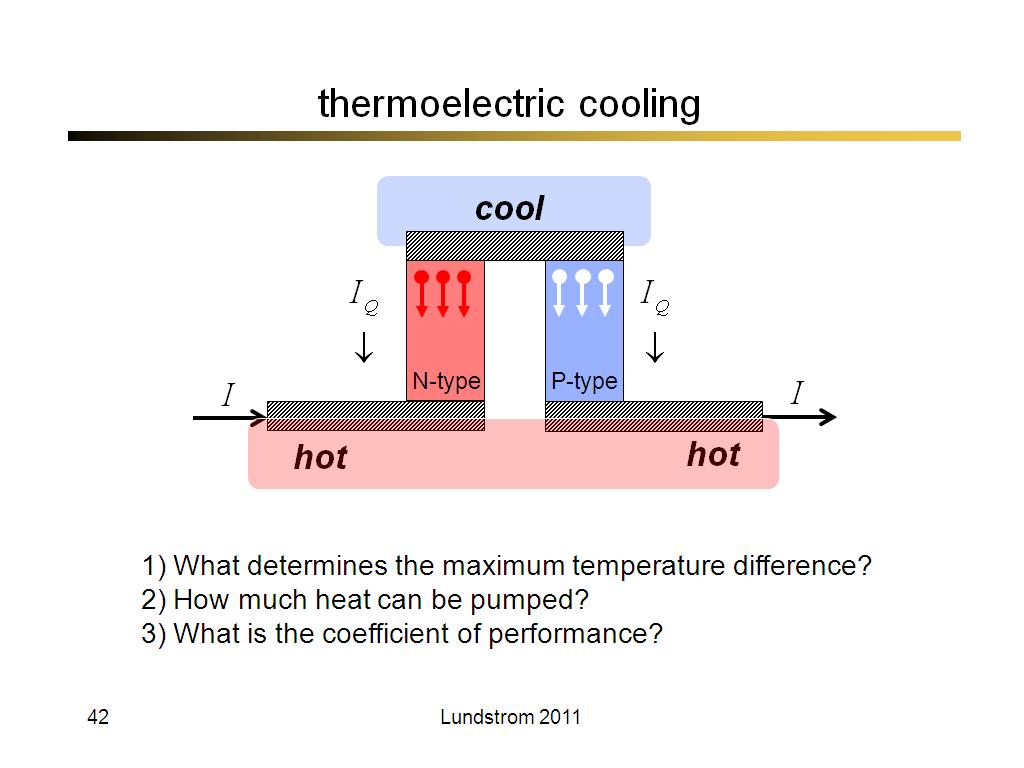 42. thermoelectric cooling
2411.4666666666667
00:00/00:00
42. thermoelectric cooling
2411.4666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
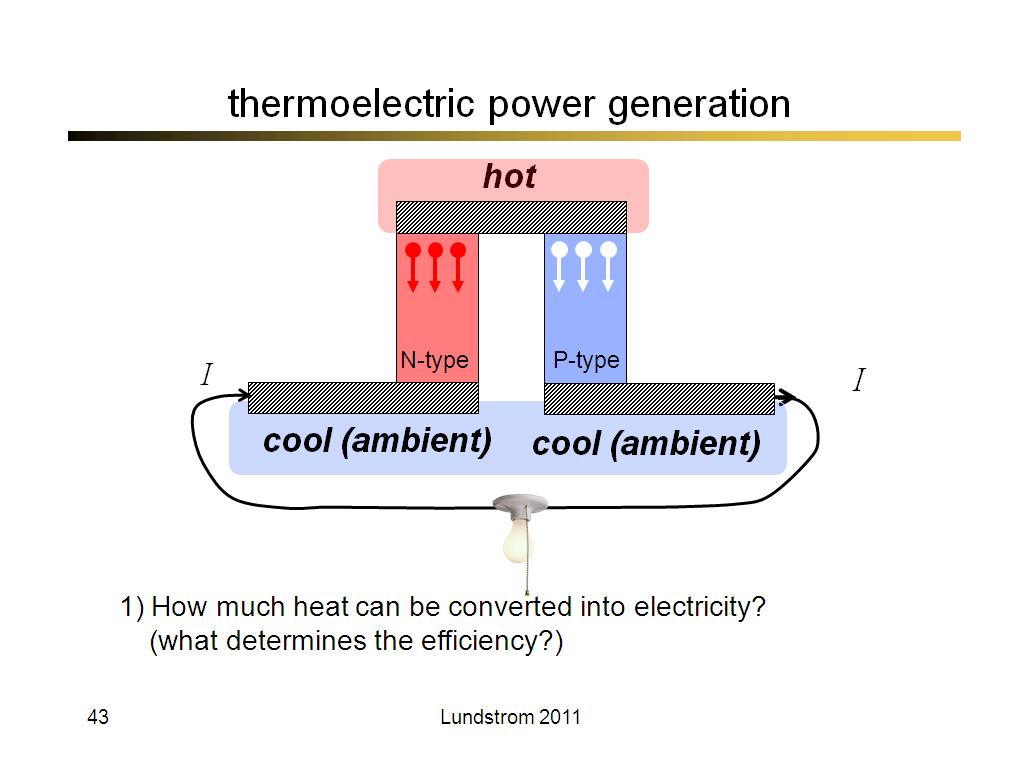 43. thermoelectric power generatio…
2480.2333333333331
00:00/00:00
43. thermoelectric power generatio…
2480.2333333333331
00:00/00:00 -
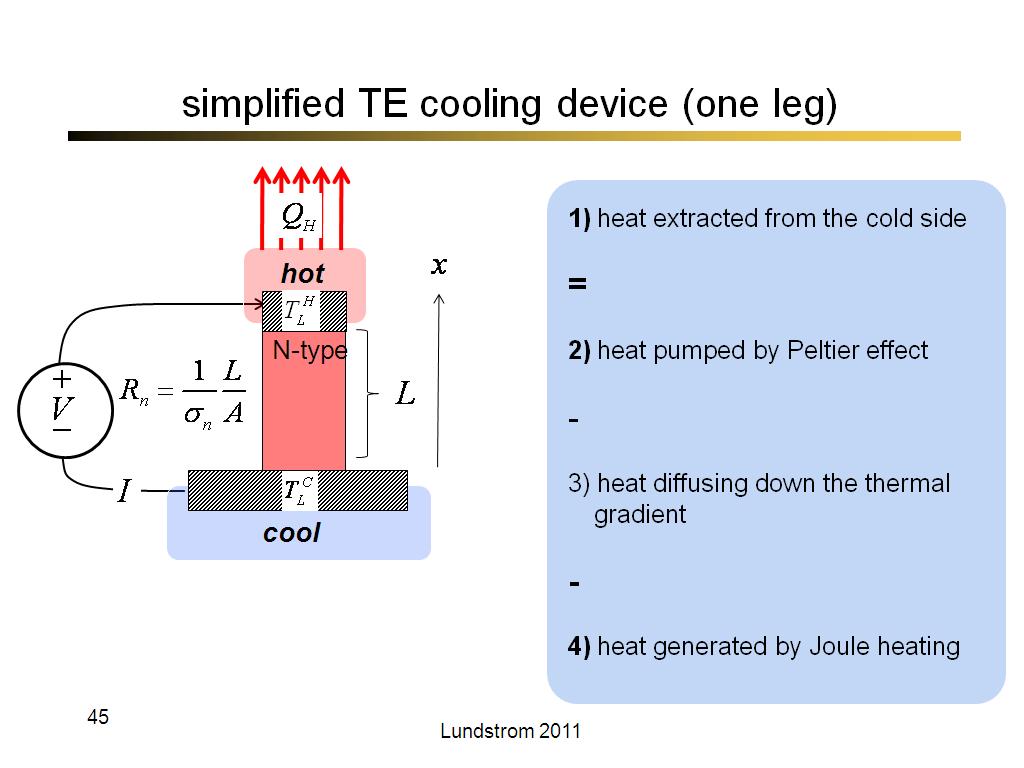
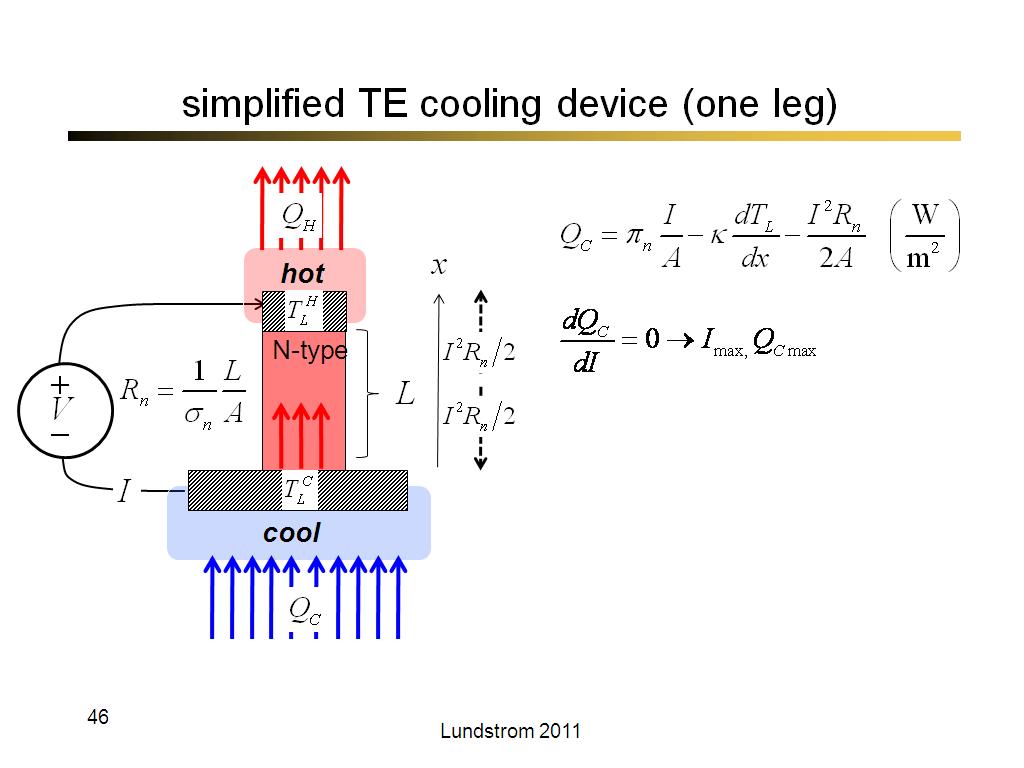
