Lecture 2: General Model for Transport
Lecture 2: General Model for Transport
-
 1. NCN Summer School: July 2011 …
0
00:00/00:00
1. NCN Summer School: July 2011 …
0
00:00/00:00 -
 2. copyright 2011
37.466666666666669
00:00/00:00
2. copyright 2011
37.466666666666669
00:00/00:00 -
 3. outline
38.5
00:00/00:00
3. outline
38.5
00:00/00:00 -
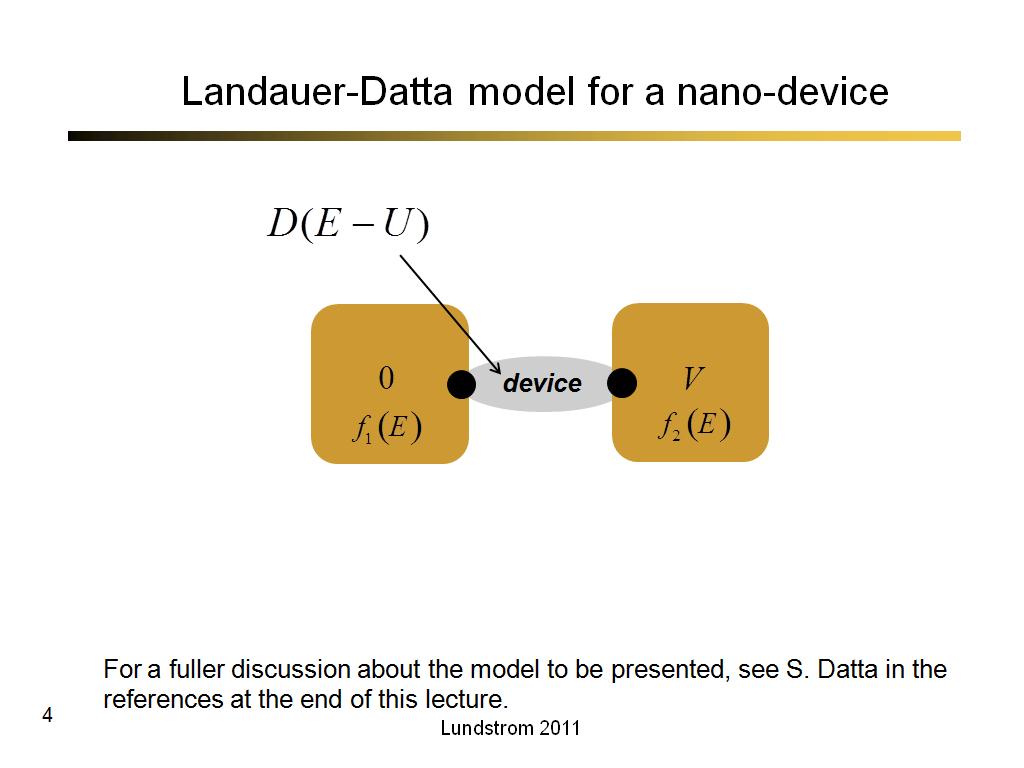
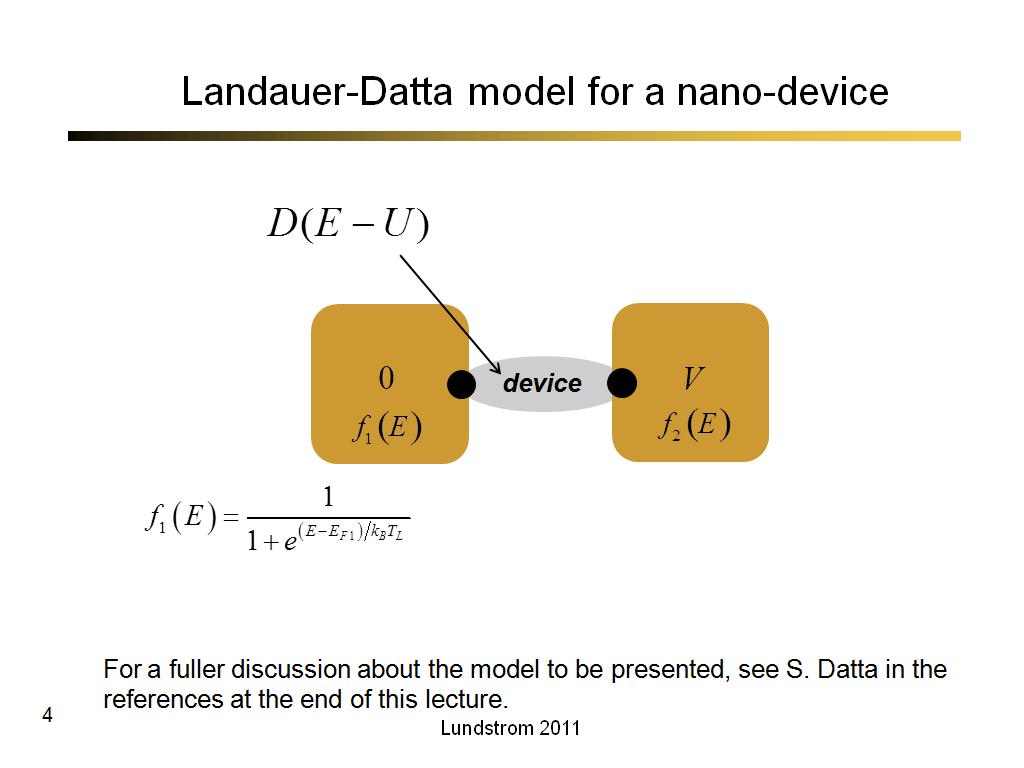
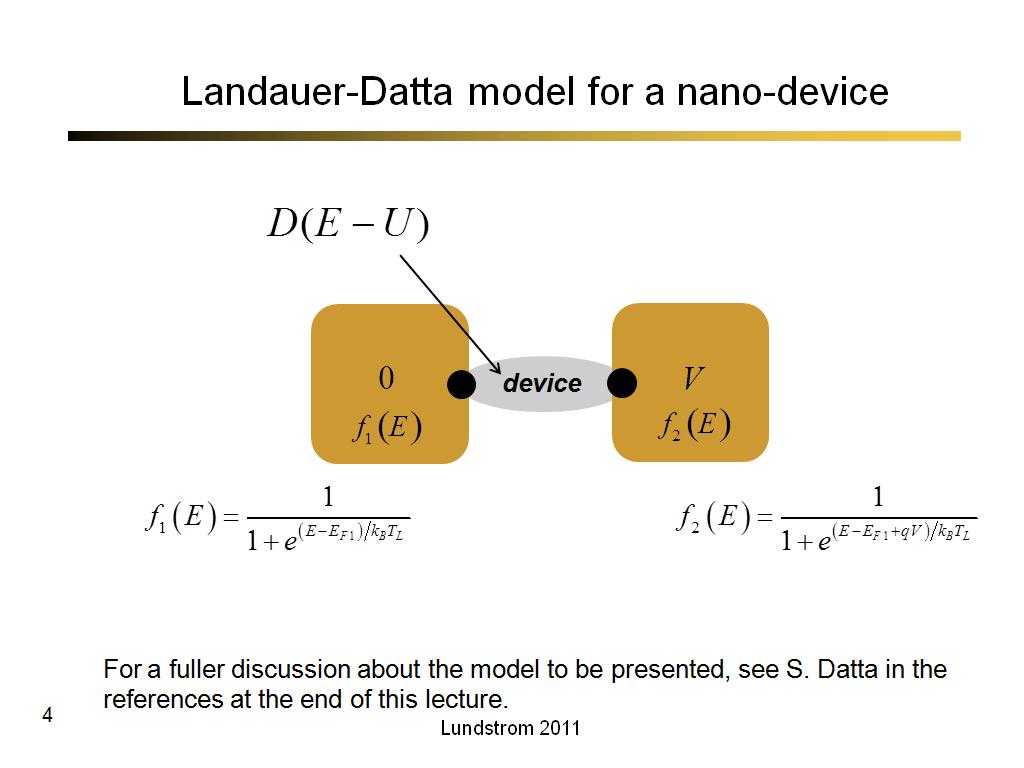
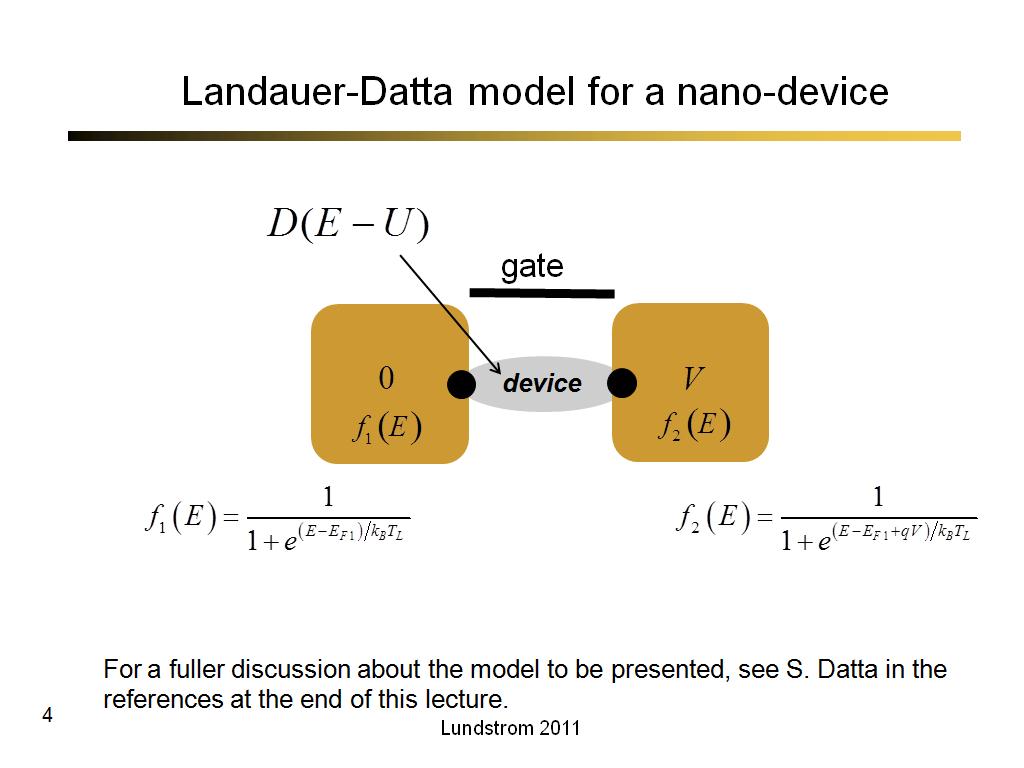
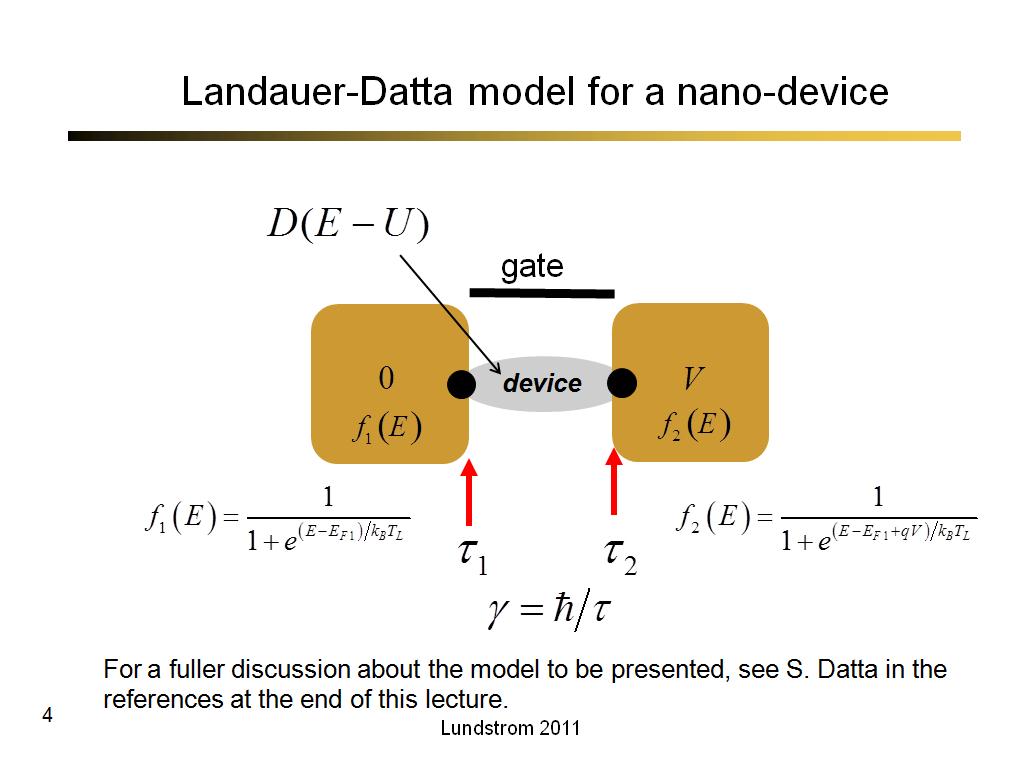