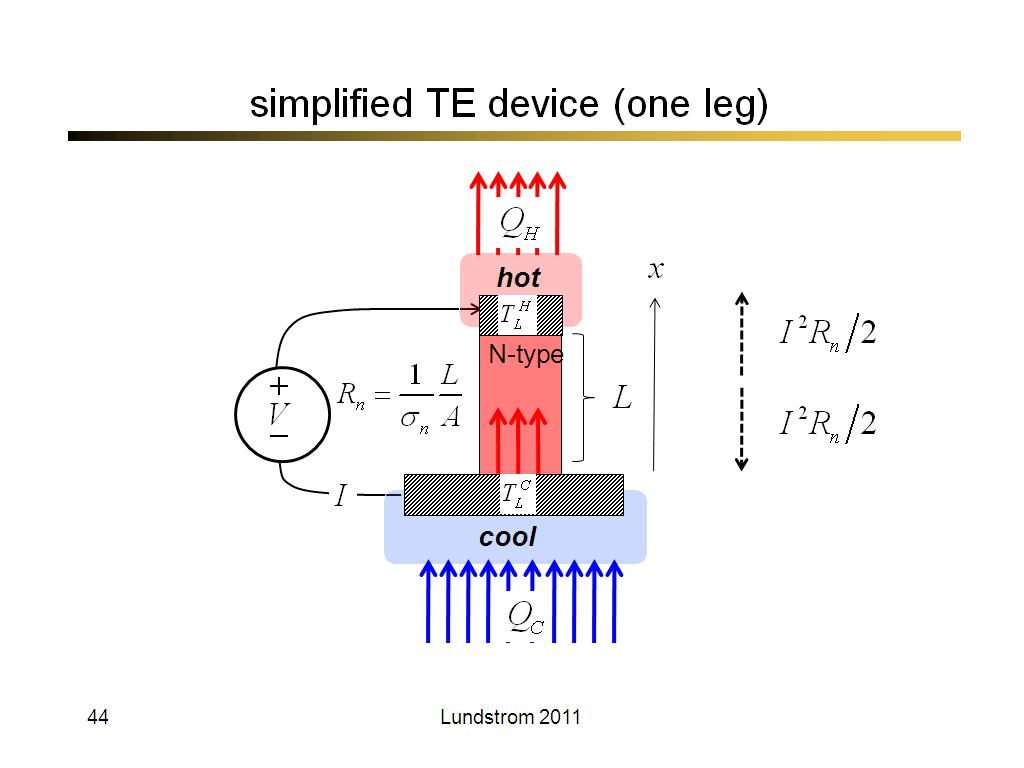 44. simplified TE device (one leg)
2527.8666666666668
00:00/00:00
44. simplified TE device (one leg)
2527.8666666666668
00:00/00:00 -
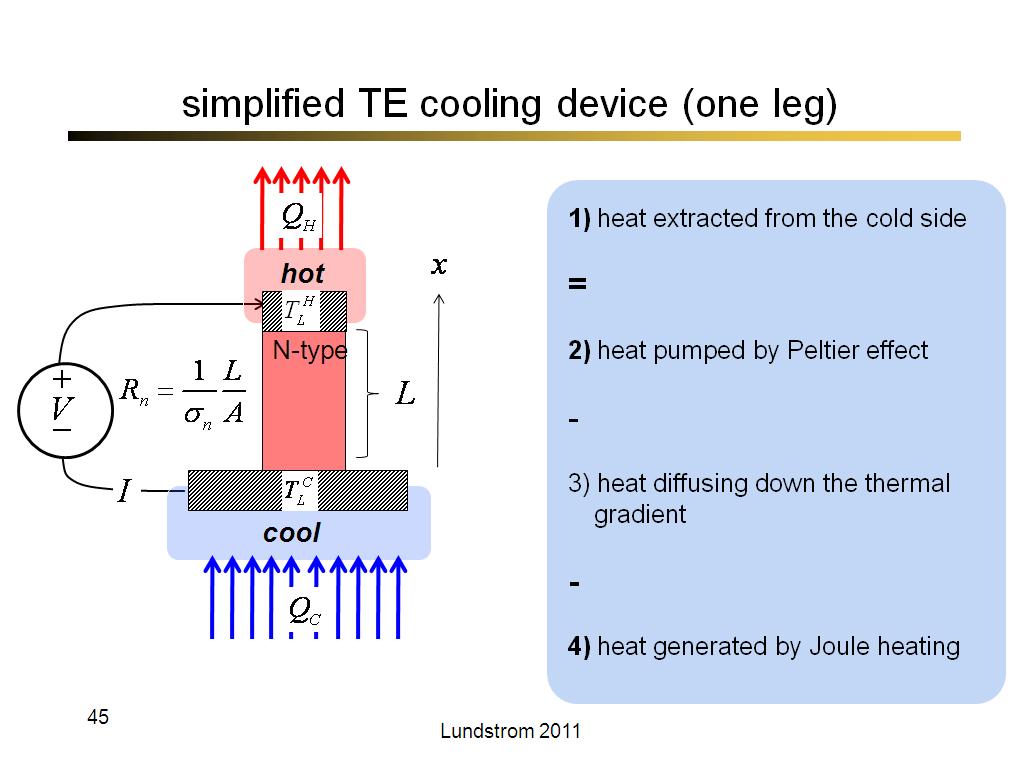
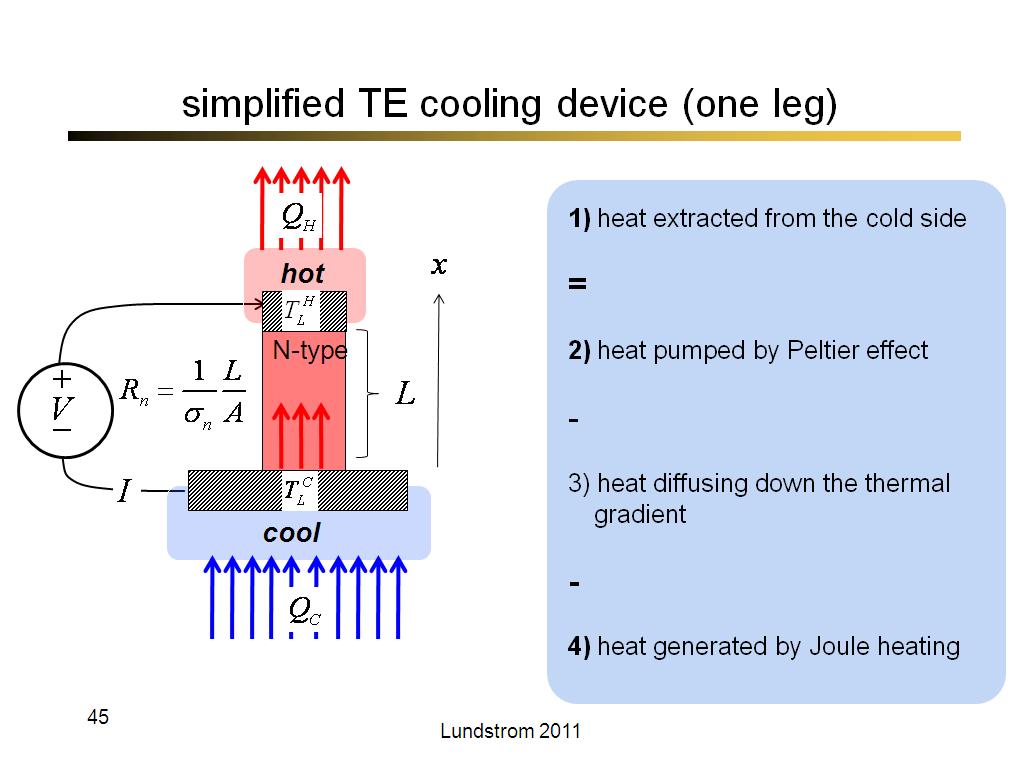
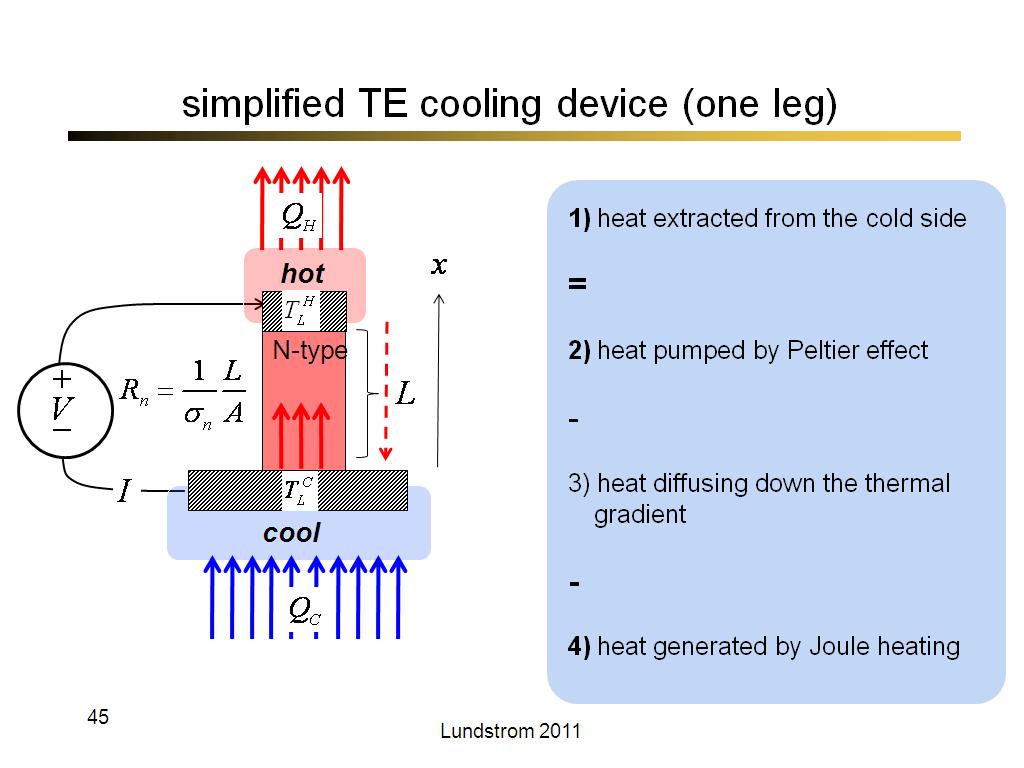
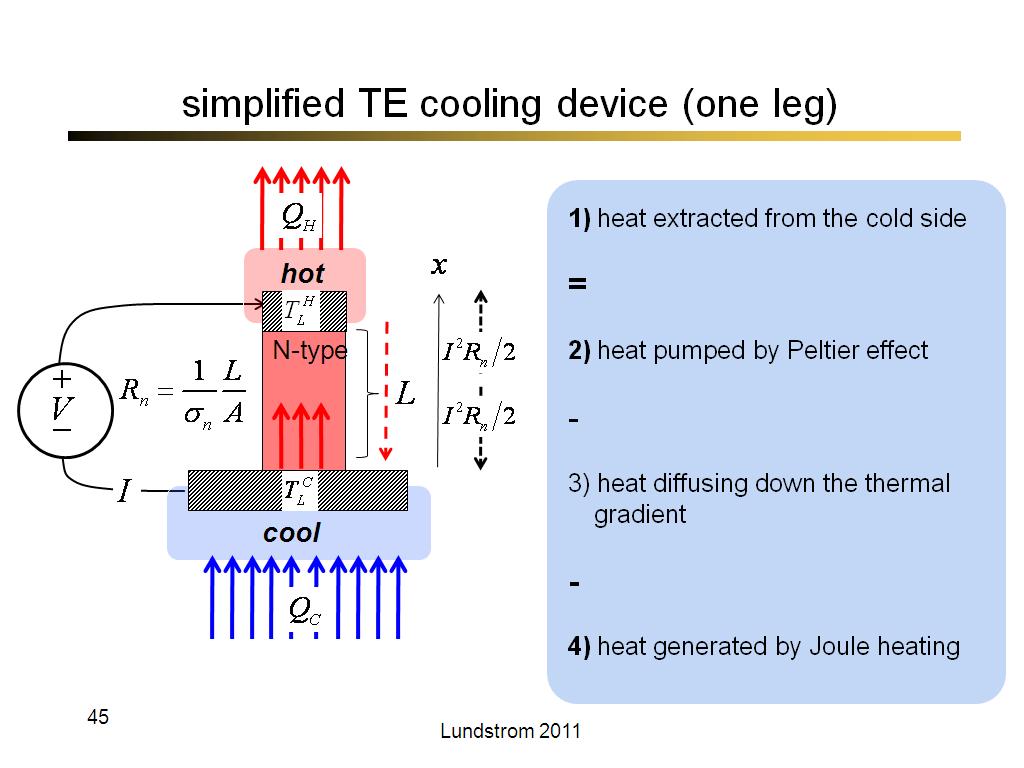 45. simplified TE cooling device (…
2567.9
00:00/00:00
45. simplified TE cooling device (…
2567.9
00:00/00:00 -
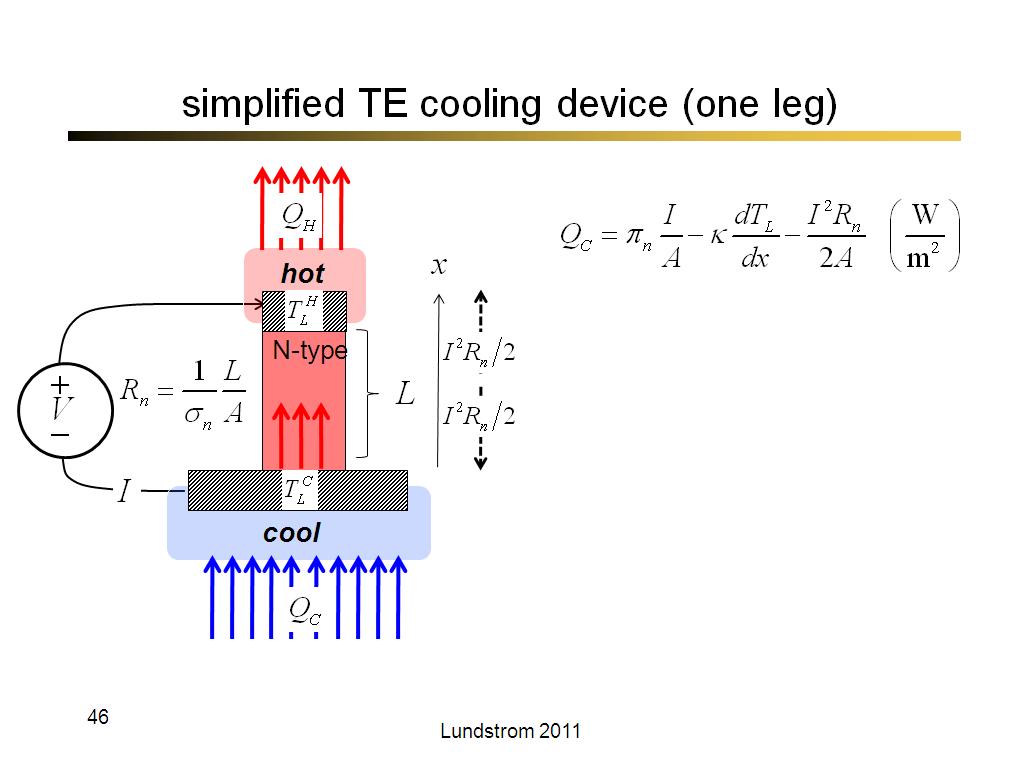
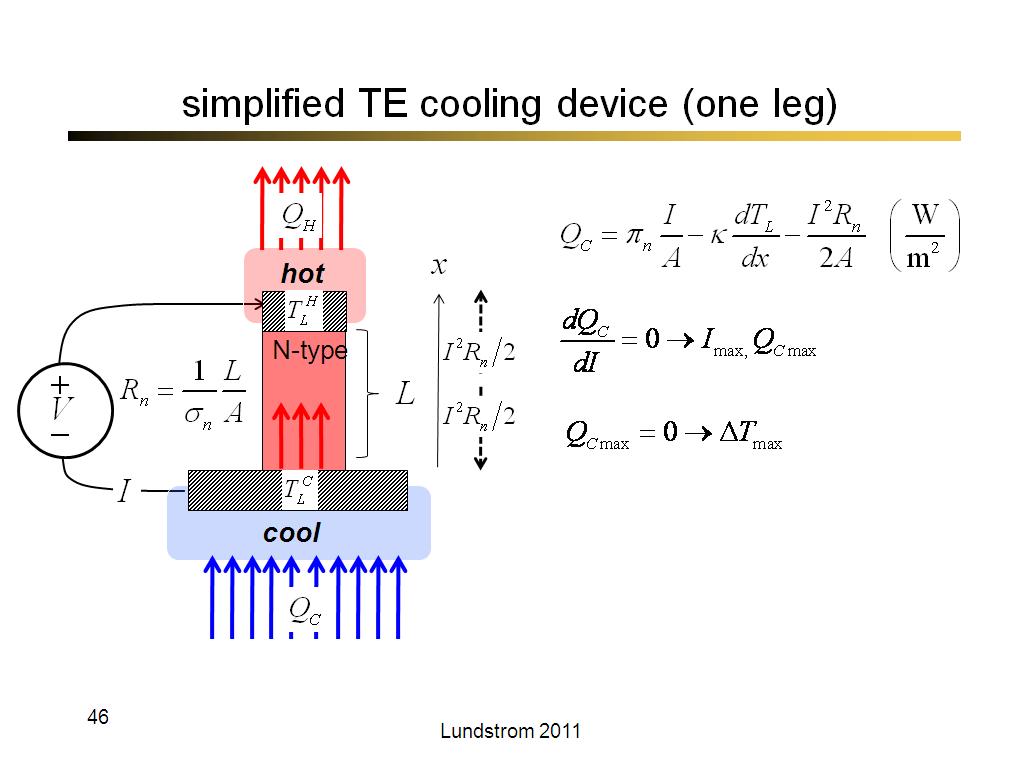
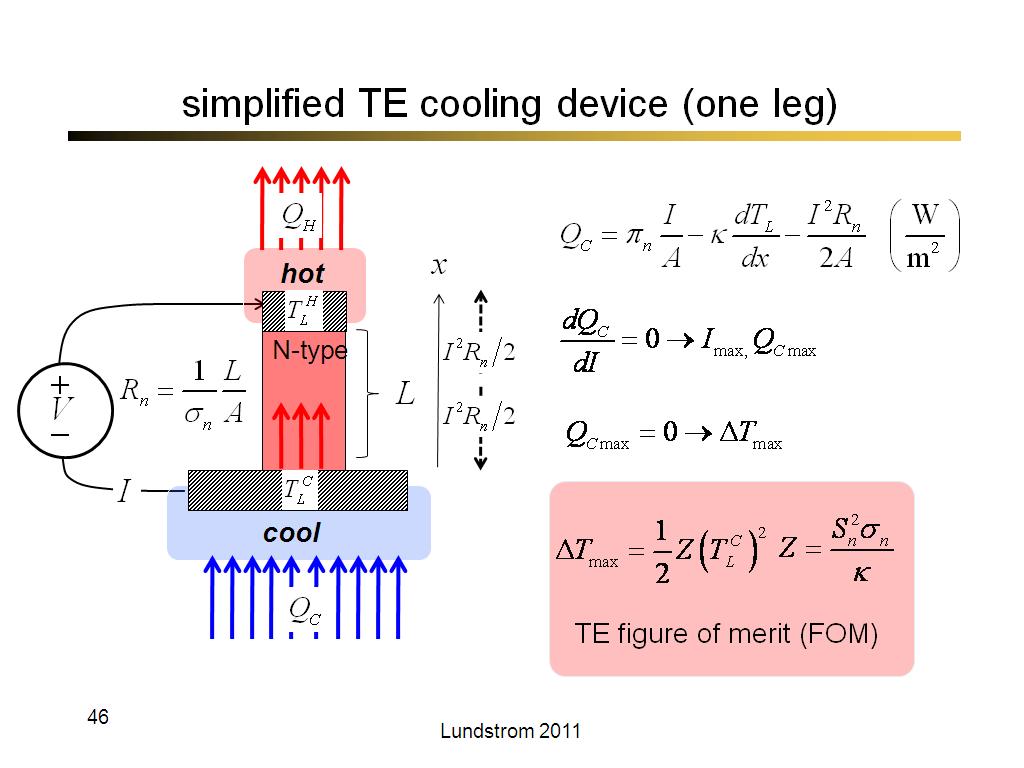 46. simplified TE cooling device (…
2609.8
00:00/00:00
46. simplified TE cooling device (…
2609.8
00:00/00:00 -
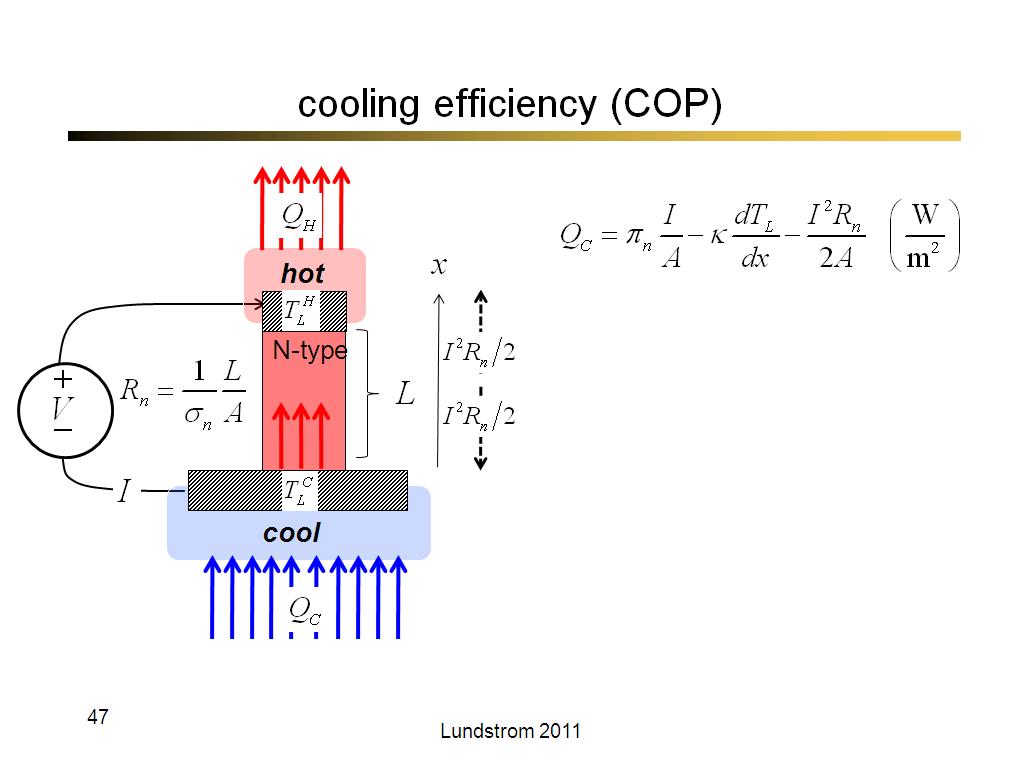
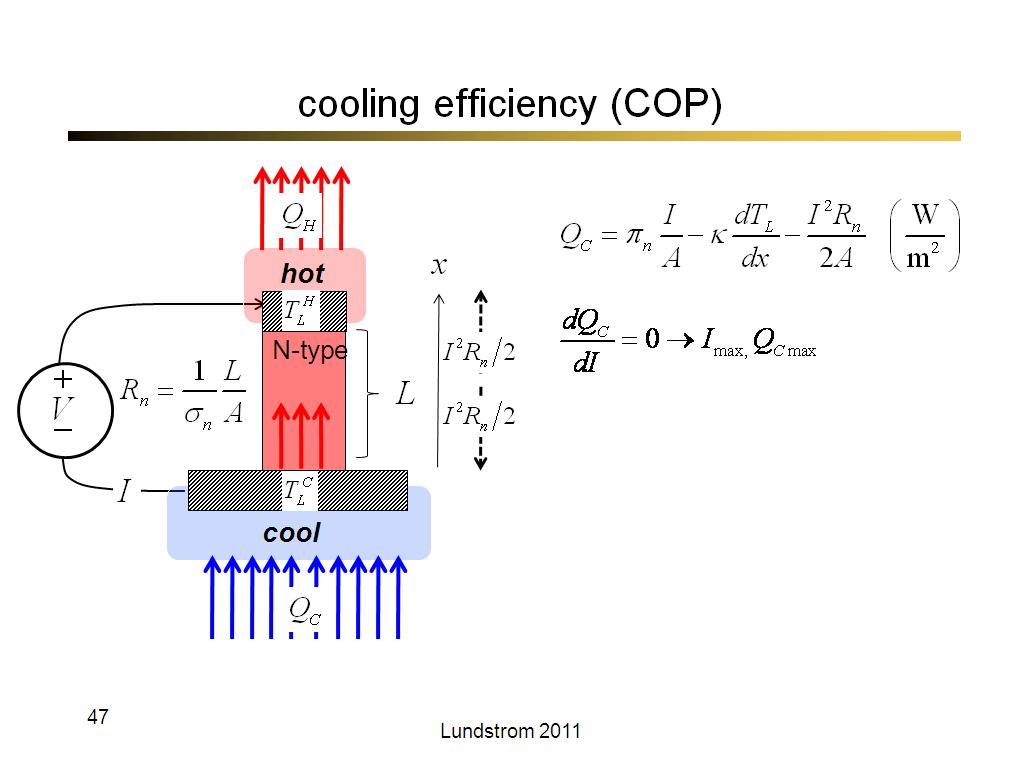
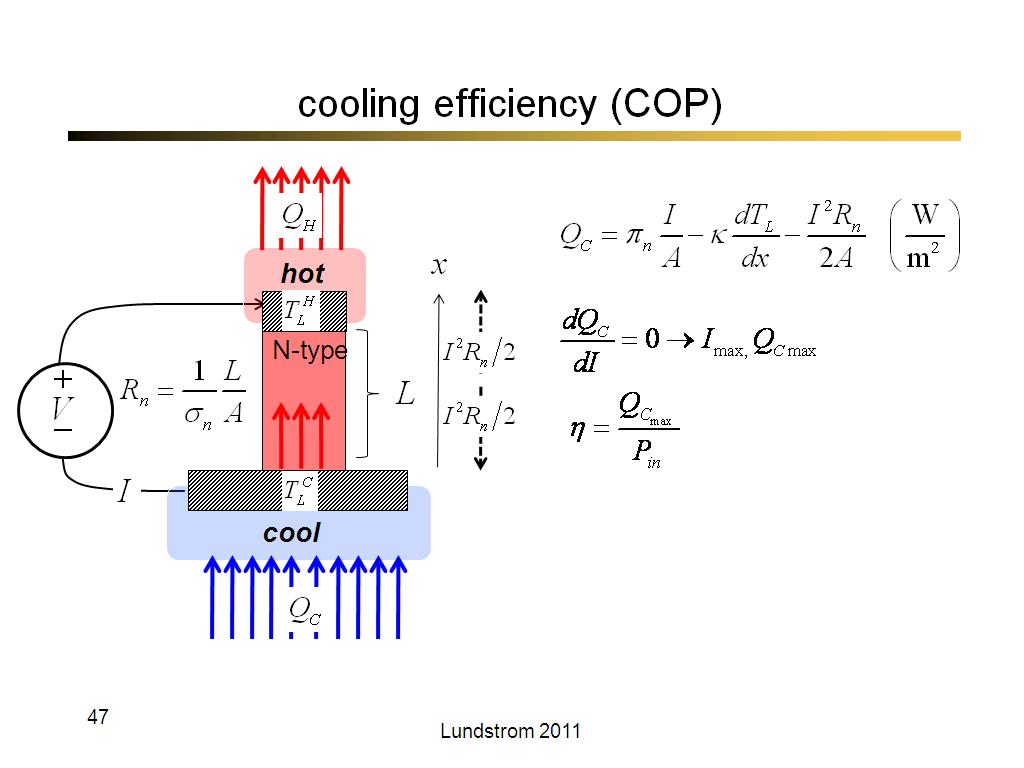
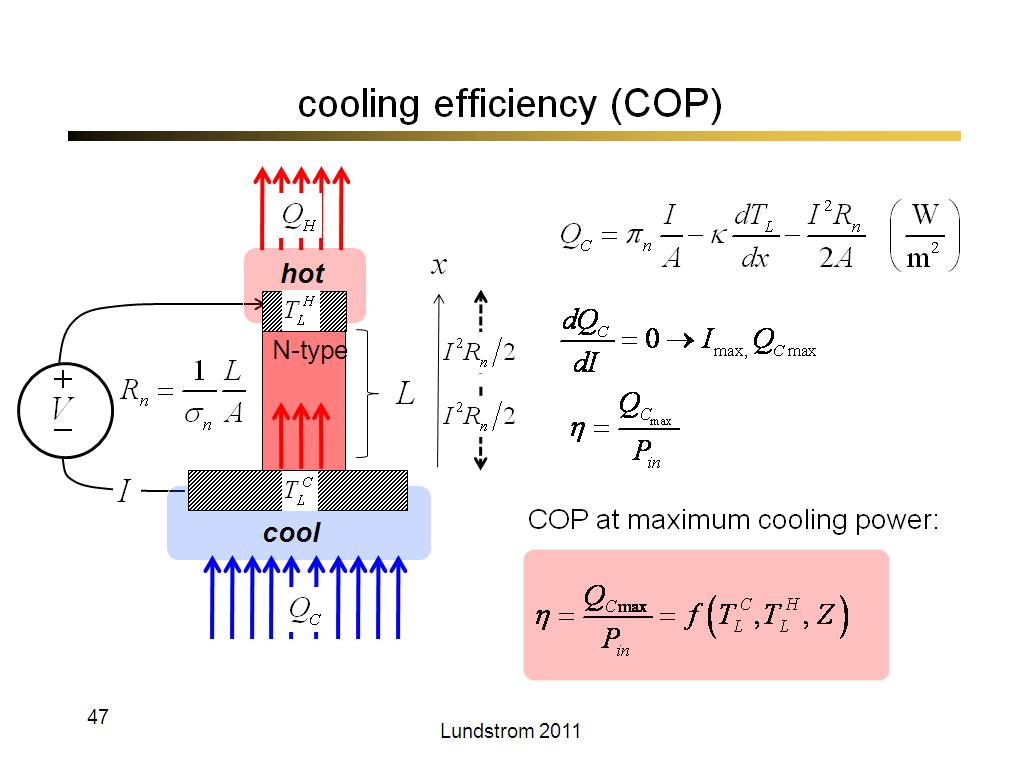 47. cooling efficiency (COP)