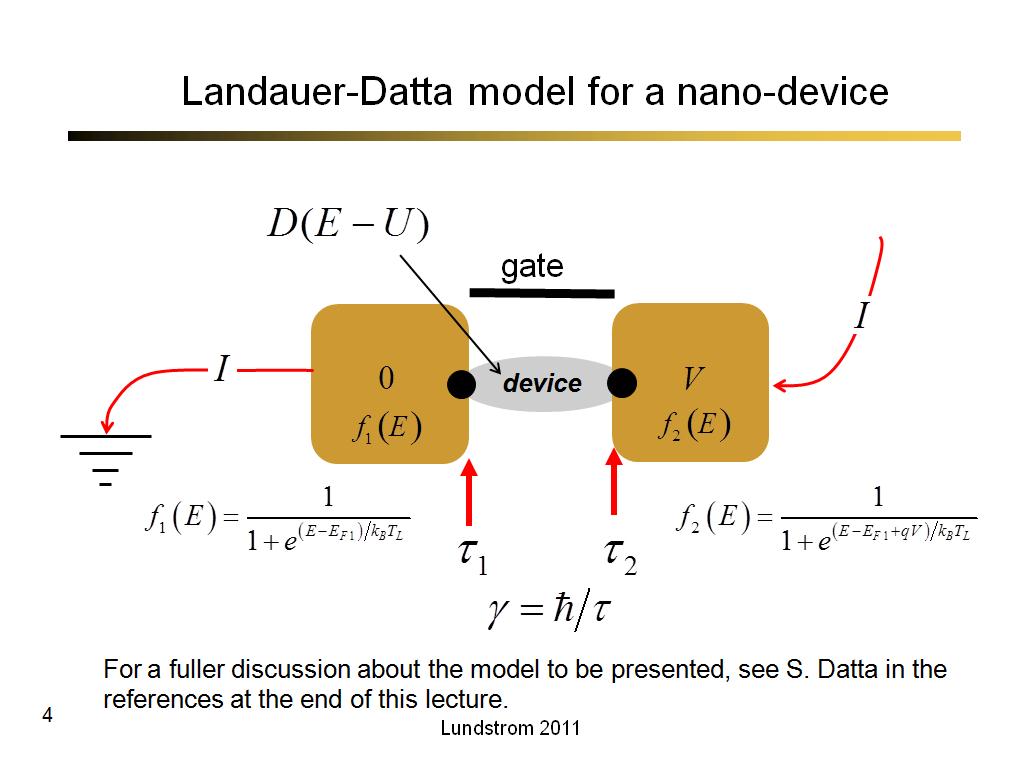
 4. Landauer-Datta model for a nan…
47.166666666666664
00:00/00:00
4. Landauer-Datta model for a nan…
47.166666666666664
00:00/00:00 -
 5. questions
288.86666666666667
00:00/00:00
5. questions
288.86666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
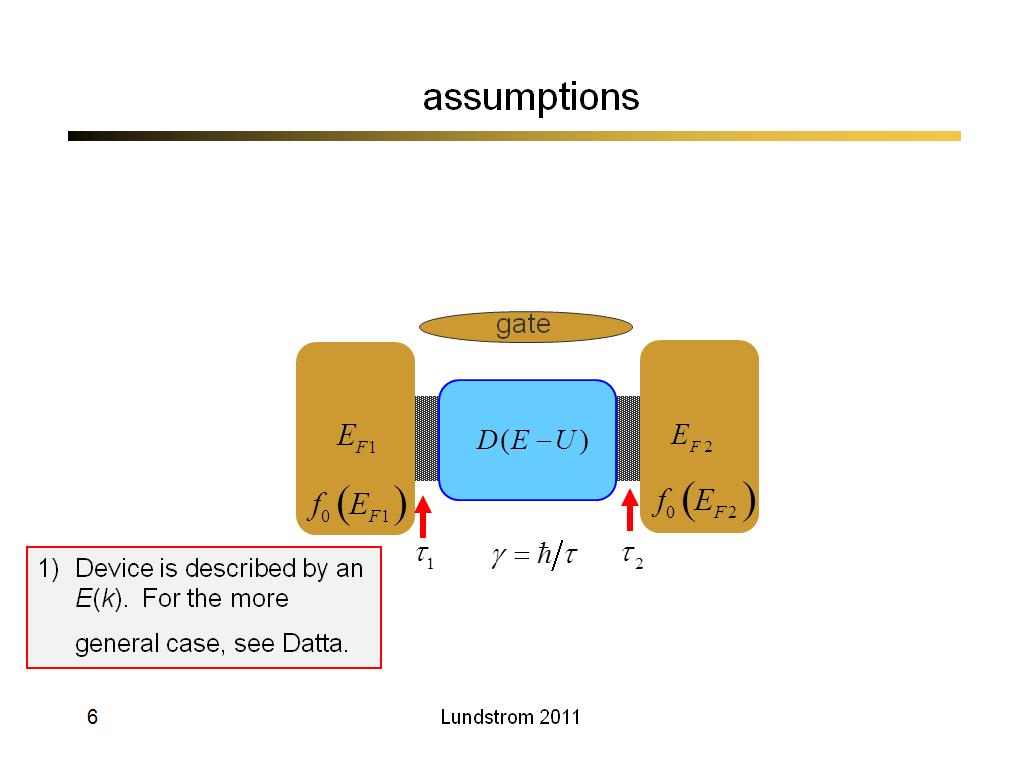
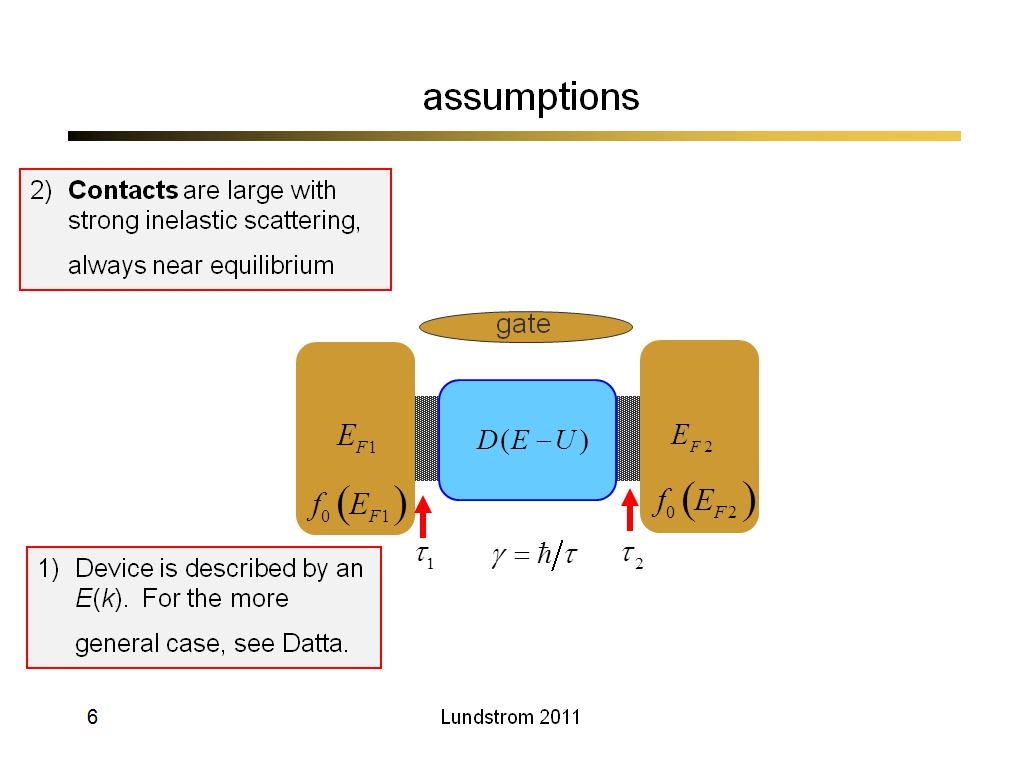
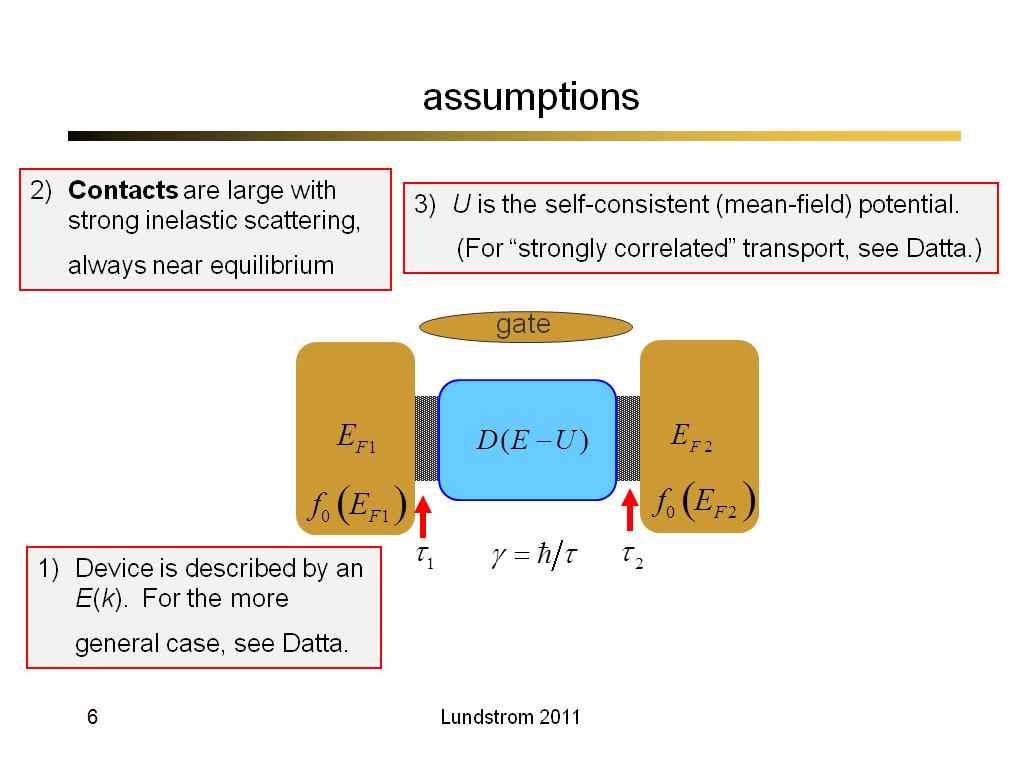
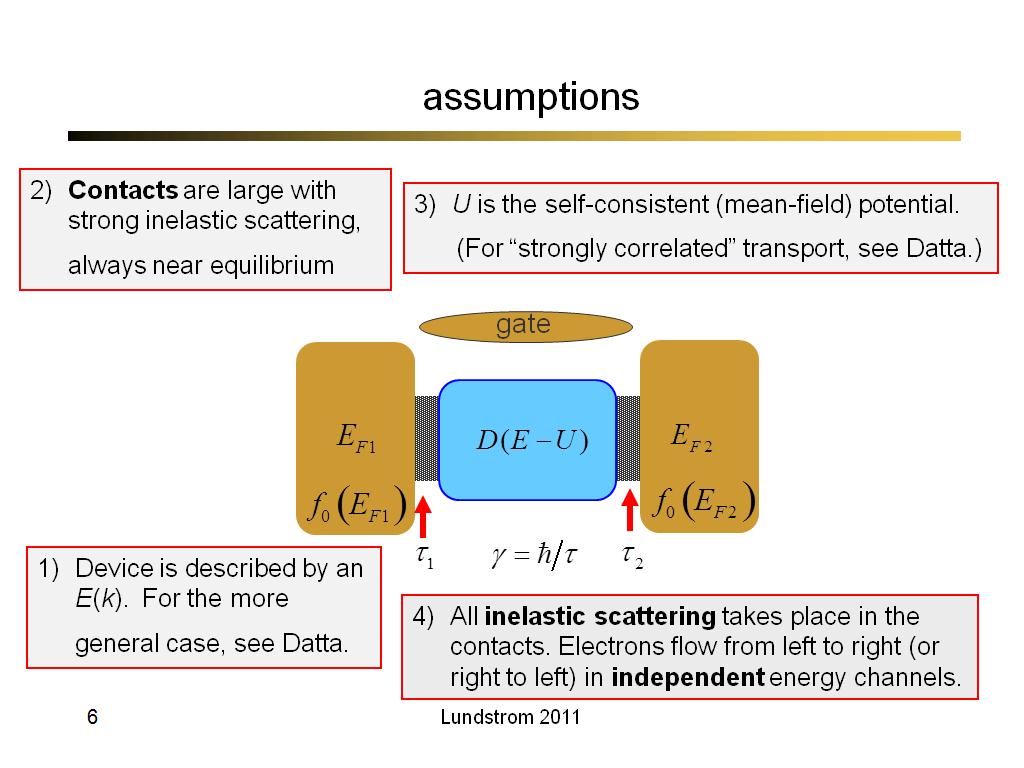
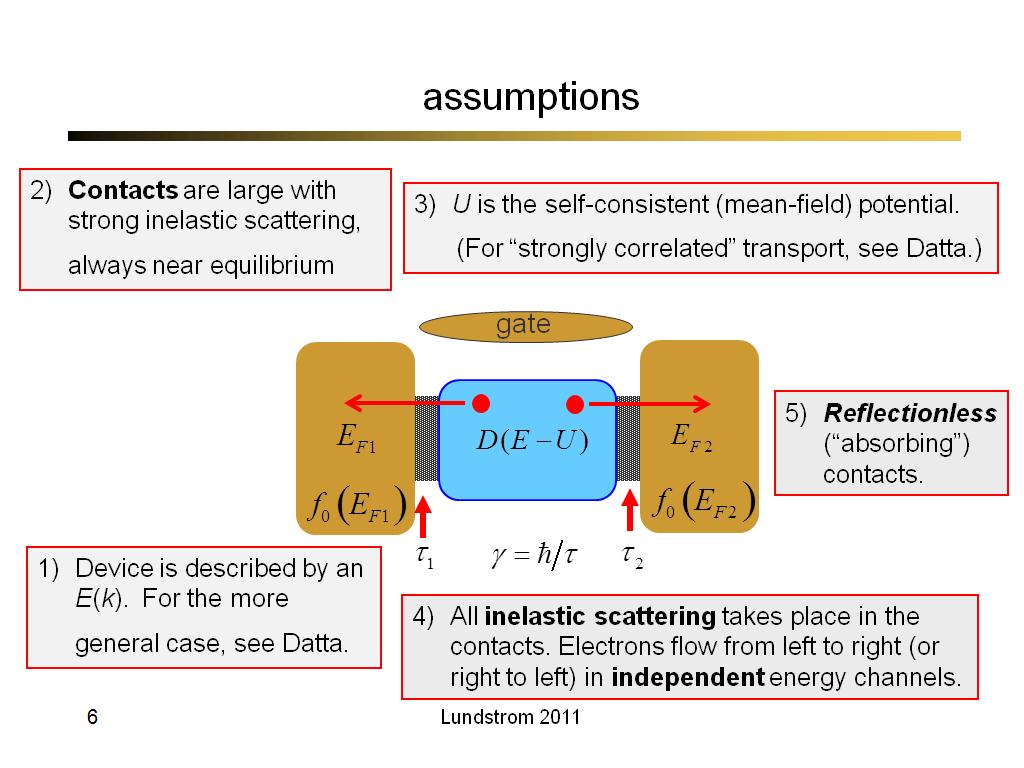
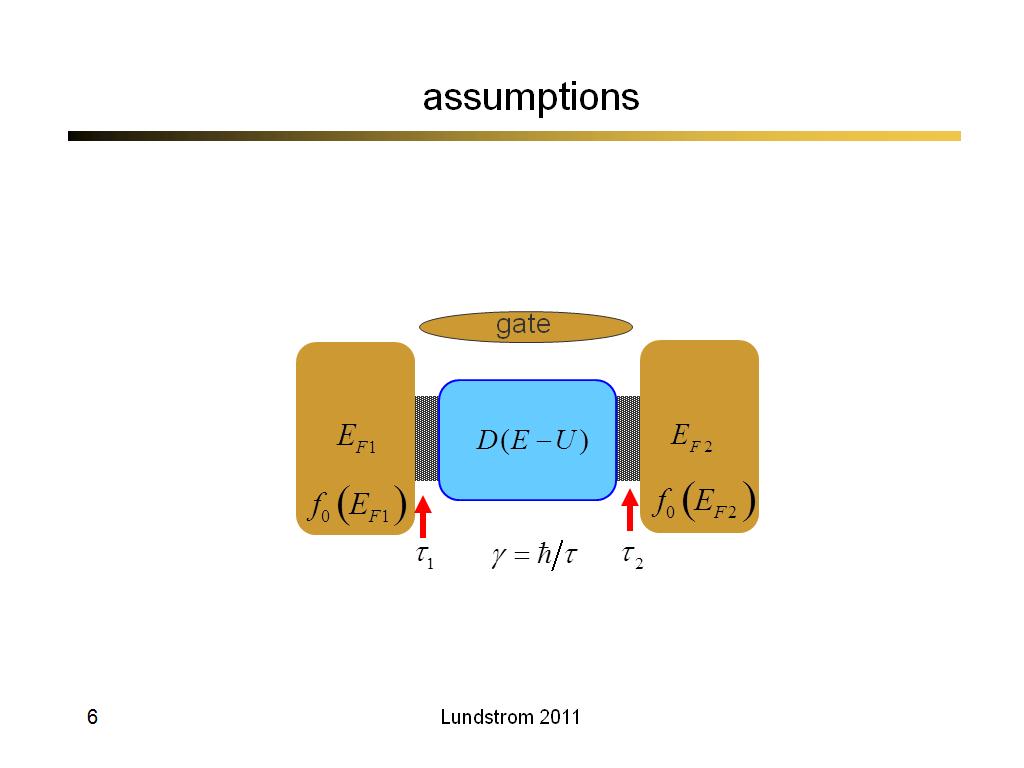 6. assumptions