2758.4666666666667
00:00/00:00
47. cooling efficiency (COP)
2758.4666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
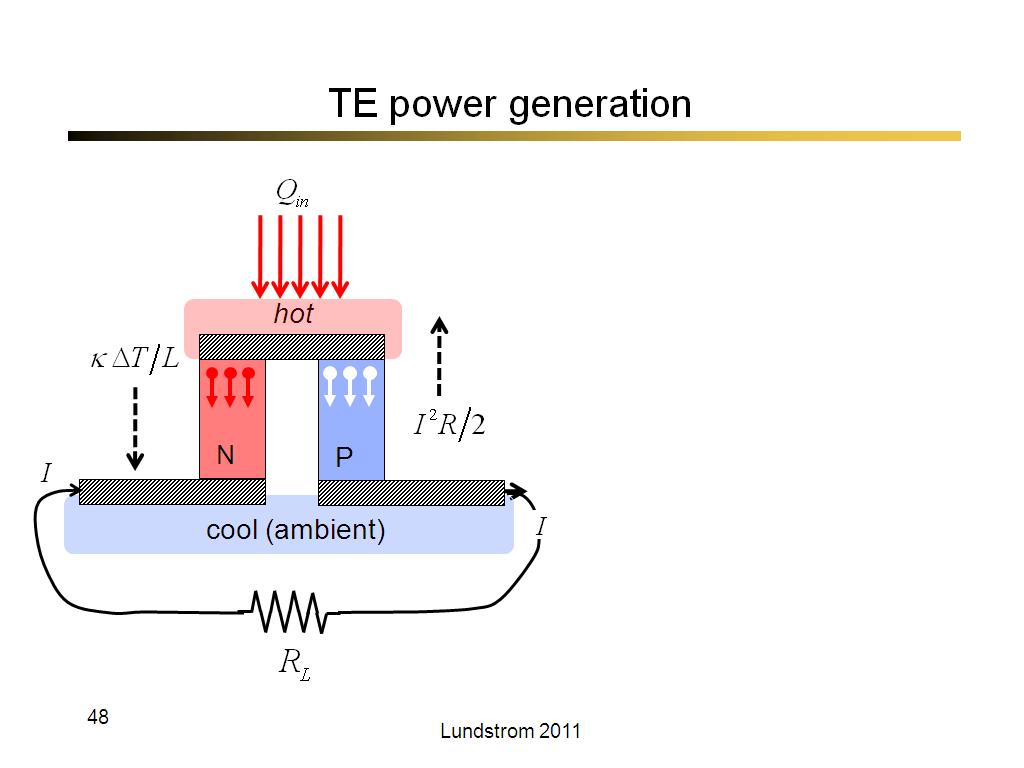
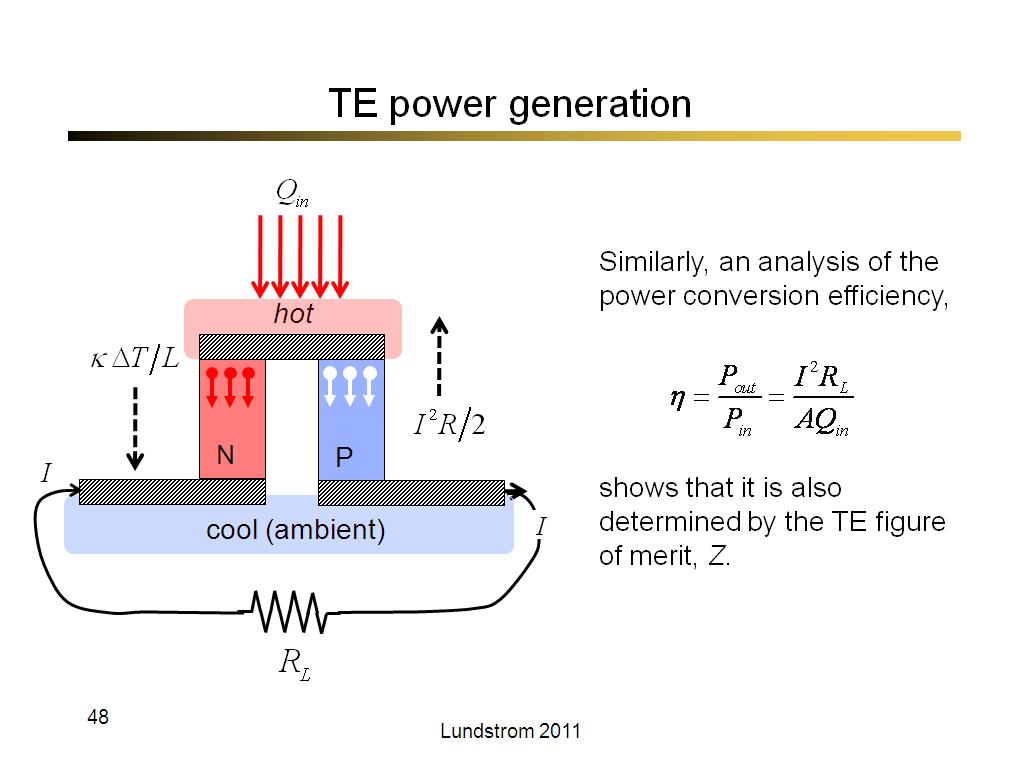 48. TE power generation
2802.4
00:00/00:00
48. TE power generation
2802.4
00:00/00:00 -
 49. outline
2819.4333333333334
00:00/00:00
49. outline
2819.4333333333334
00:00/00:00 -
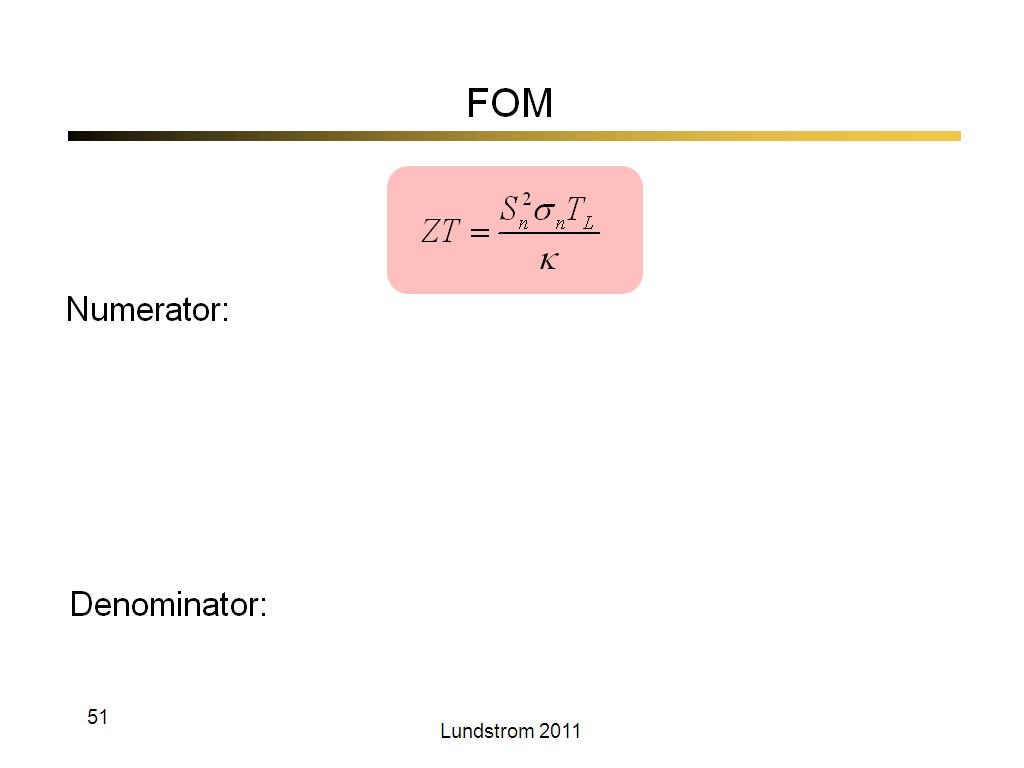
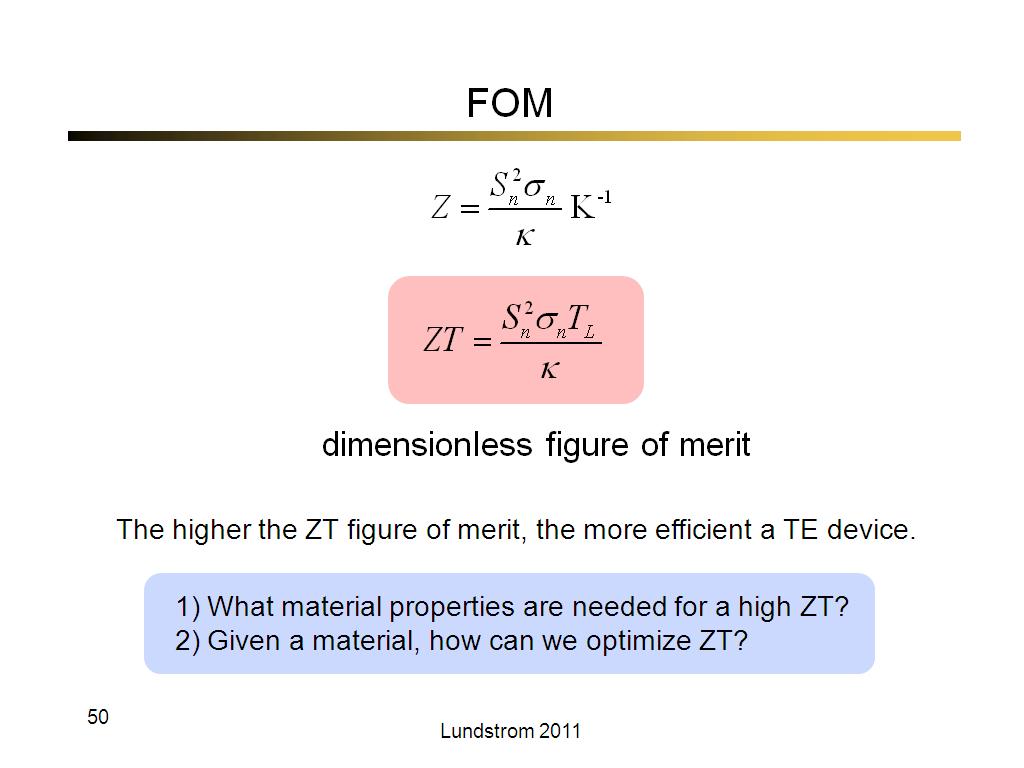 50. FOM
2822
00:00/00:00
50. FOM
2822
00:00/00:00 -
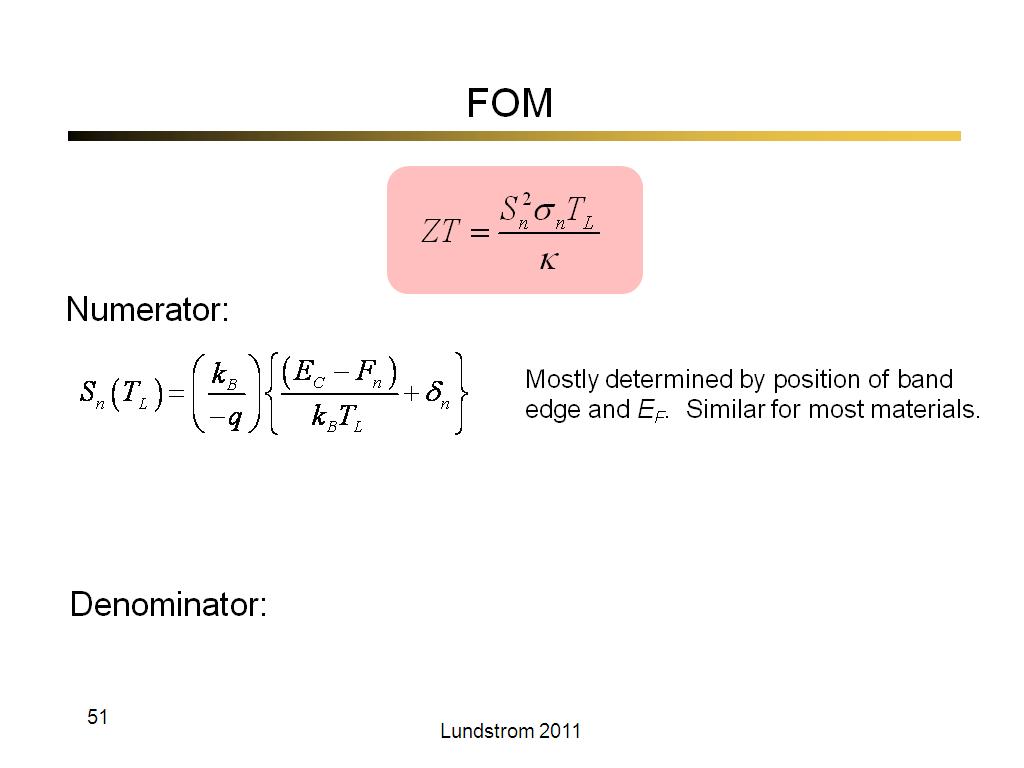
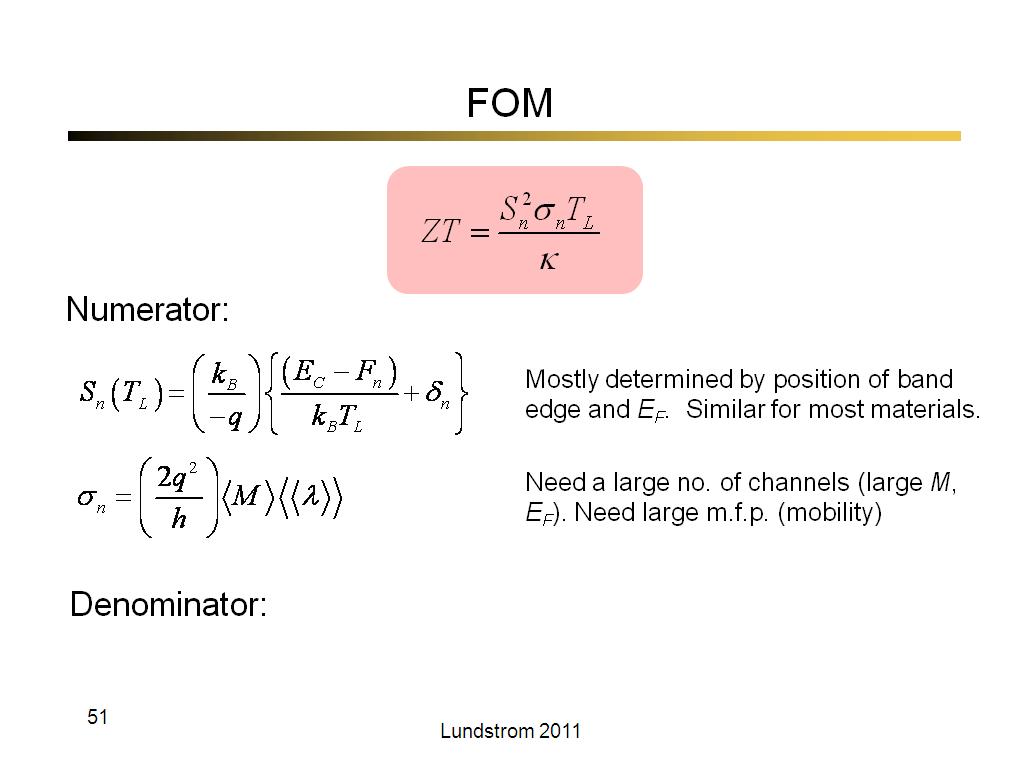
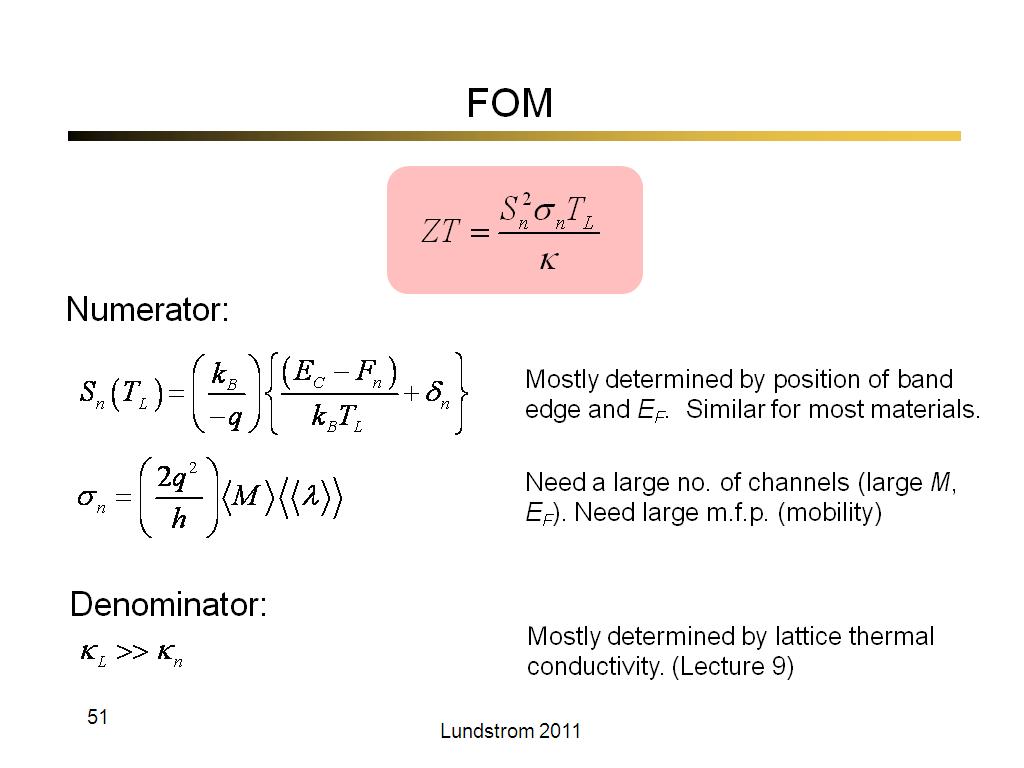 51. FOM
2962.6666666666665
00:00/00:00
51. FOM
2962.6666666666665
00:00/00:00 -
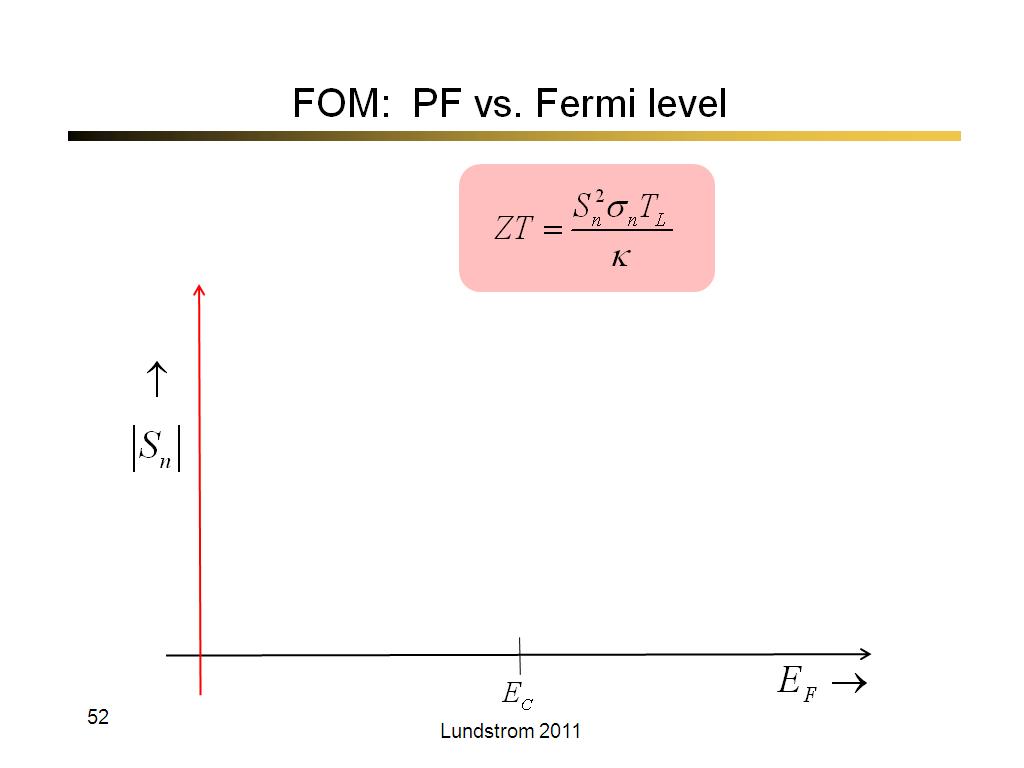
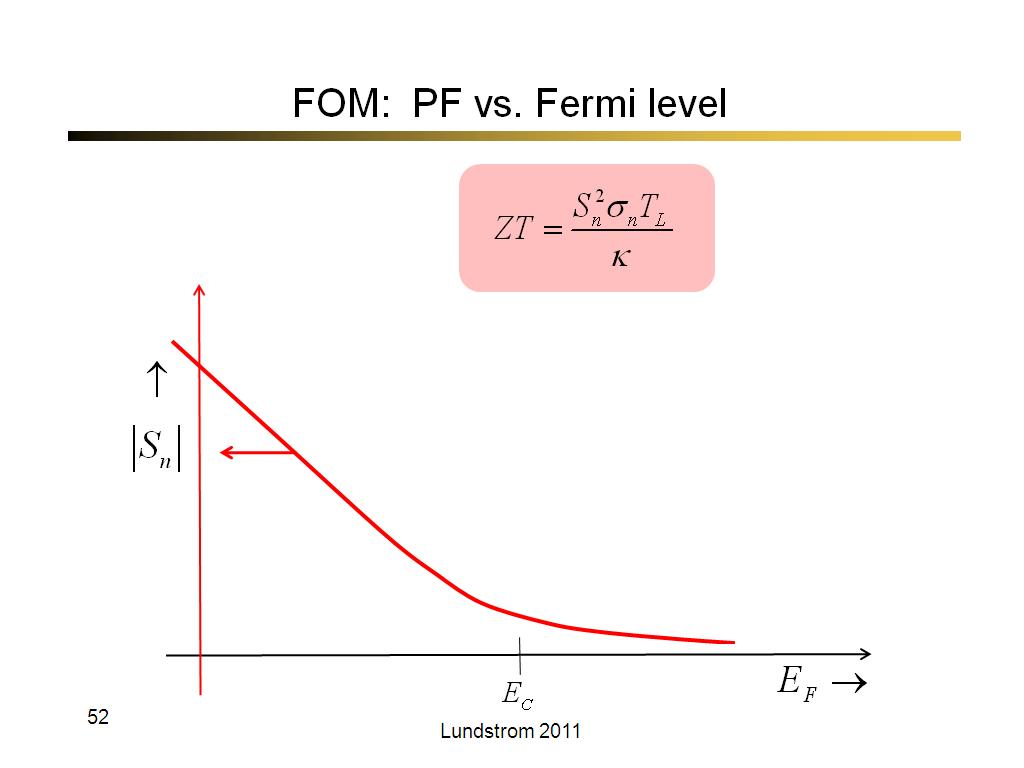
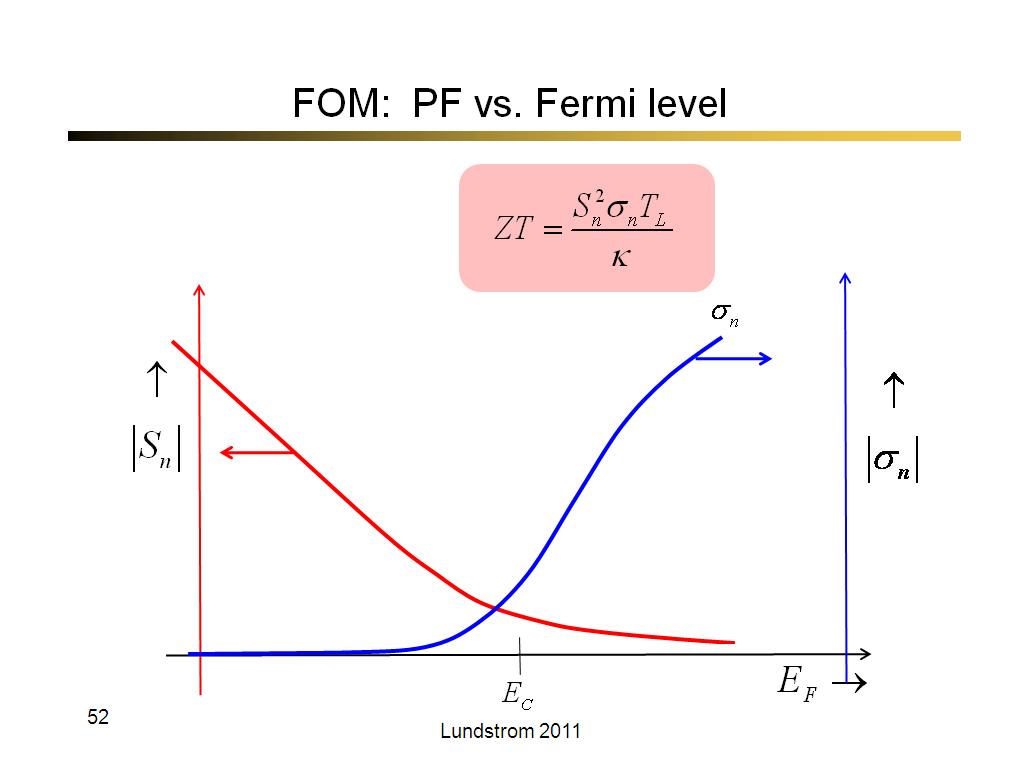