315.3
00:00/00:00
6. assumptions
315.3
00:00/00:00 -
 7. outline
498.06666666666666
00:00/00:00
7. outline
498.06666666666666
00:00/00:00 -
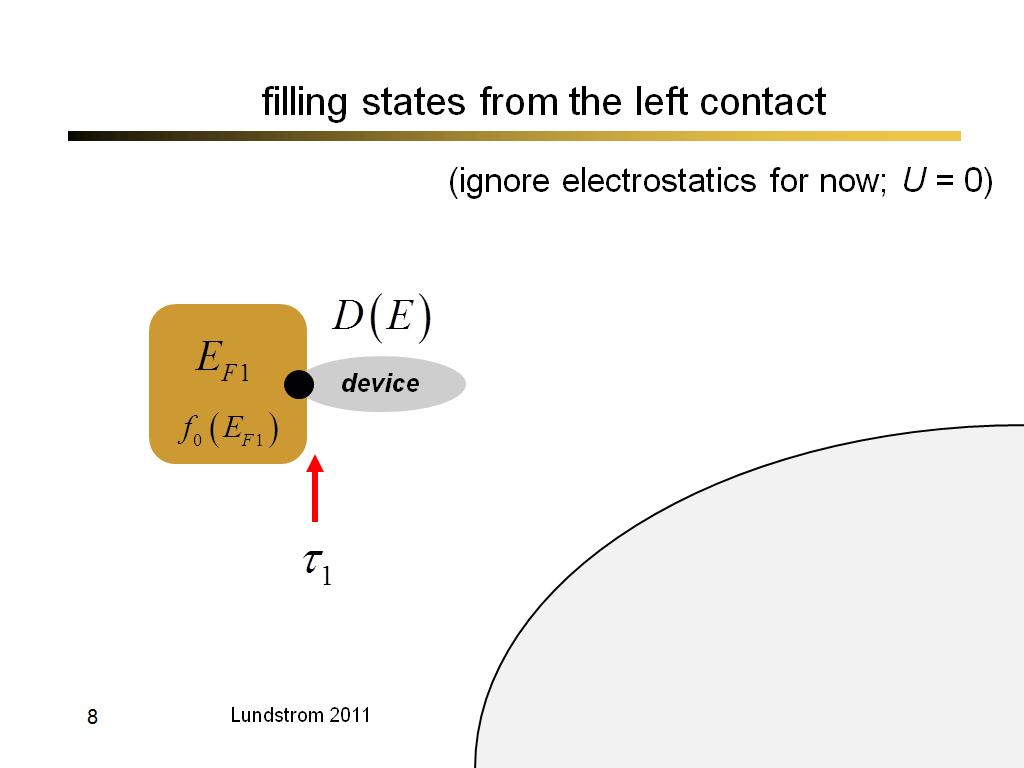
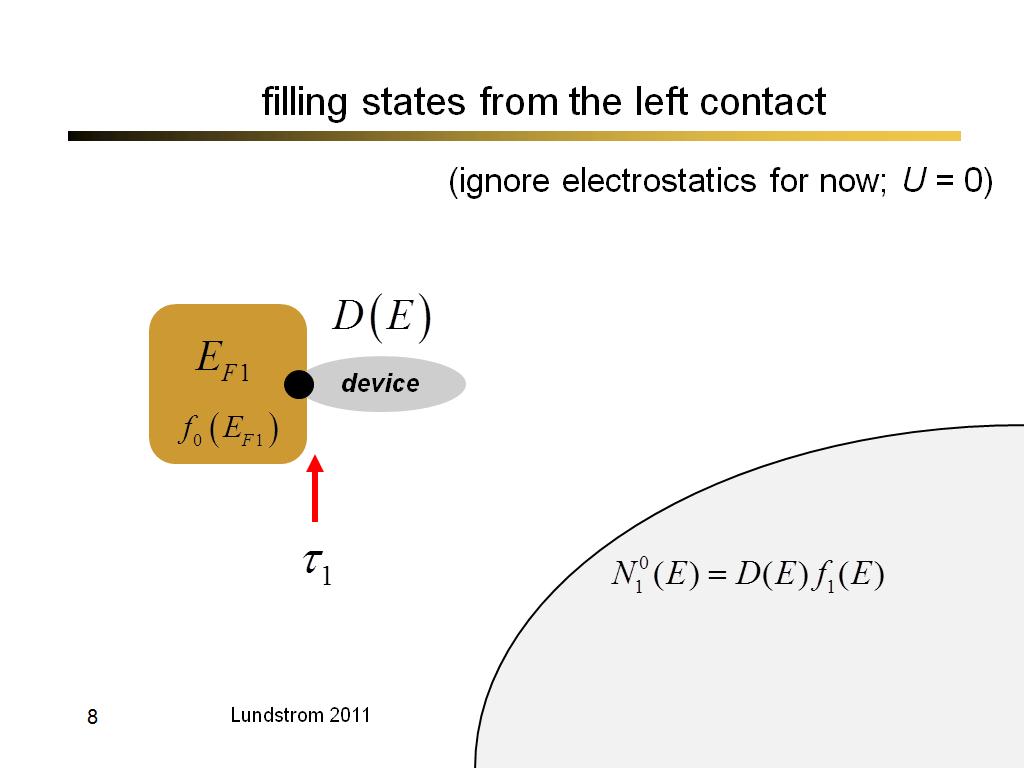
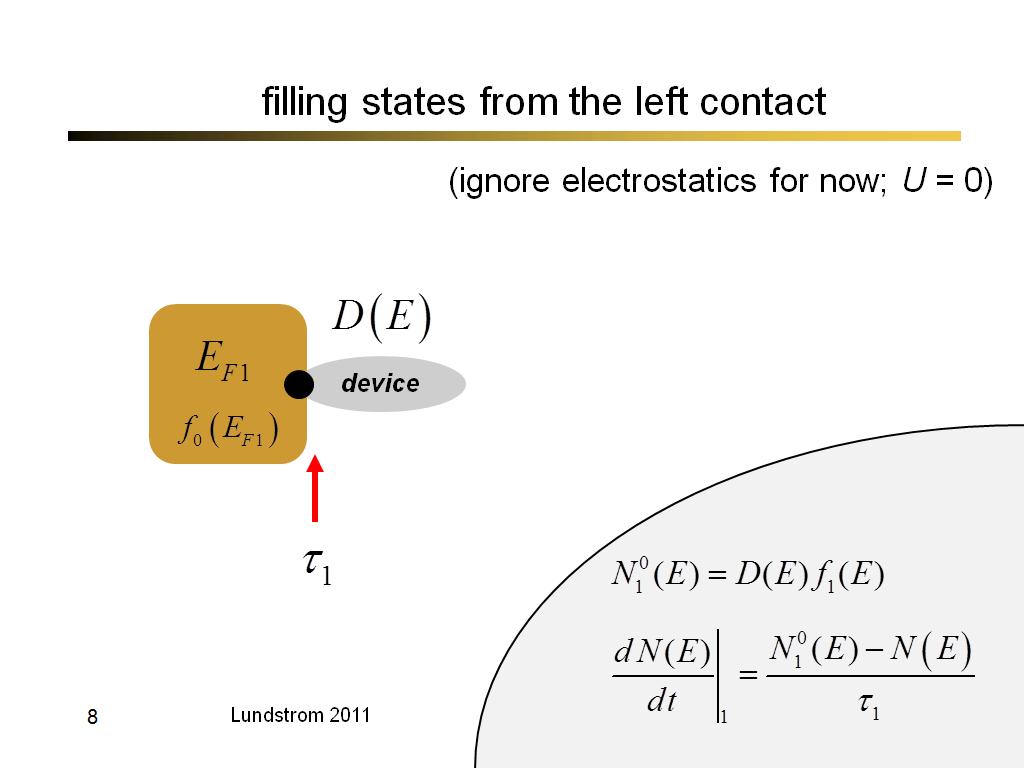
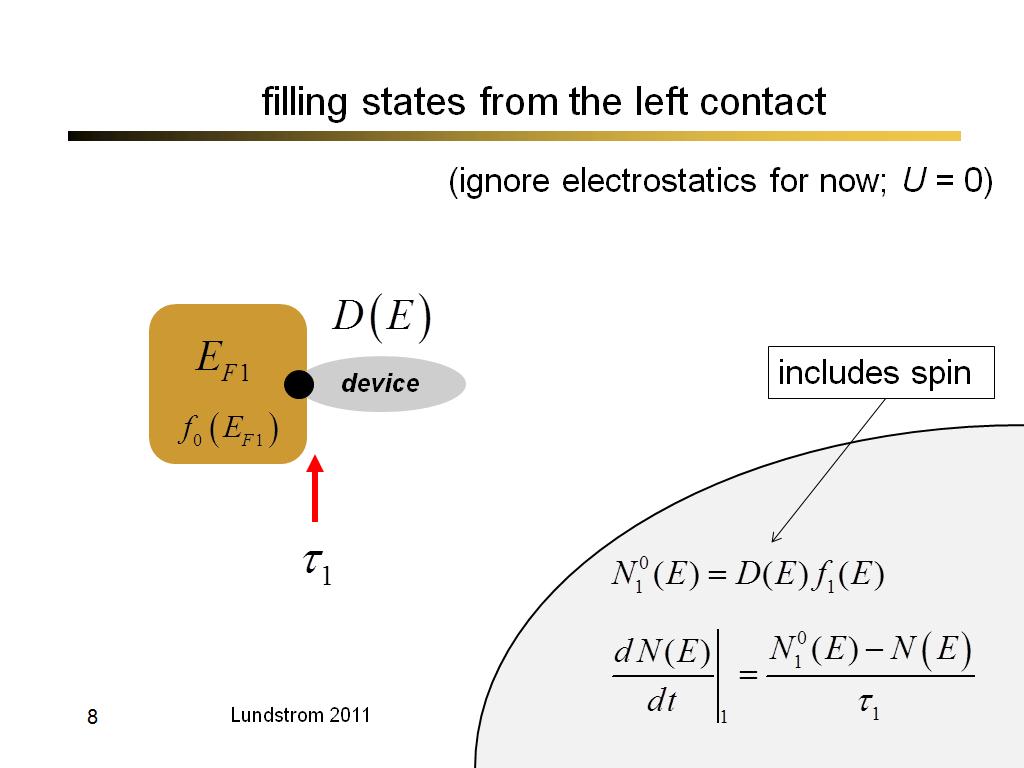
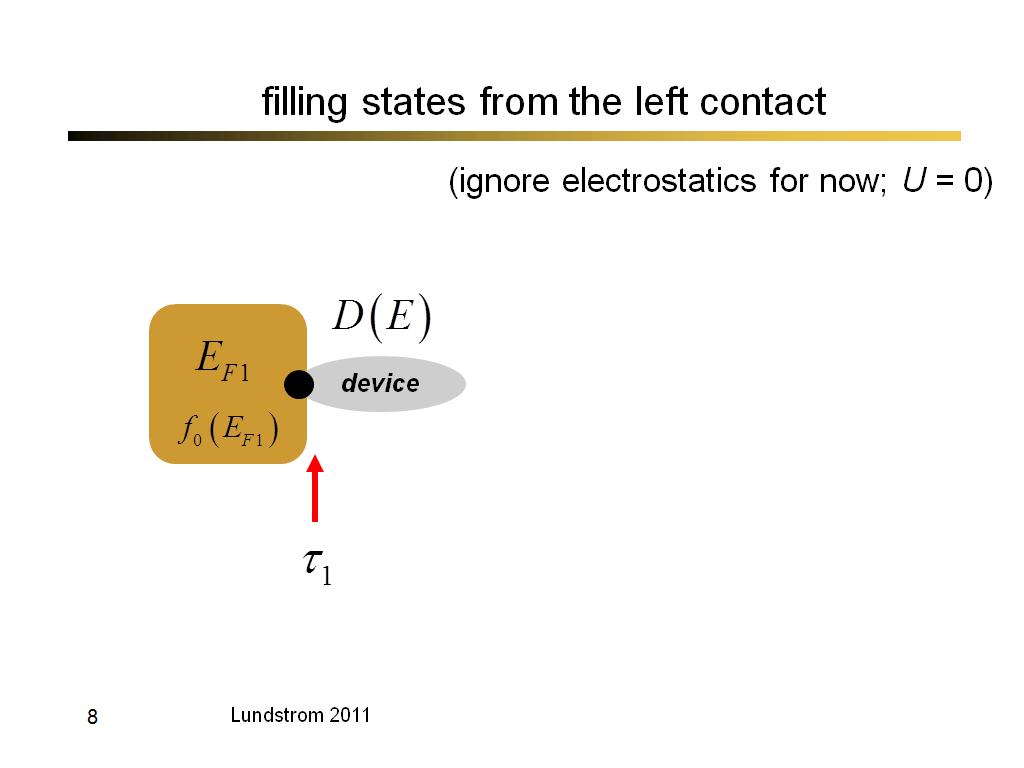 8. filling states from the left c…
510.83333333333331
00:00/00:00
8. filling states from the left c…
510.83333333333331
00:00/00:00 -
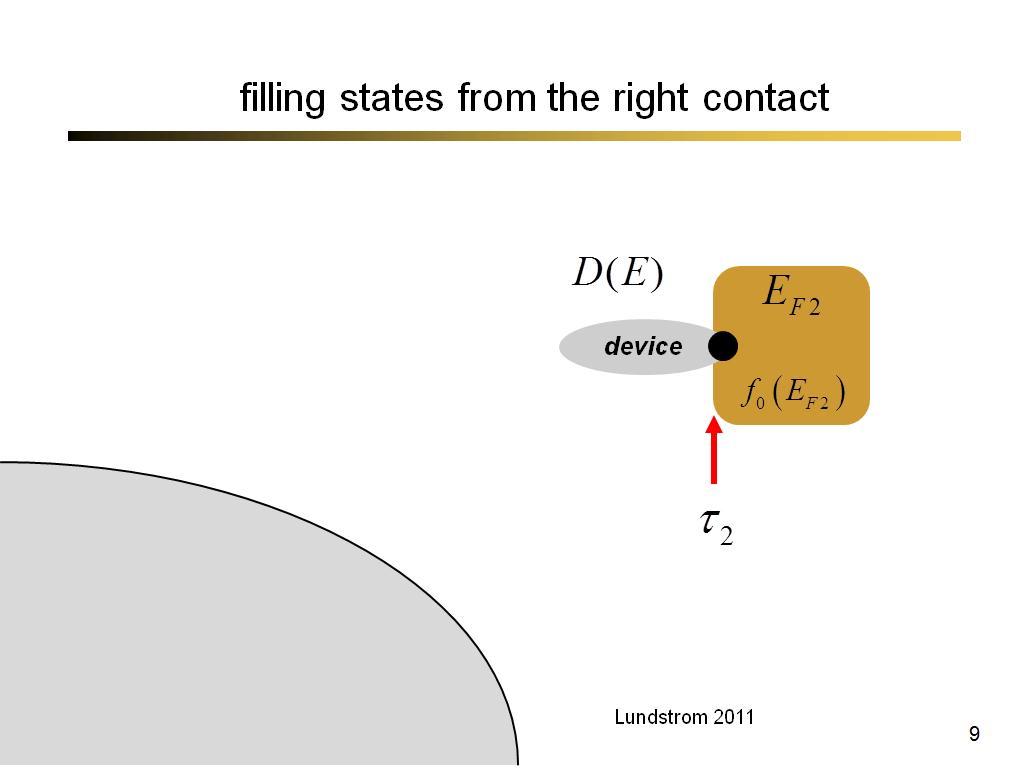