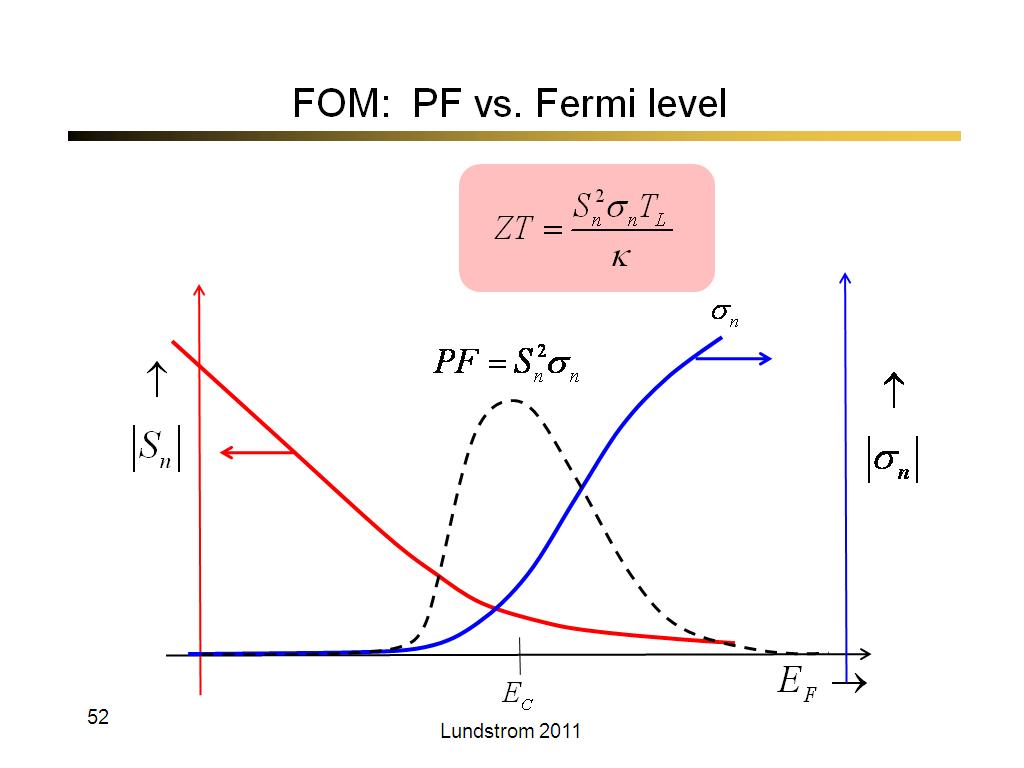
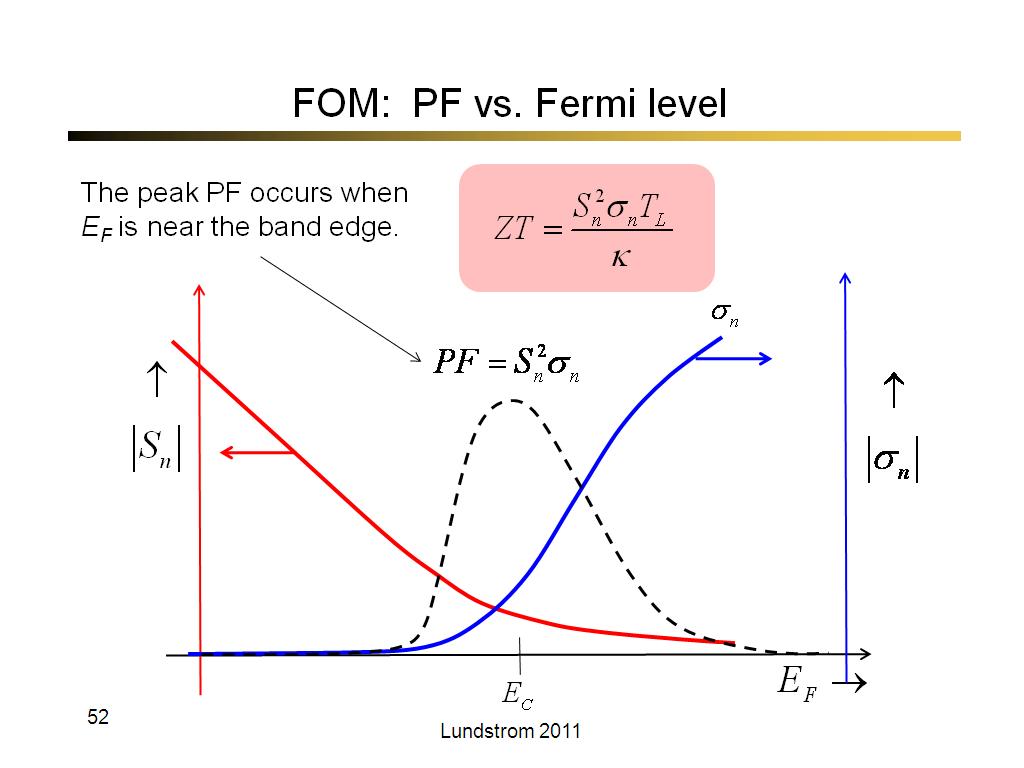 52. FOM: PF vs. Fermi level
3043.3333333333335
00:00/00:00
52. FOM: PF vs. Fermi level
3043.3333333333335
00:00/00:00 -
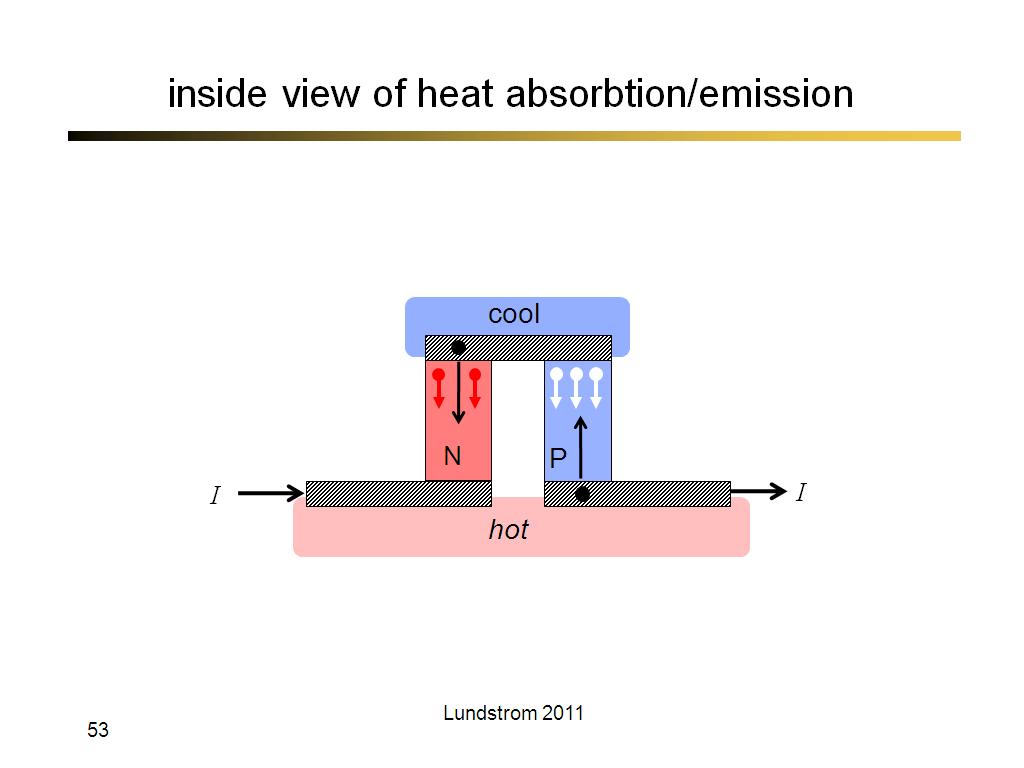
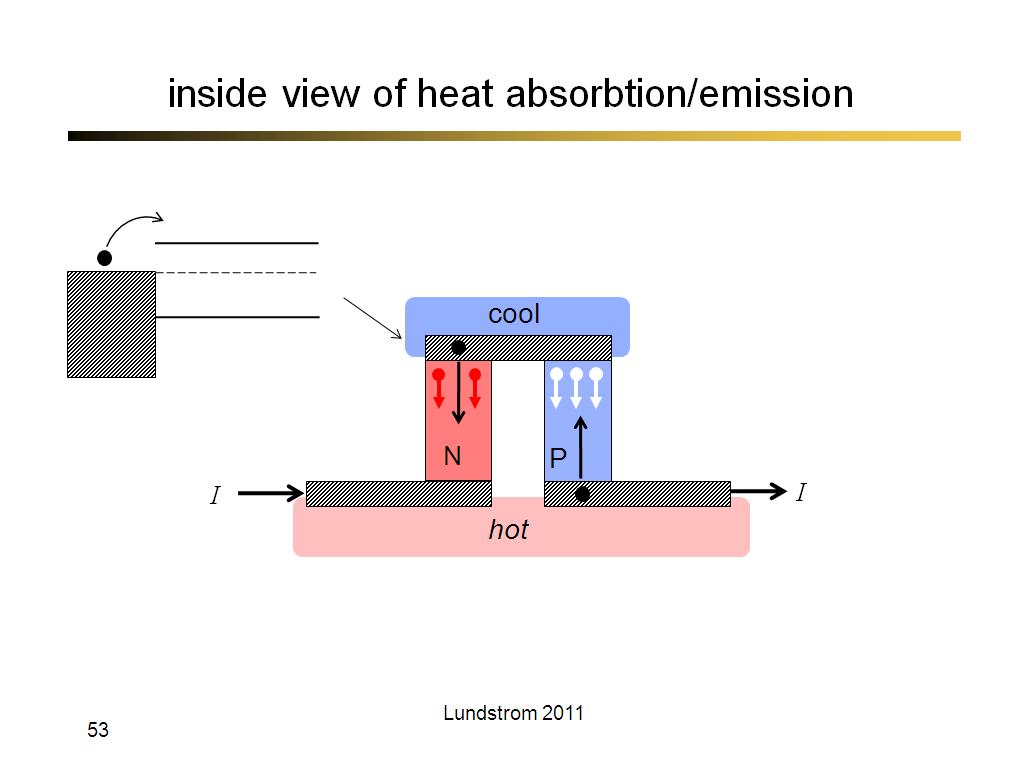
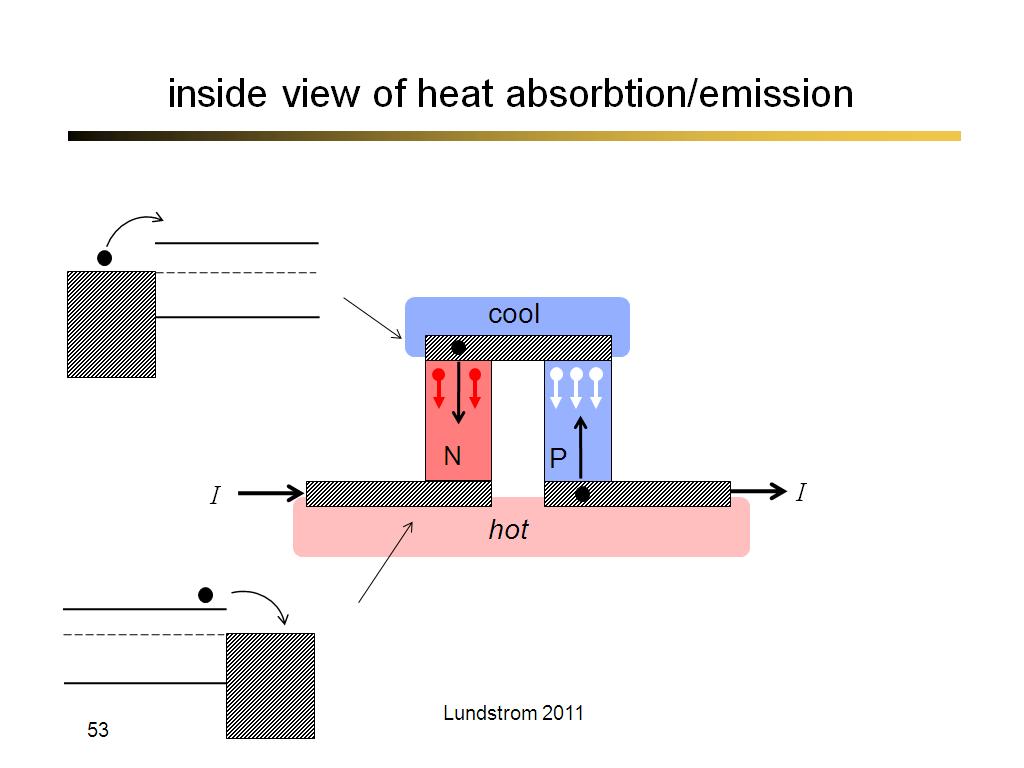
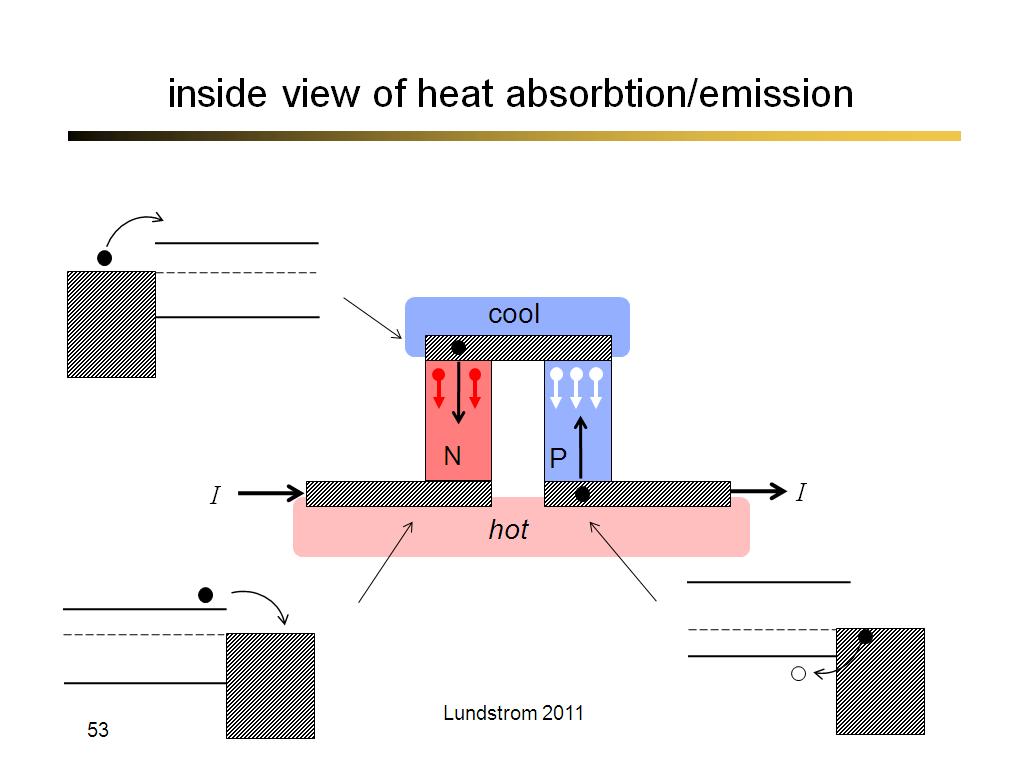
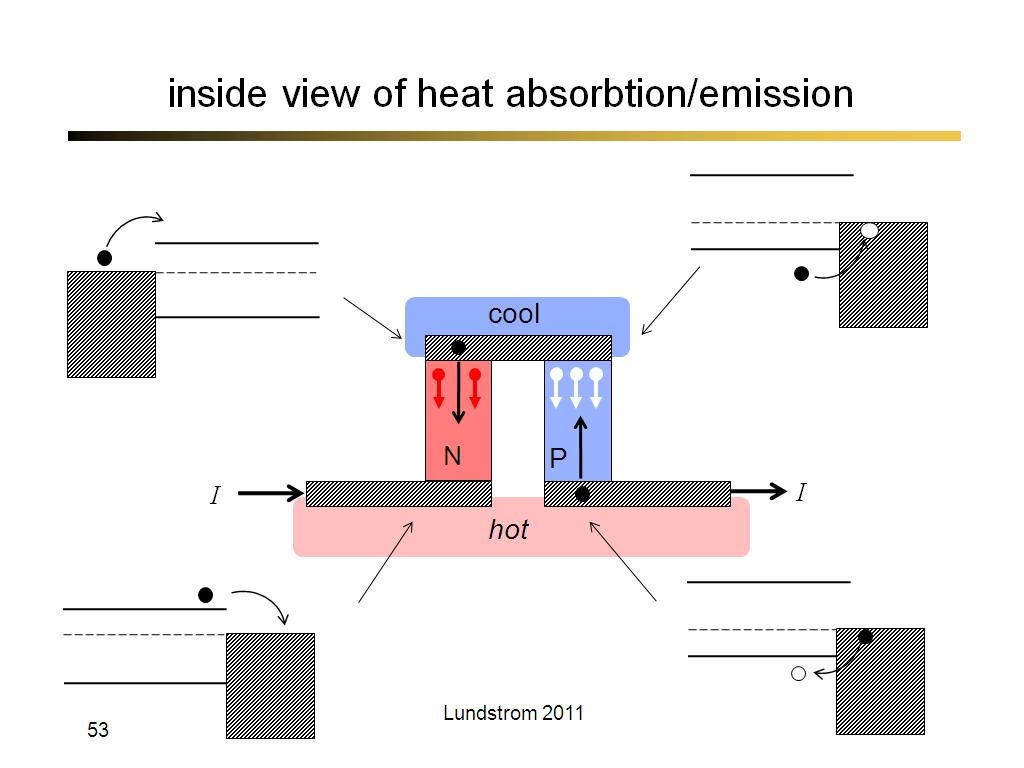 53. inside view of heat absorbtion…