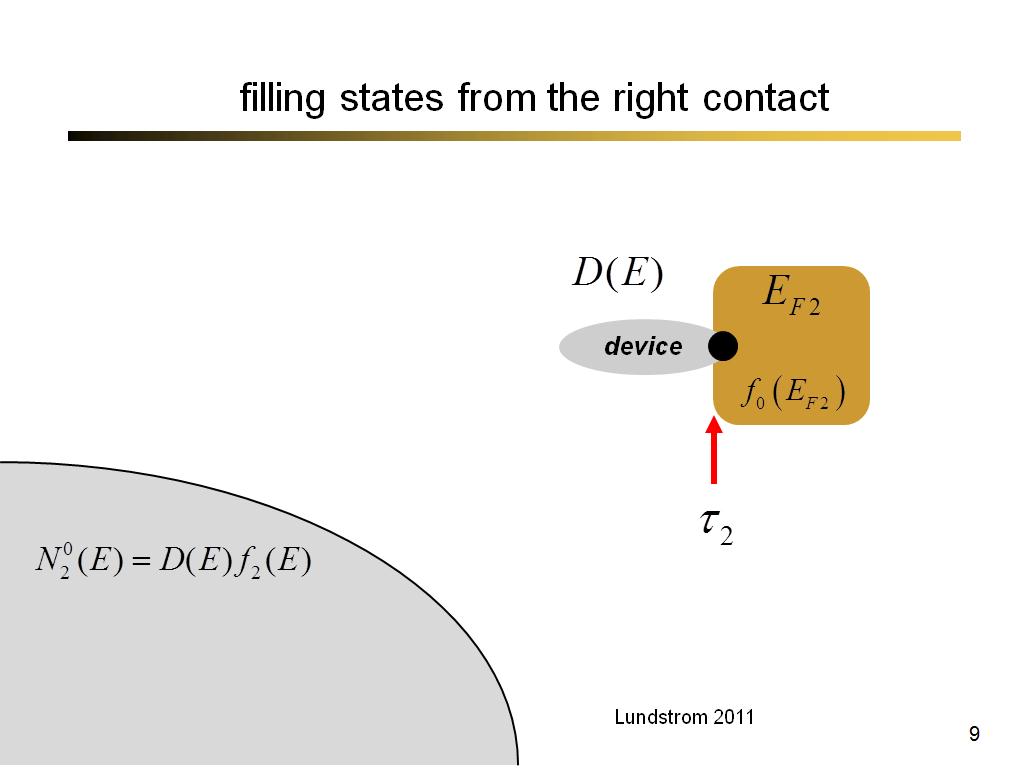
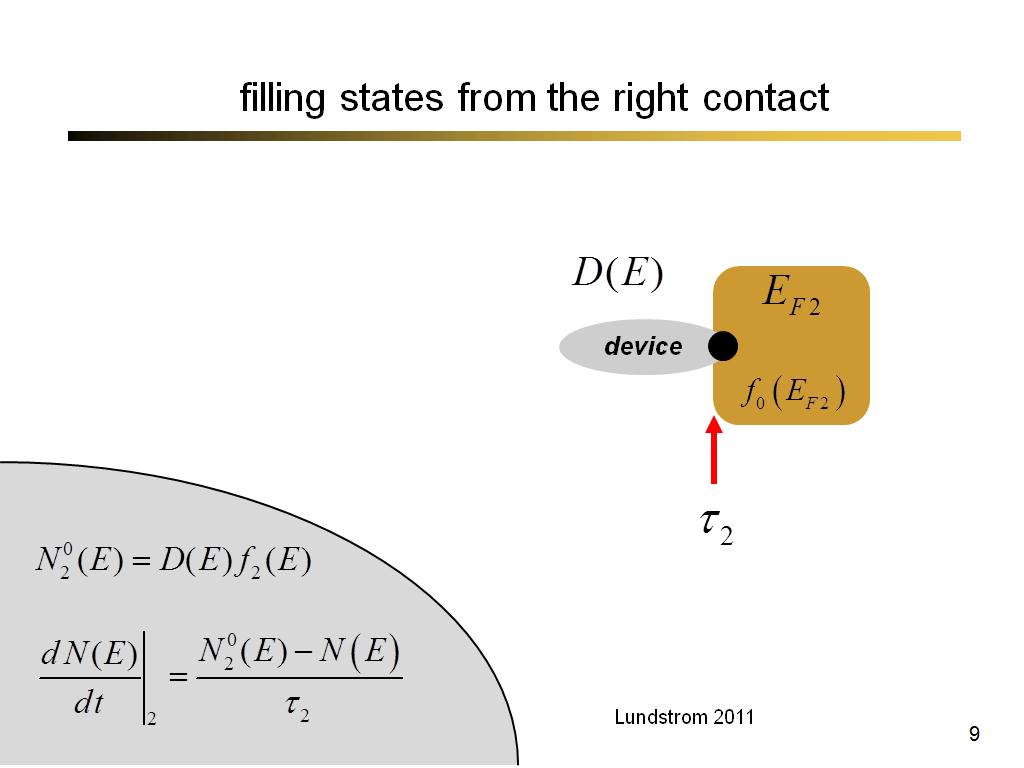
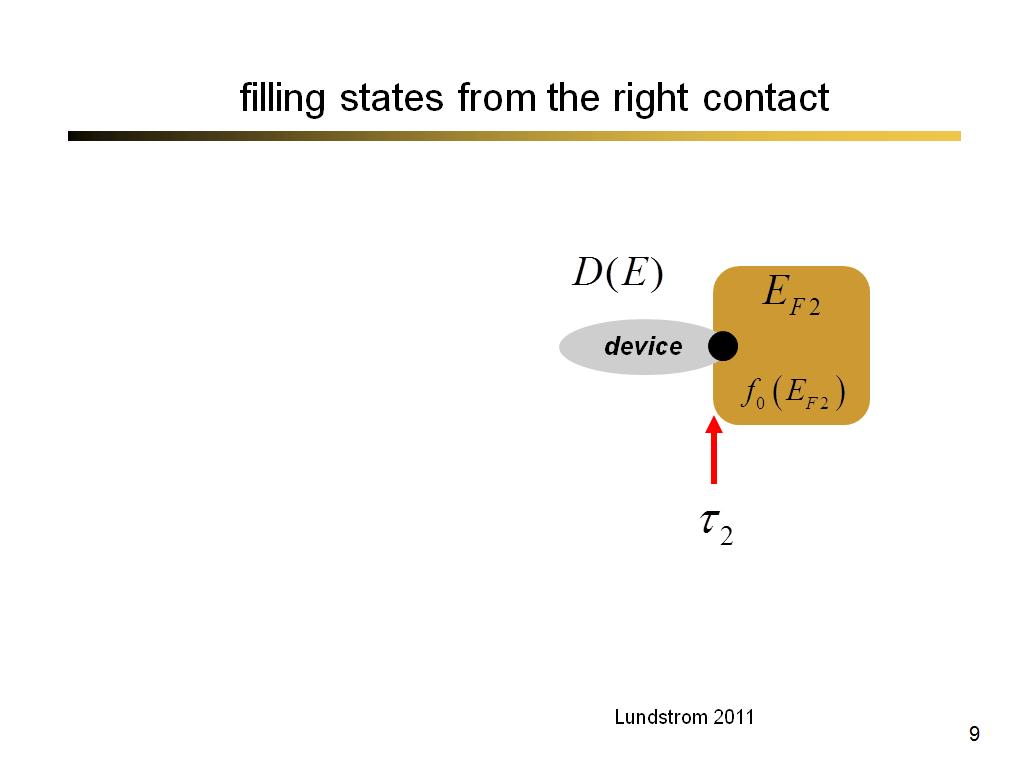 9. filling states from the right …
649.73333333333335
00:00/00:00
9. filling states from the right …
649.73333333333335
00:00/00:00 -
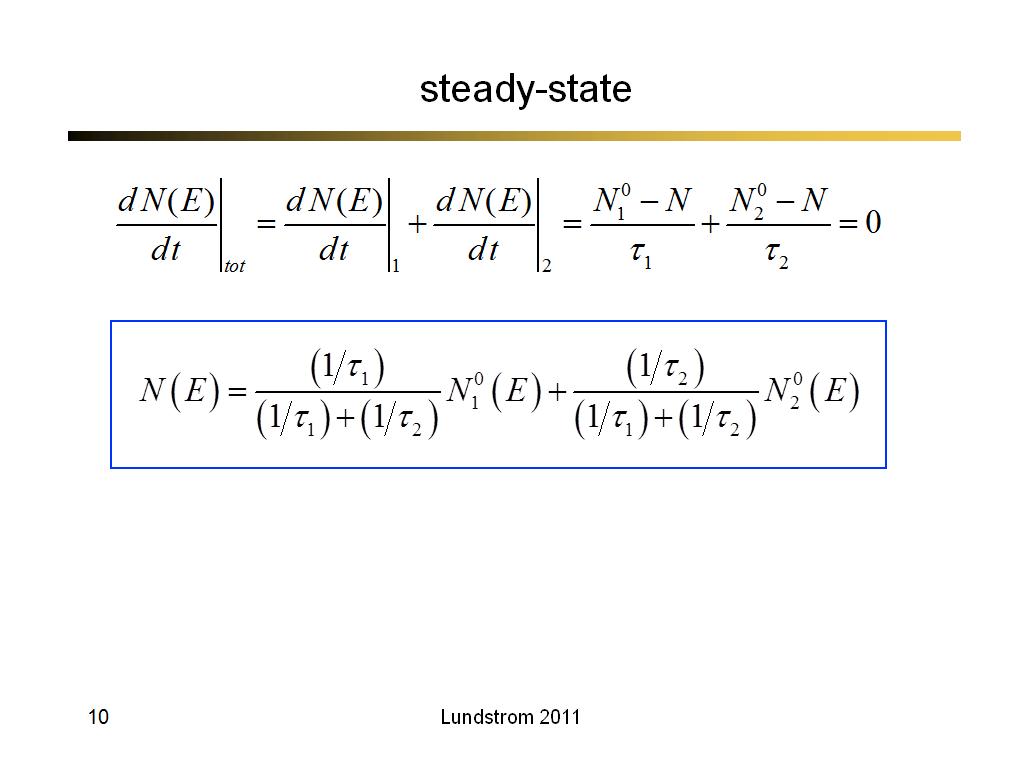
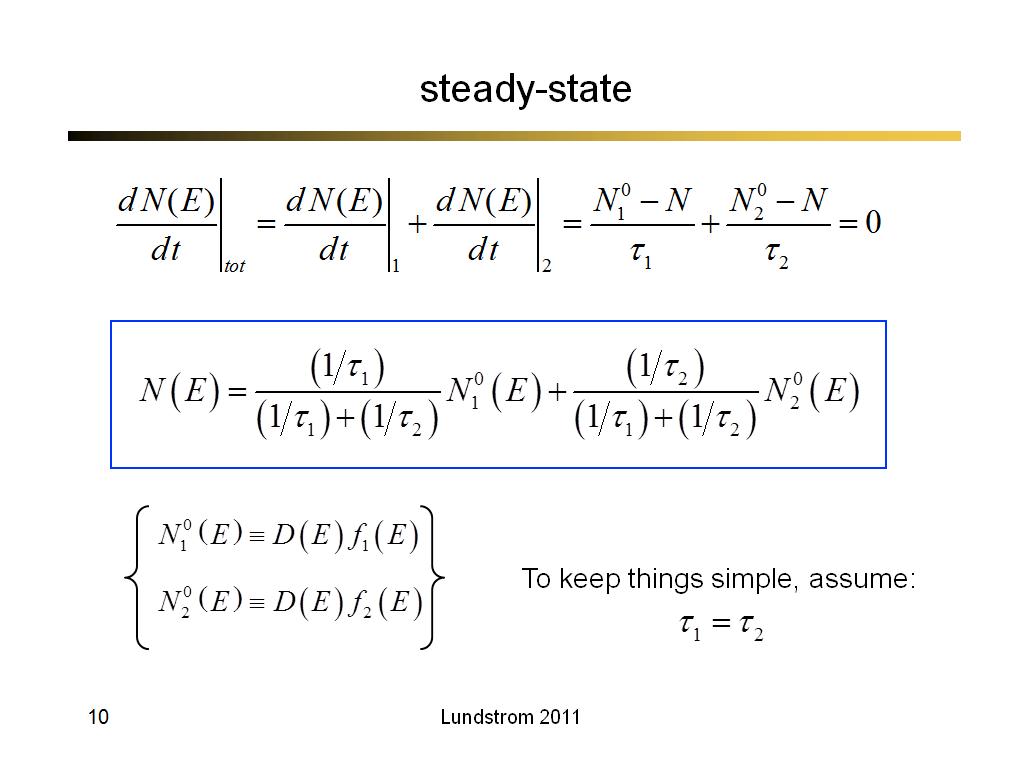
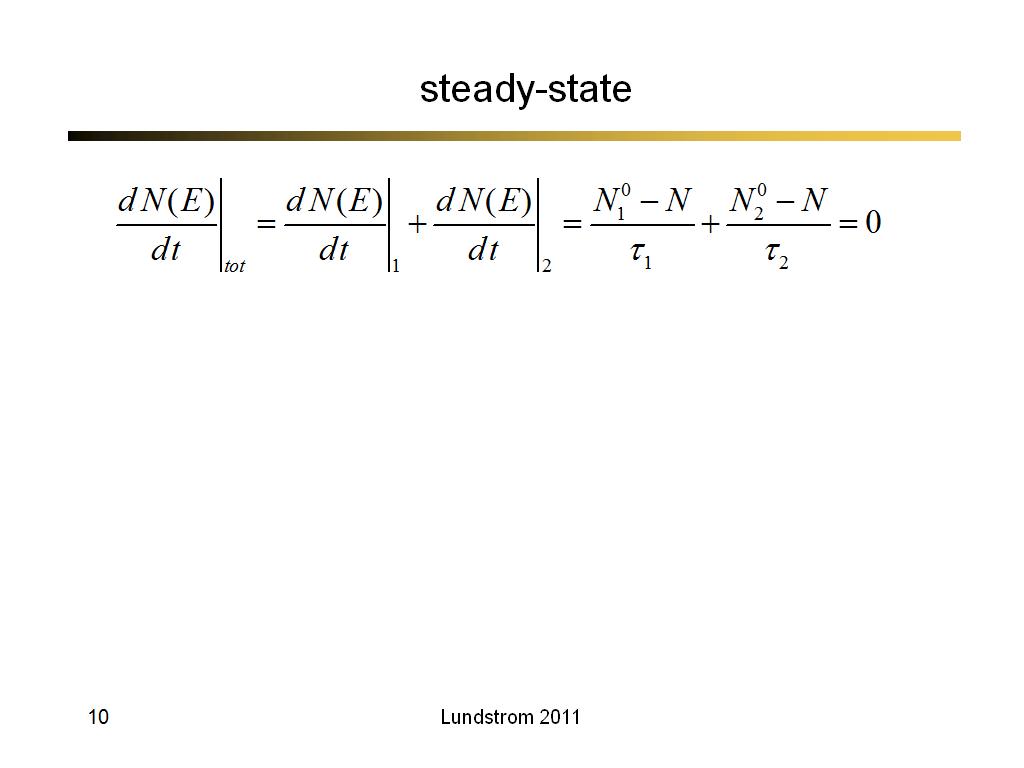 10. steady-state
684.0333333333333
00:00/00:00
10. steady-state
684.0333333333333
00:00/00:00 -
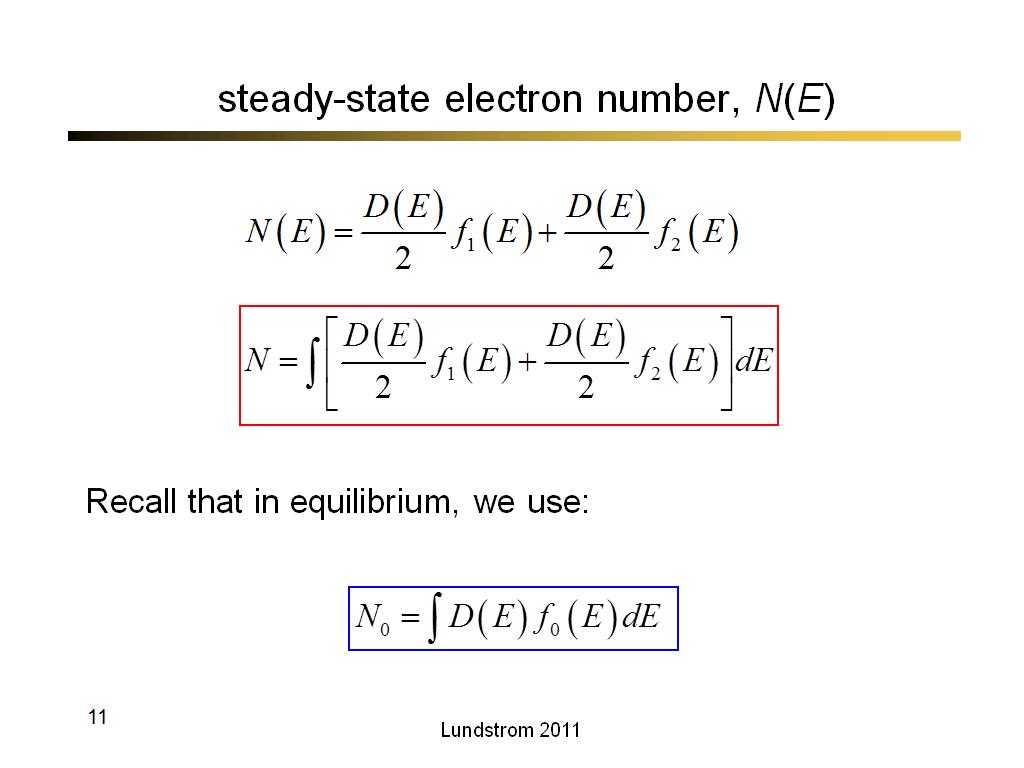
 11. steady-state electron number, …