3134.5333333333333
00:00/00:00
53. inside view of heat absorbtion…
3134.5333333333333
00:00/00:00 -
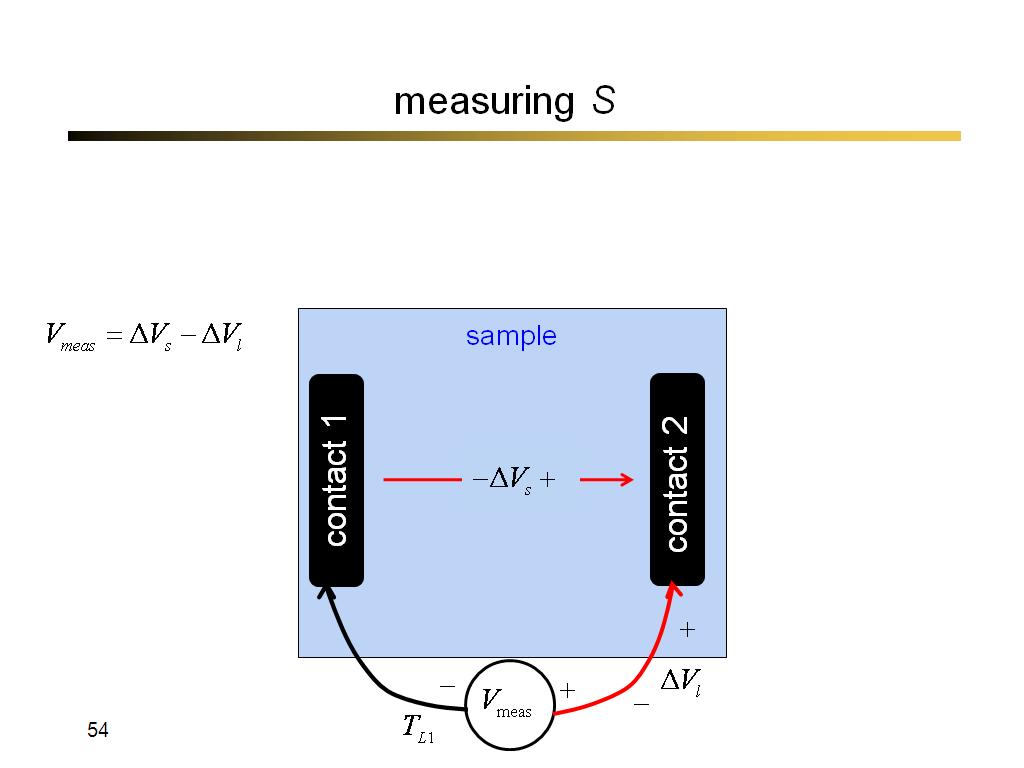
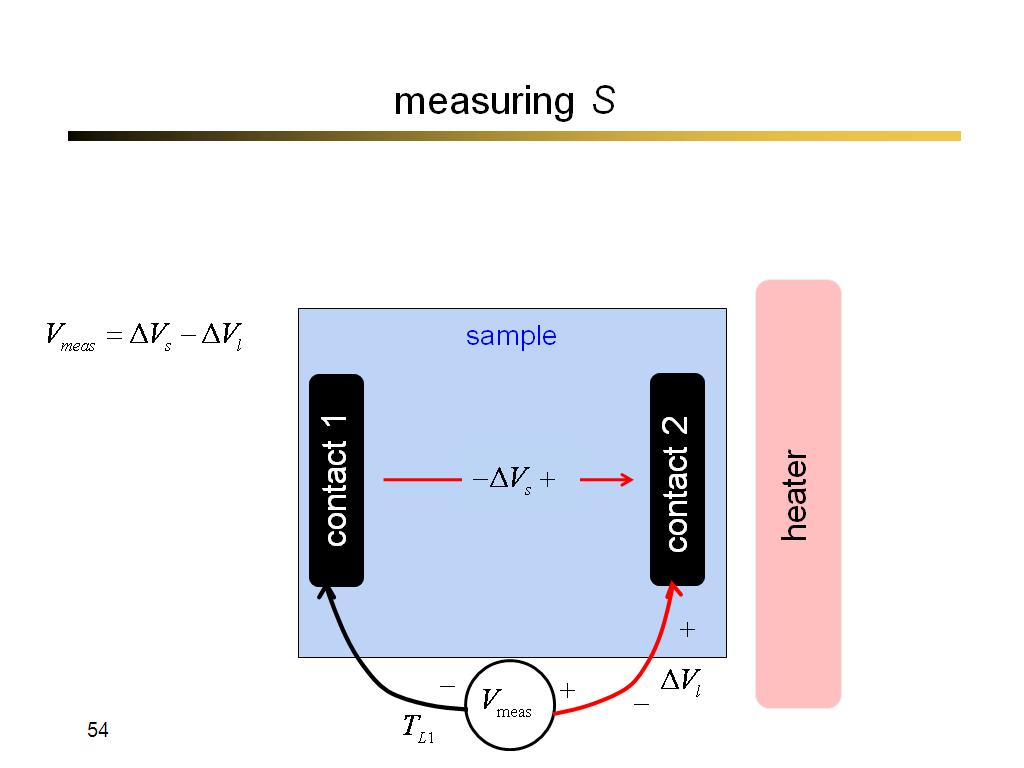
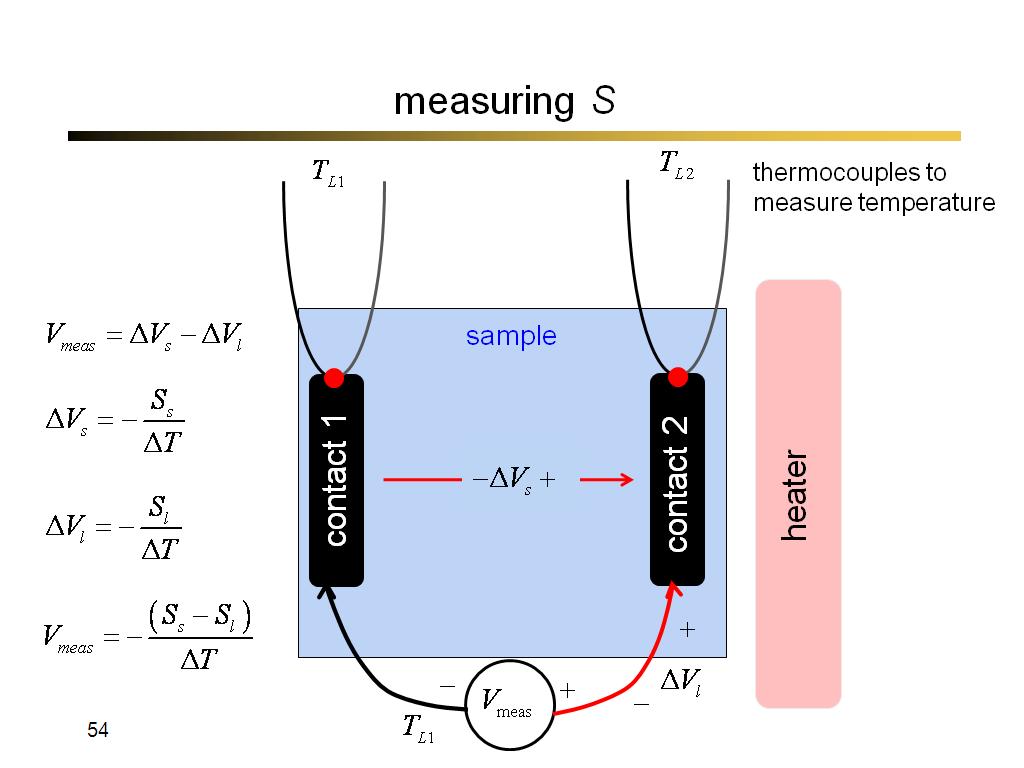 54. measuring S
3262.3333333333335
00:00/00:00
54. measuring S
3262.3333333333335
00:00/00:00 -
 55. outline
3406.6666666666665
00:00/00:00
55. outline
3406.6666666666665
00:00/00:00 -
 56. summary
3408.8666666666668
00:00/00:00
56. summary
3408.8666666666668
00:00/00:00 -
 57. questions
3454.7666666666669
00:00/00:00
57. questions
3454.7666666666669
00:00/00:00 -
 58. n-type semiconductor: isother…
3478.6333333333332
00:00/00:00
58. n-type semiconductor: isother…
3478.6333333333332
00:00/00:00 -
 59. TE transport parameters of n-G…
4091.6
00:00/00:00
59. TE transport parameters of n-G…
4091.6
00:00/00:00