815.1
00:00/00:00
11. steady-state electron number, …
815.1
00:00/00:00 -
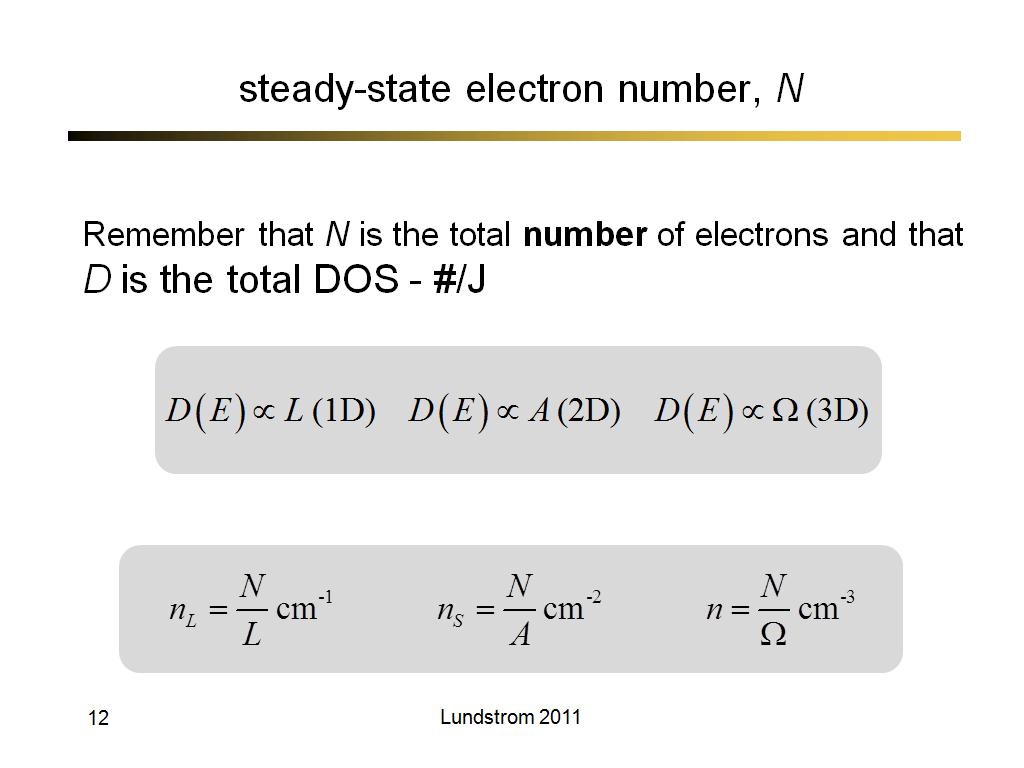
 12. steady-state electron number, …
917.6
00:00/00:00
12. steady-state electron number, …
917.6
00:00/00:00 -
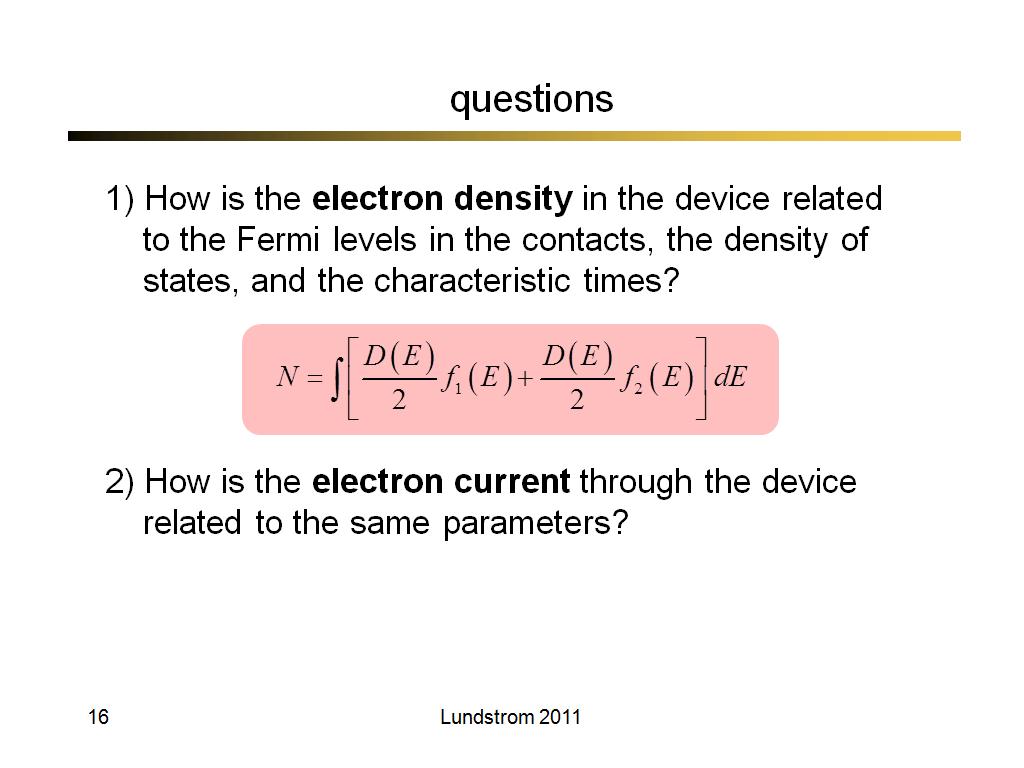
 13. questions
1005.9
00:00/00:00
13. questions
1005.9
00:00/00:00 -
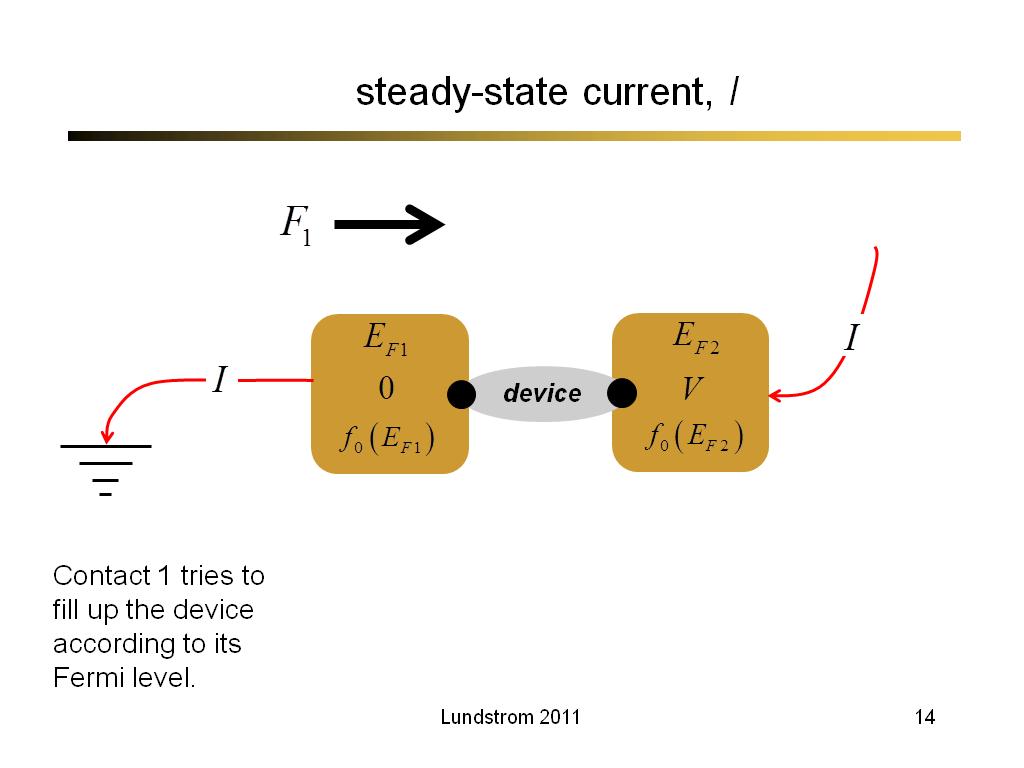
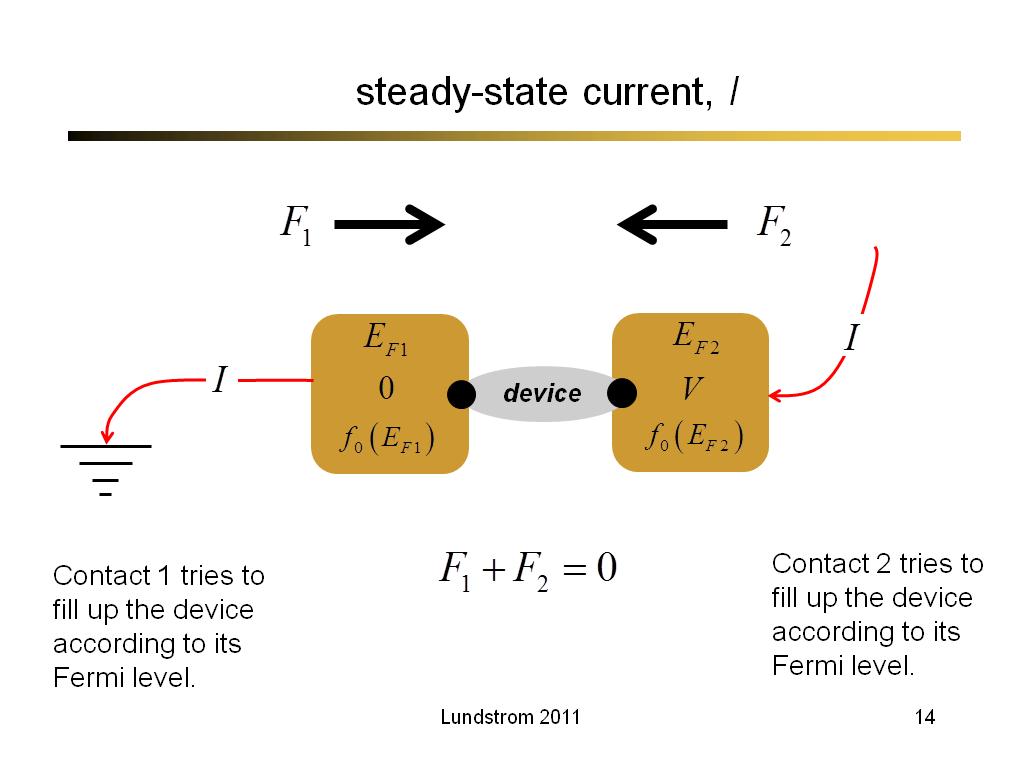
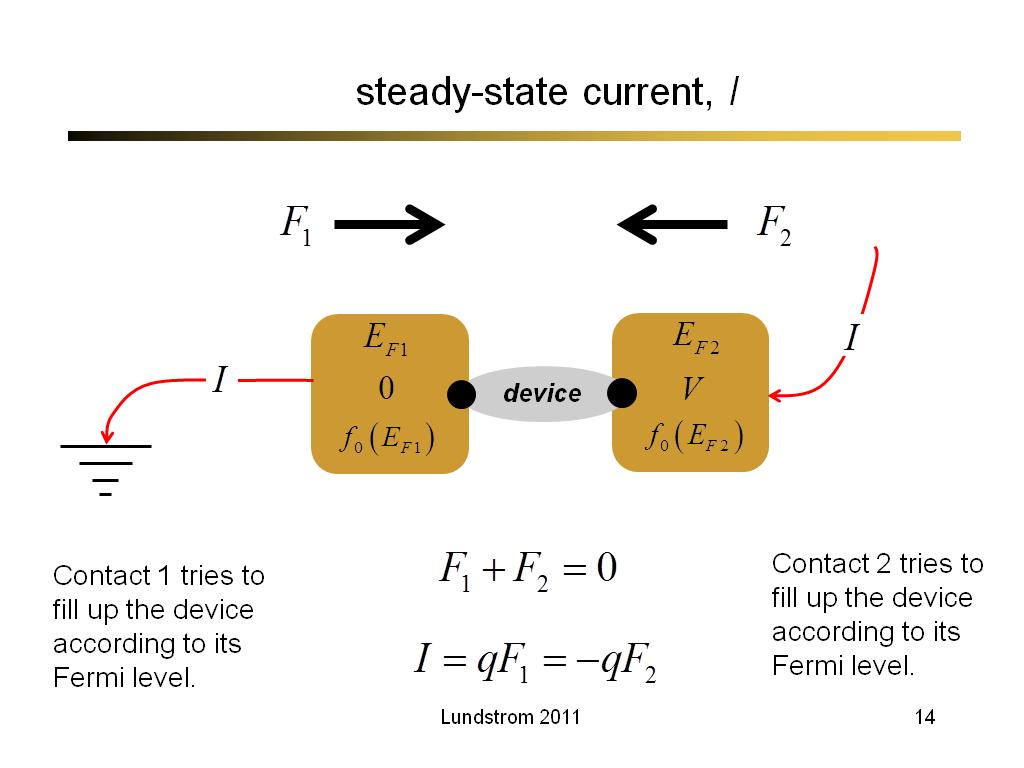
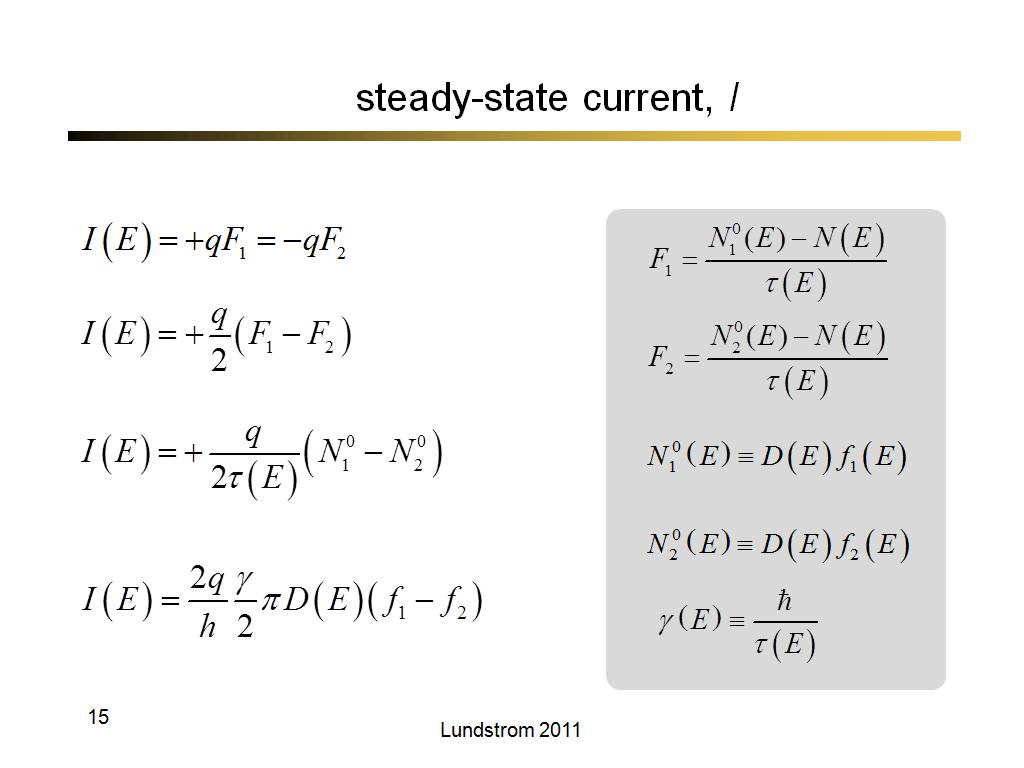
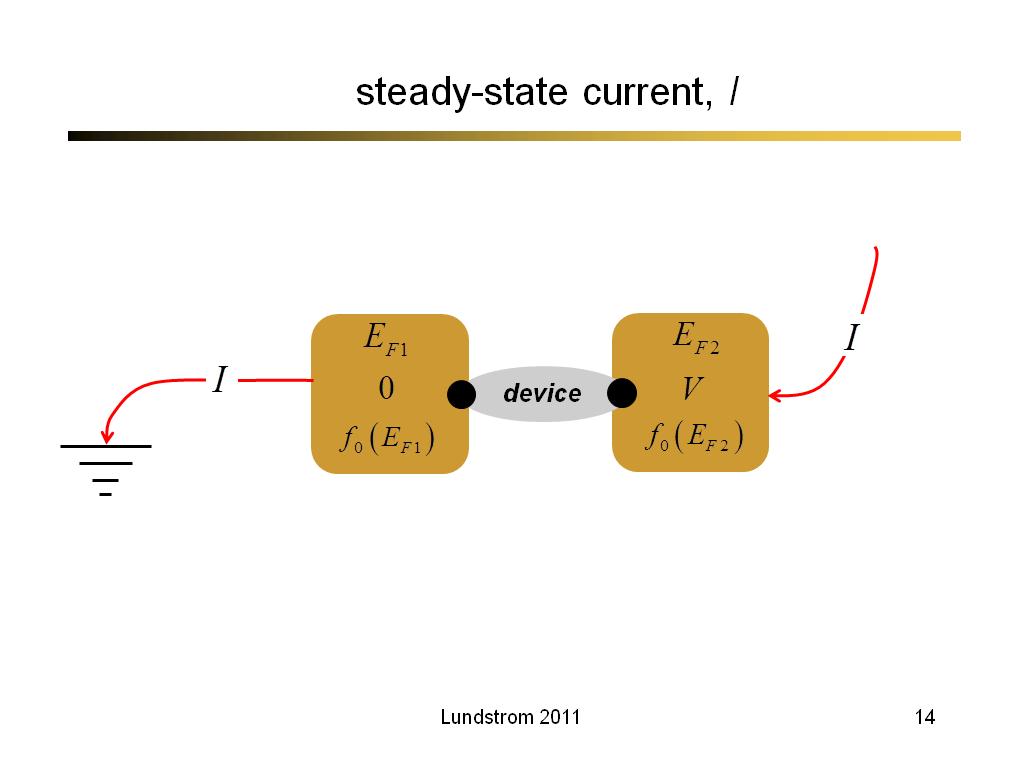 14. steady-state current, I
1018.3666666666667
00:00/00:00
14. steady-state current, I
1018.3666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
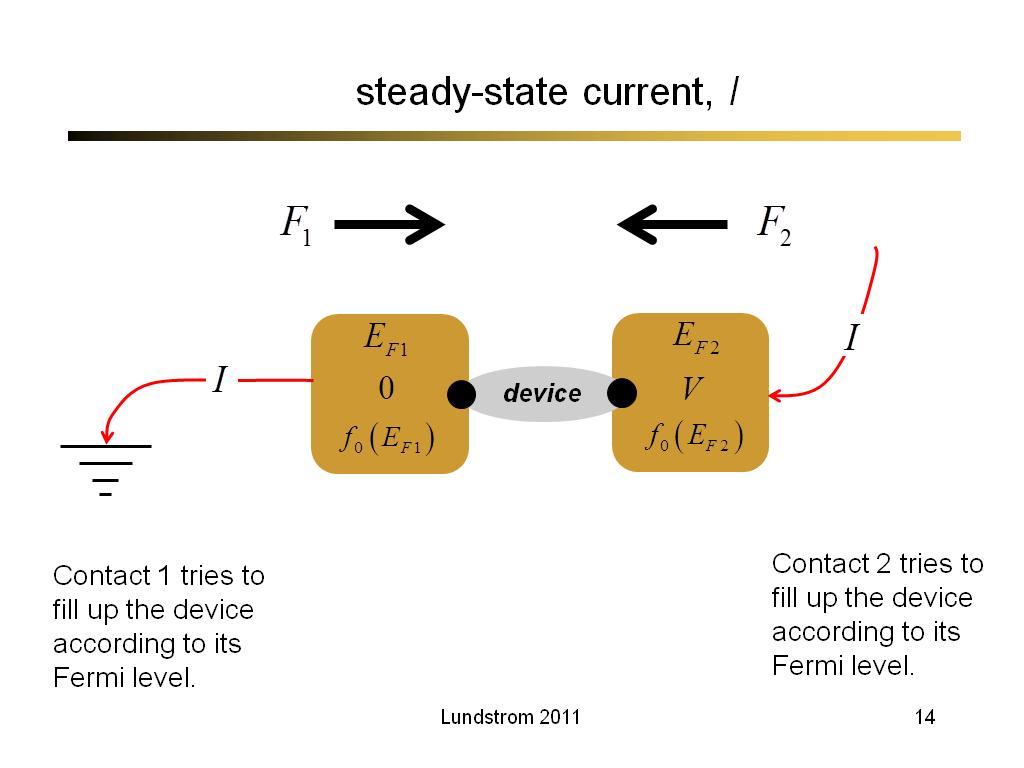
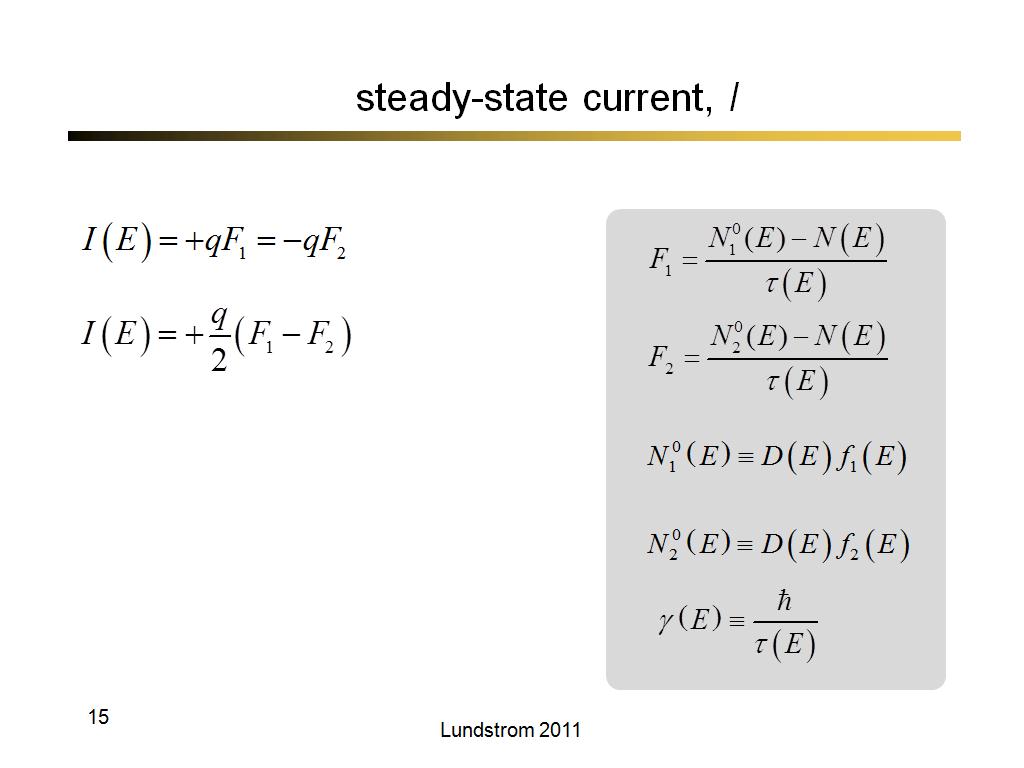
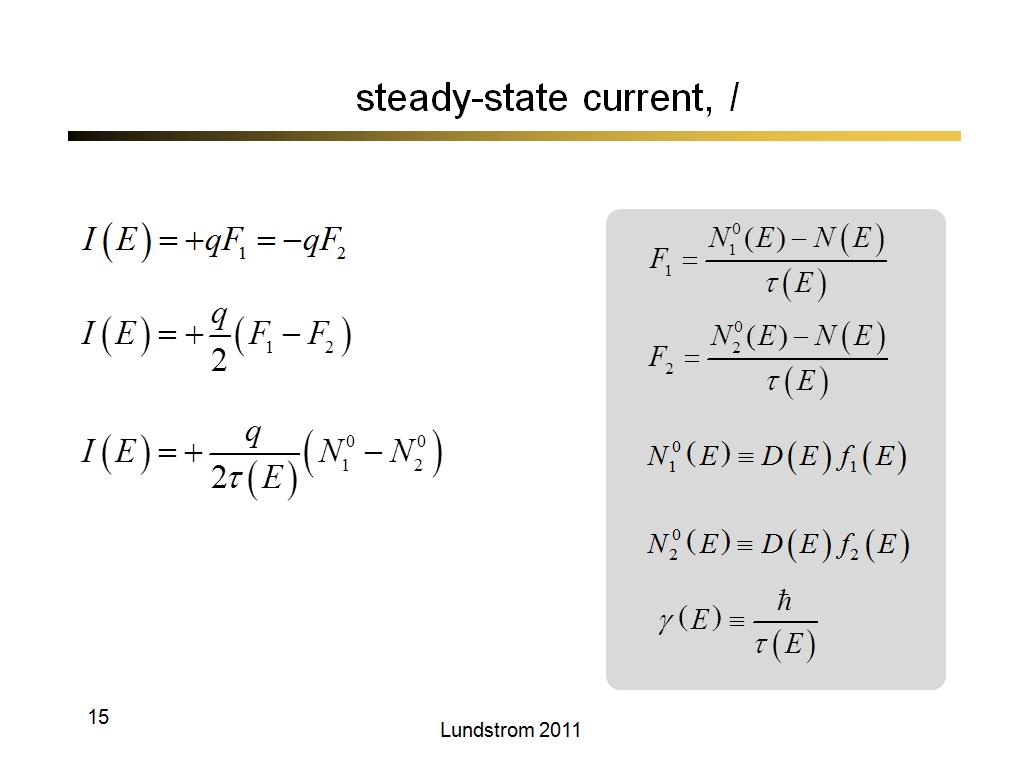
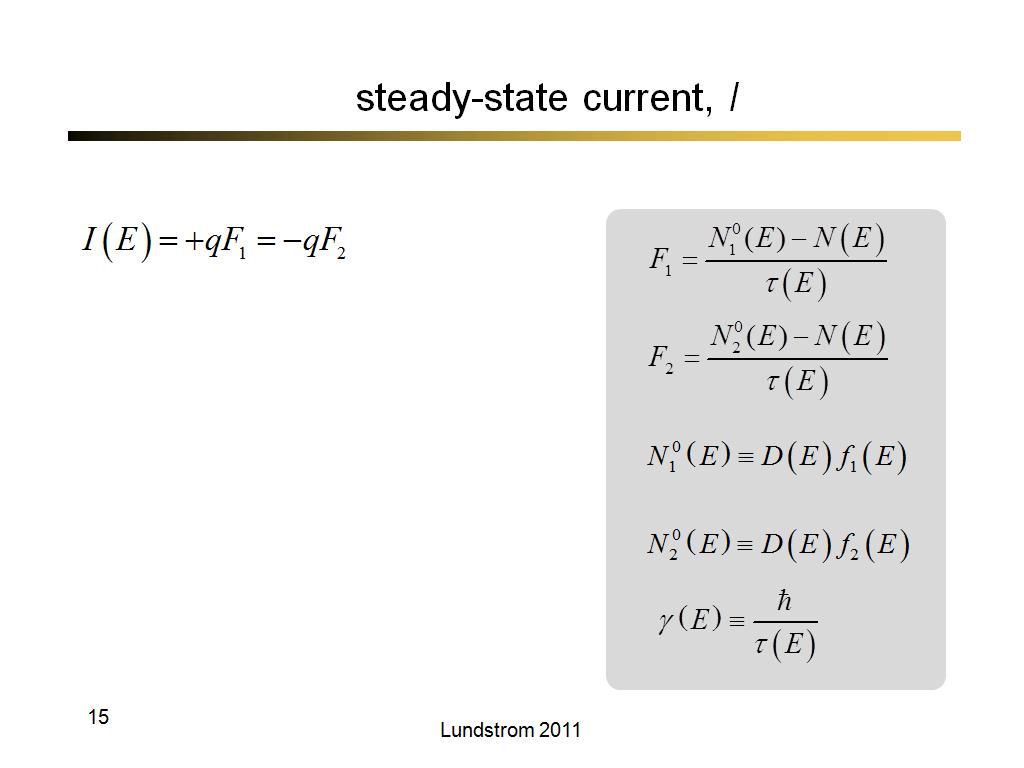 15. steady-state current, I
1104.3666666666666
00:00/00:00
15. steady-state current, I
1104.3666666666666
00:00/00:00 -
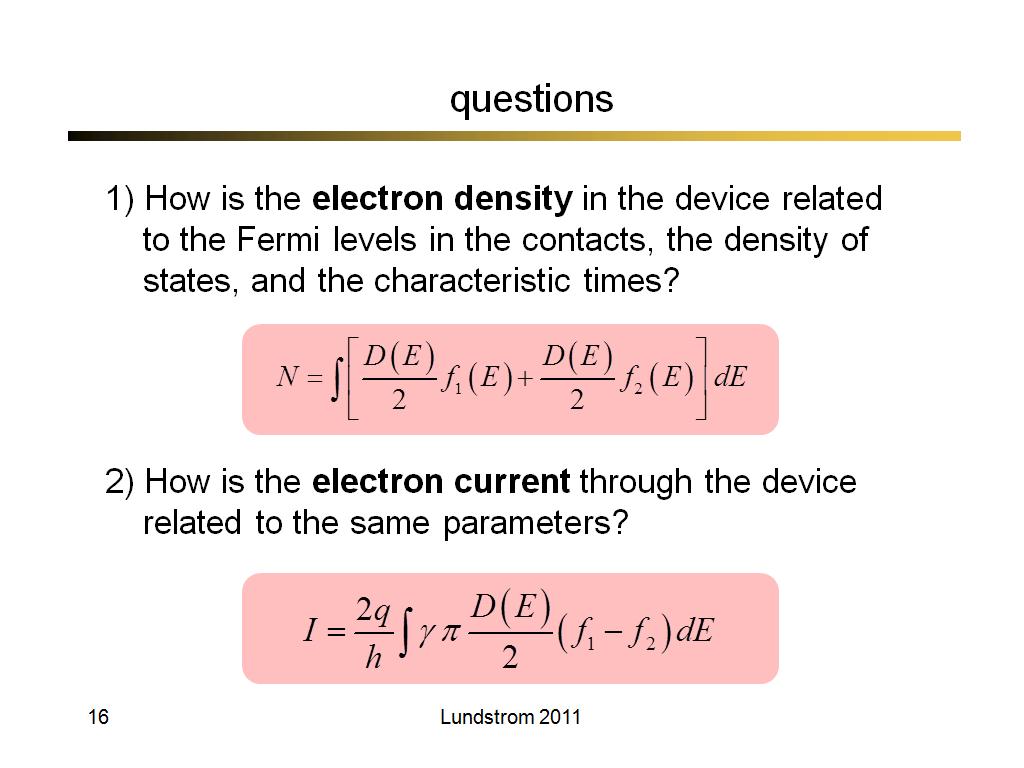
 16. questions
1148.6666666666667
00:00/00:00
16. questions
1148.6666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
 17. outline
1218.9666666666667
00:00/00:00
17. outline
1218.9666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
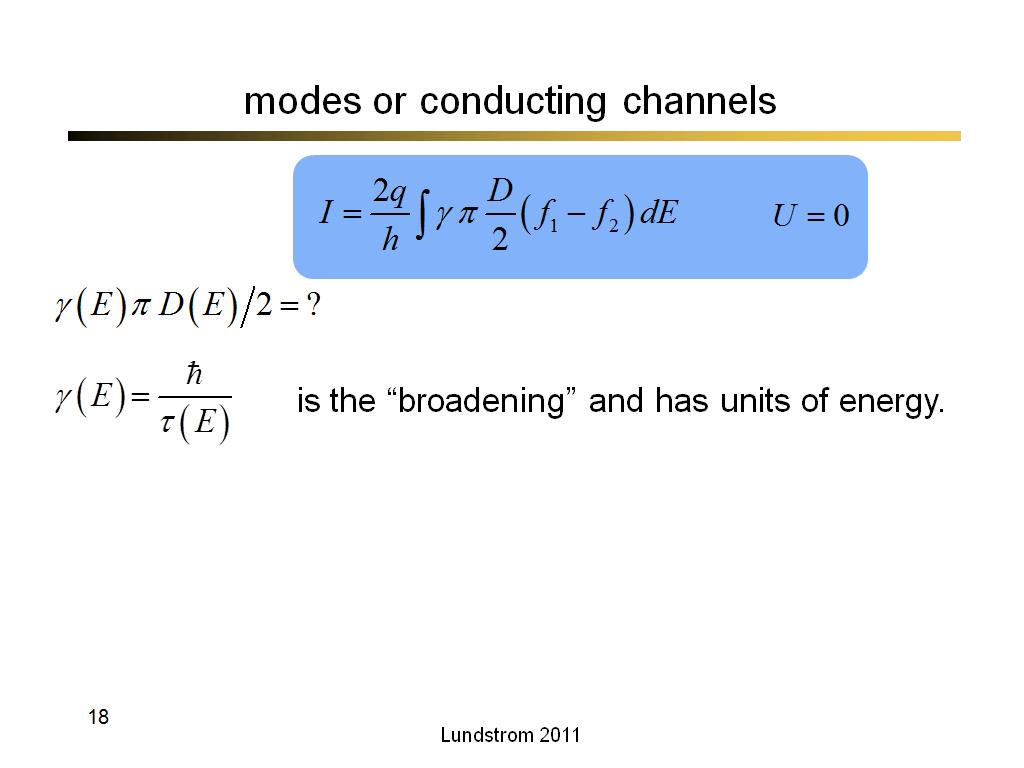
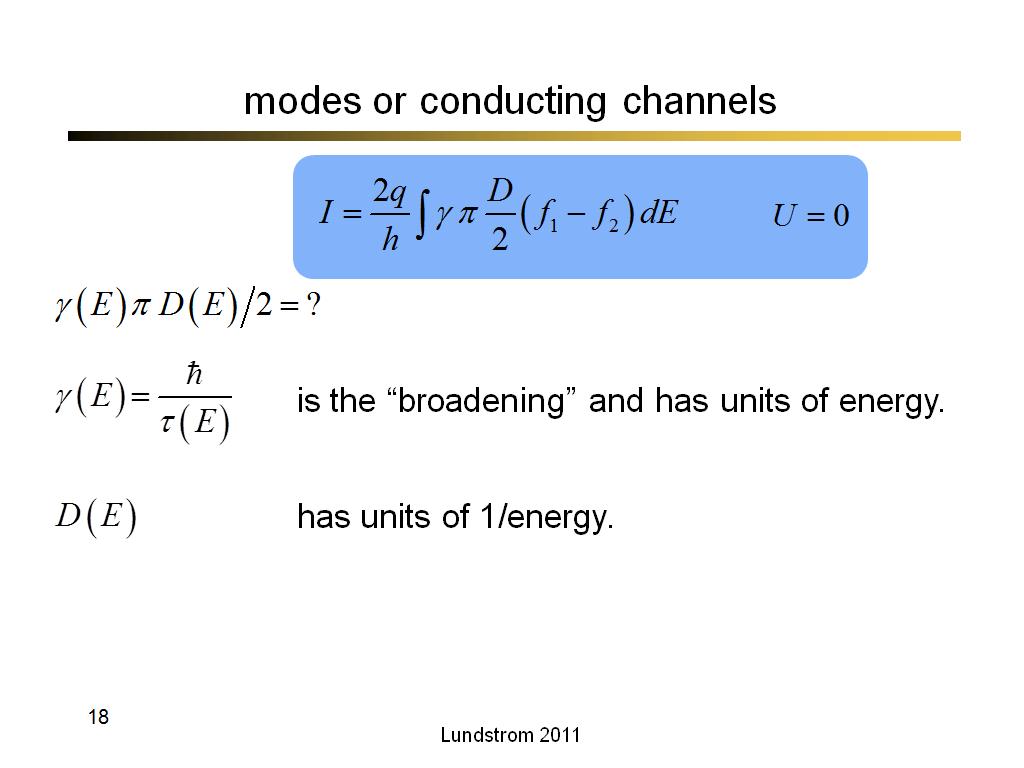
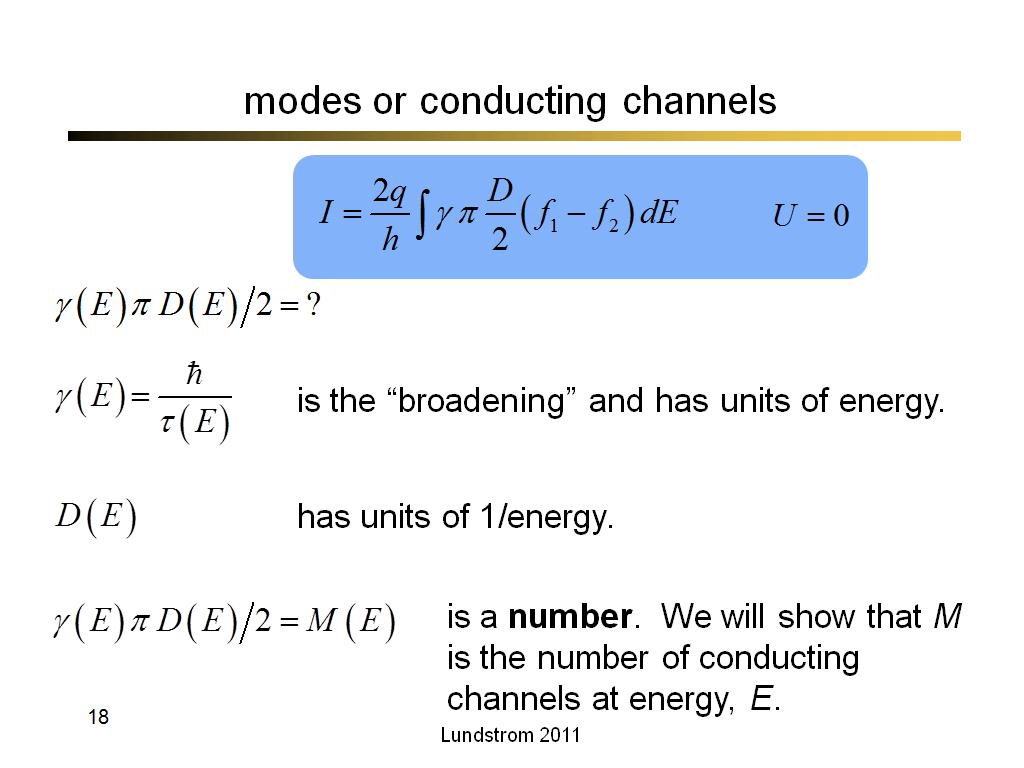
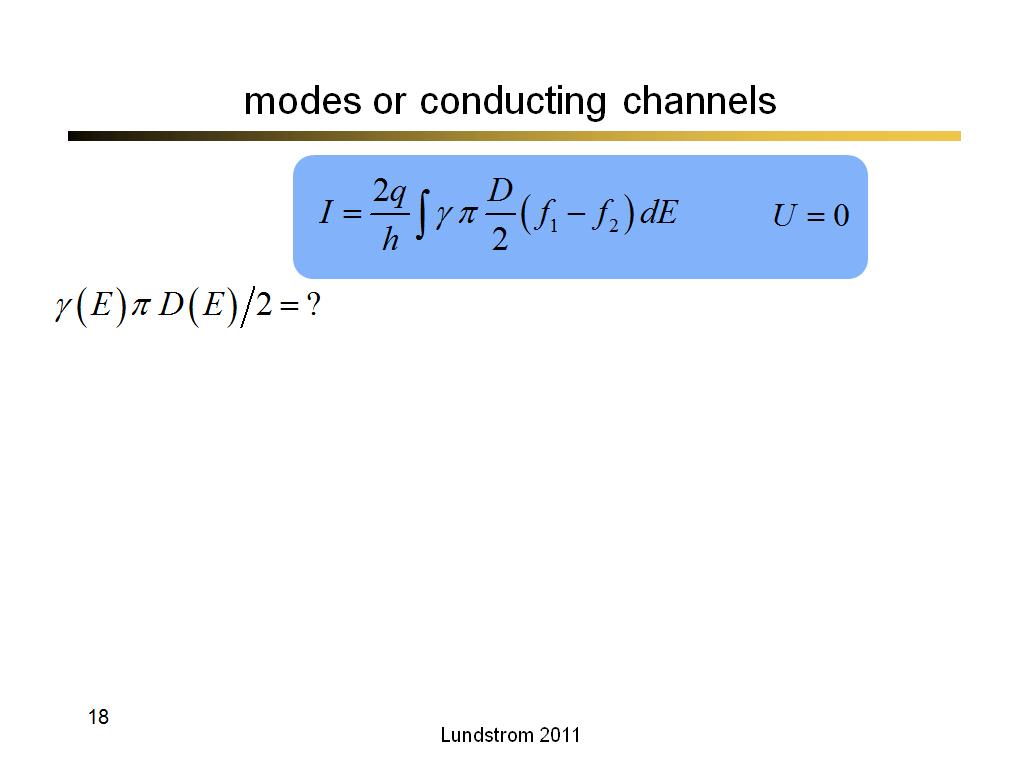 18. modes or conducting channels
1240.9333333333334
00:00/00:00
18. modes or conducting channels
1240.9333333333334
00:00/00:00 -
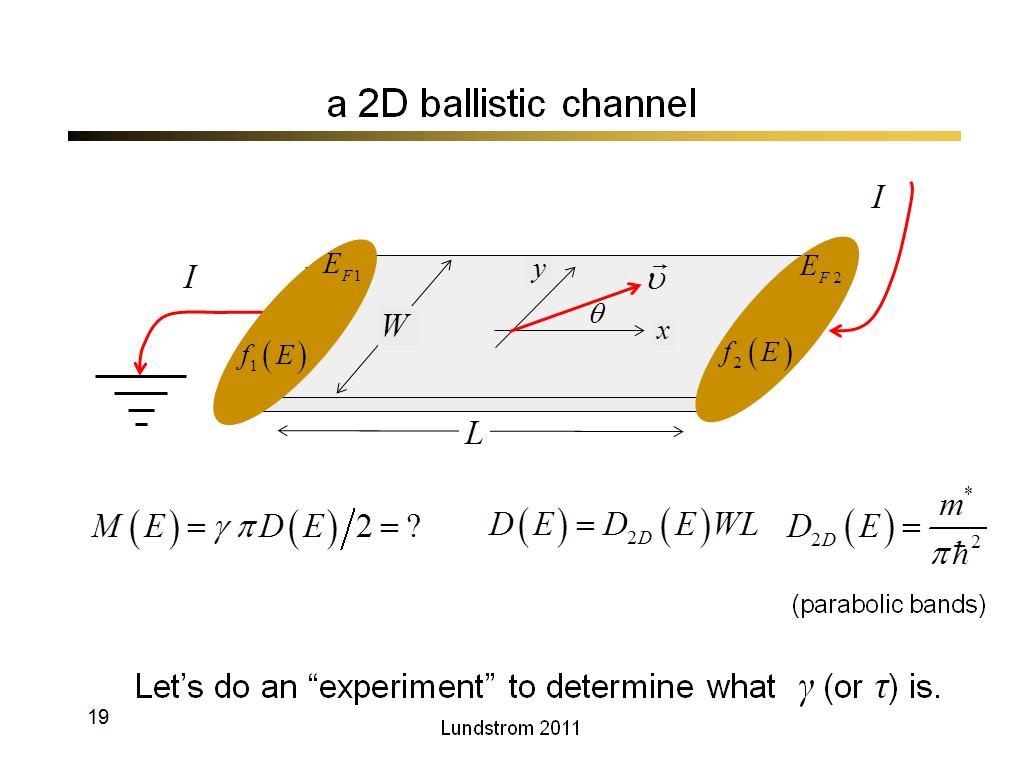
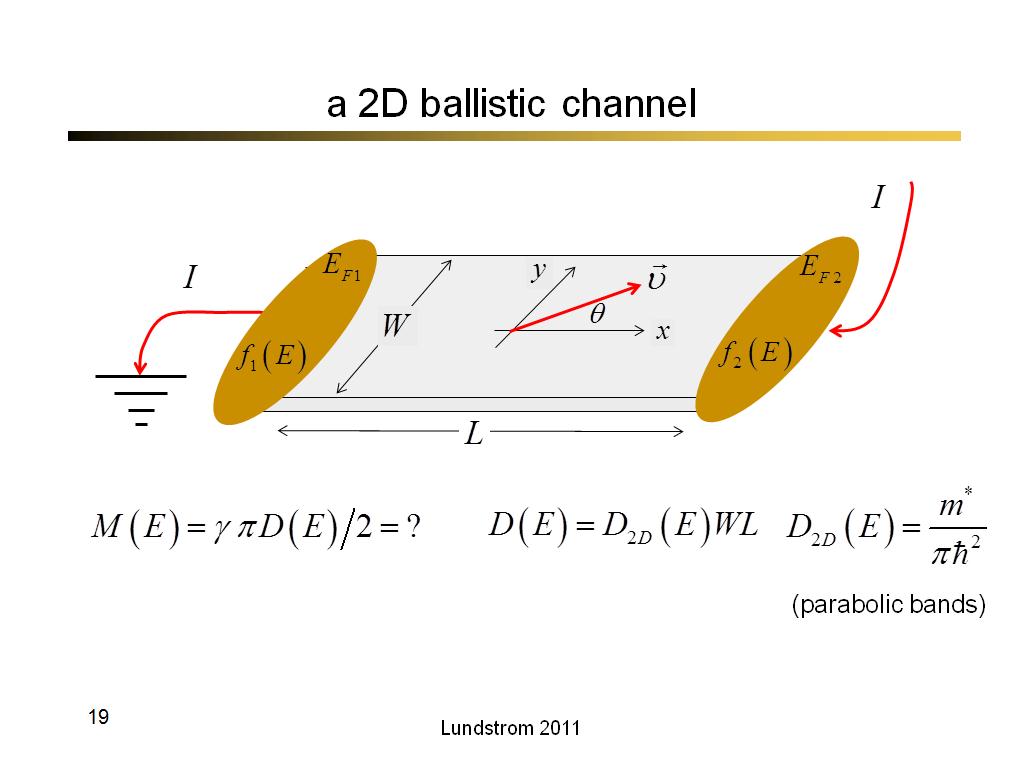 19. a 2D ballistic channel
1297.4333333333334
00:00/00:00
19. a 2D ballistic channel
1297.4333333333334
00:00/00:00 -
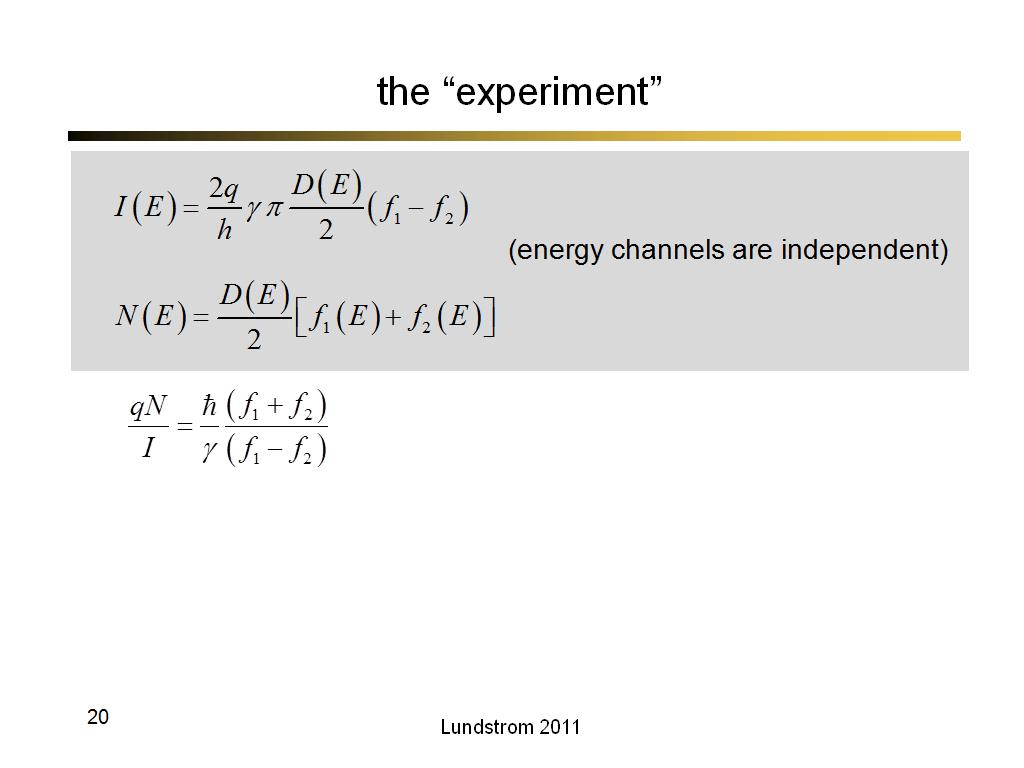
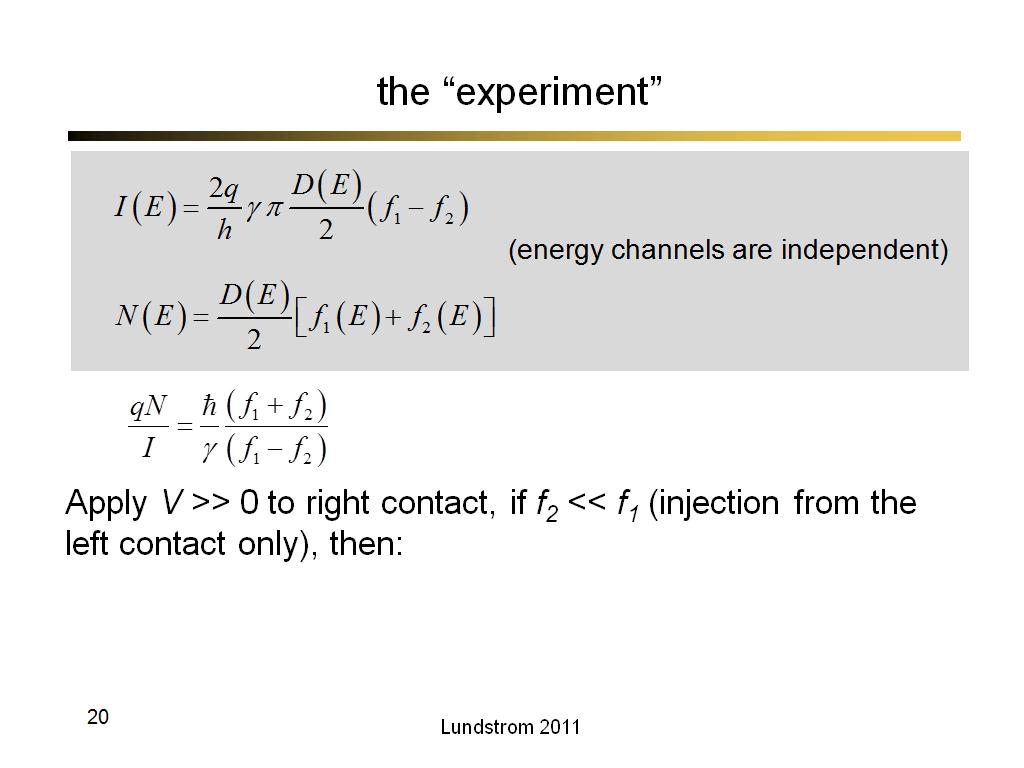
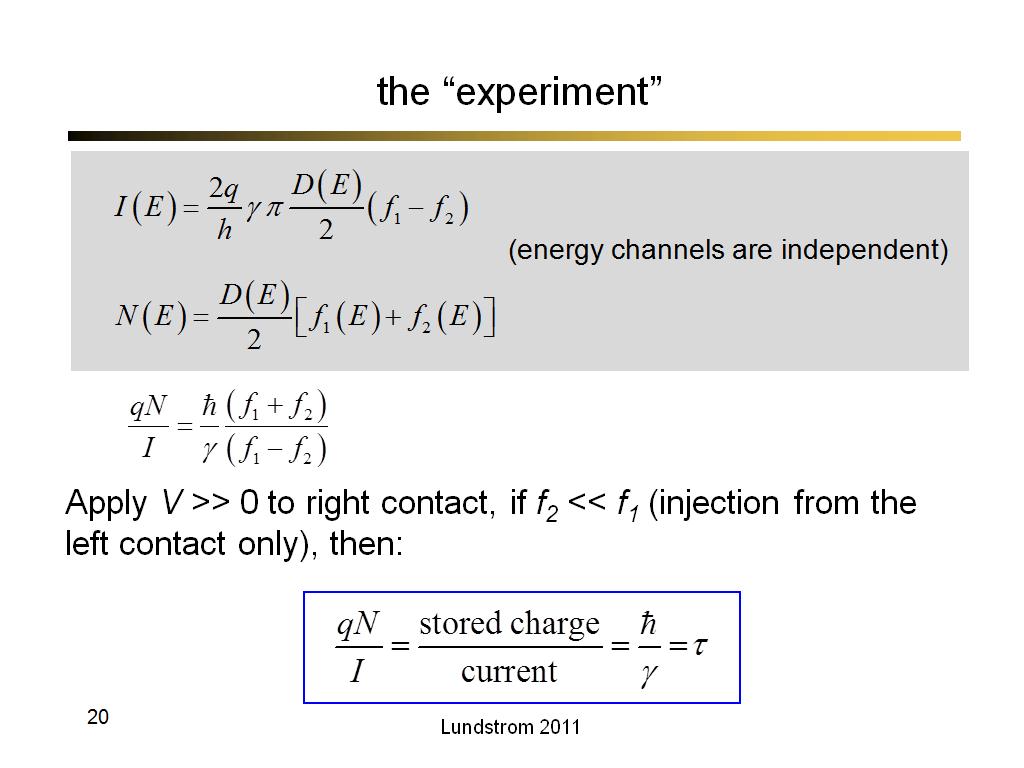
 20. the “experiment”
1378.4
00:00/00:00
20. the “experiment”
1378.4
00:00/00:00 -
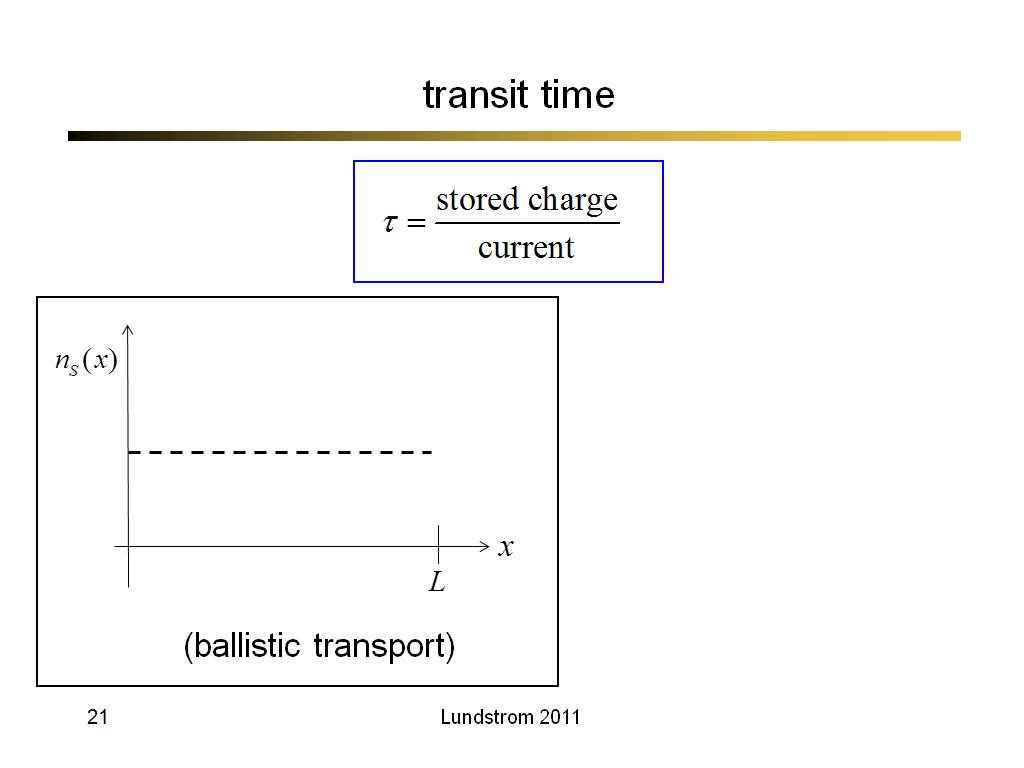
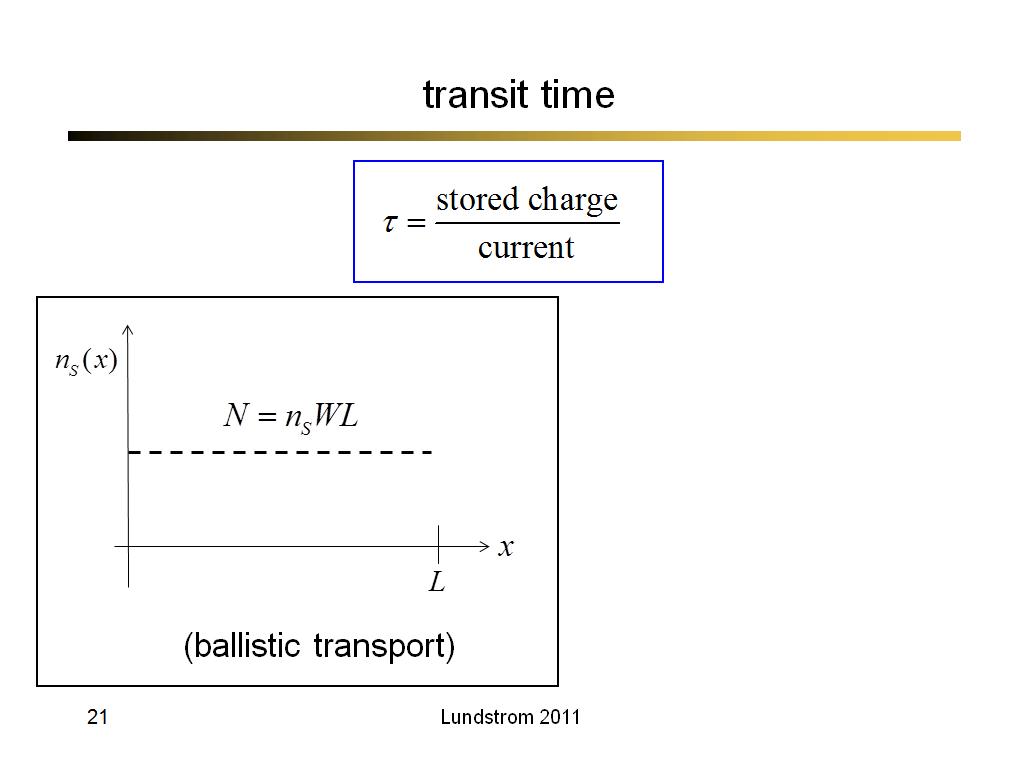
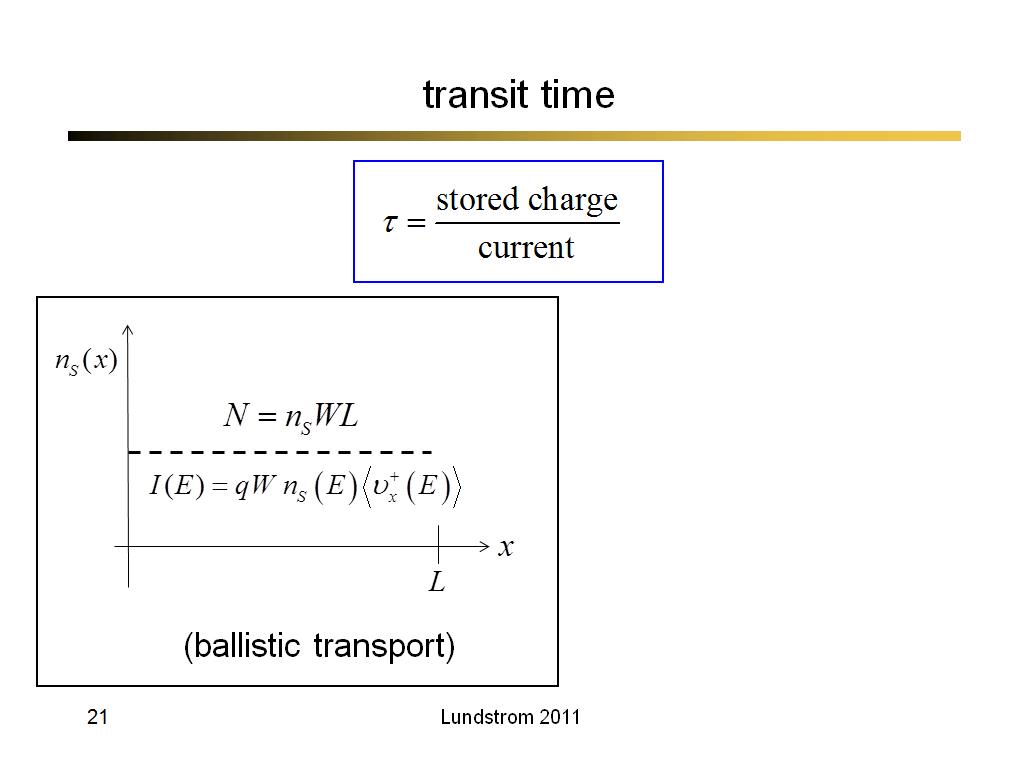
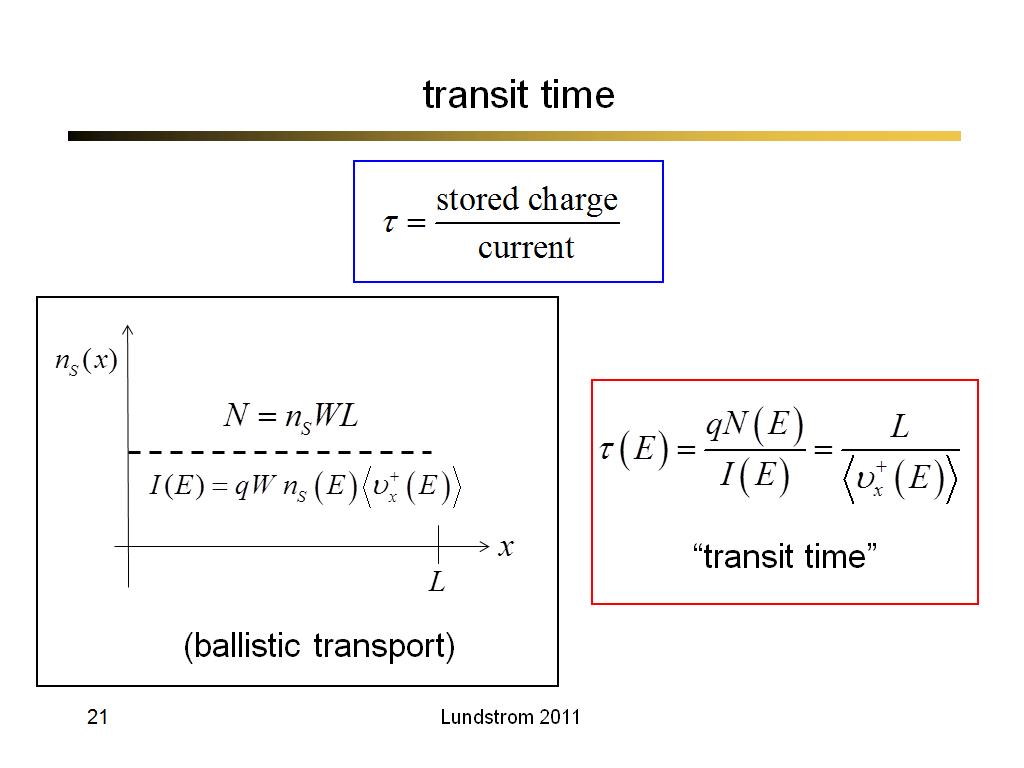
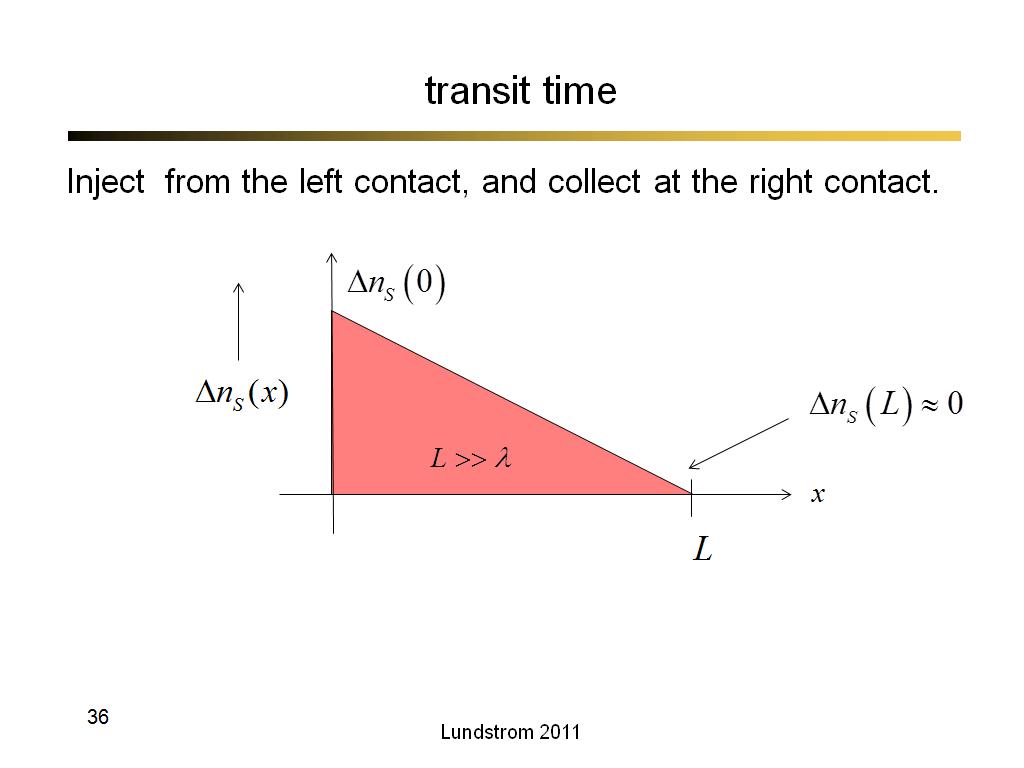
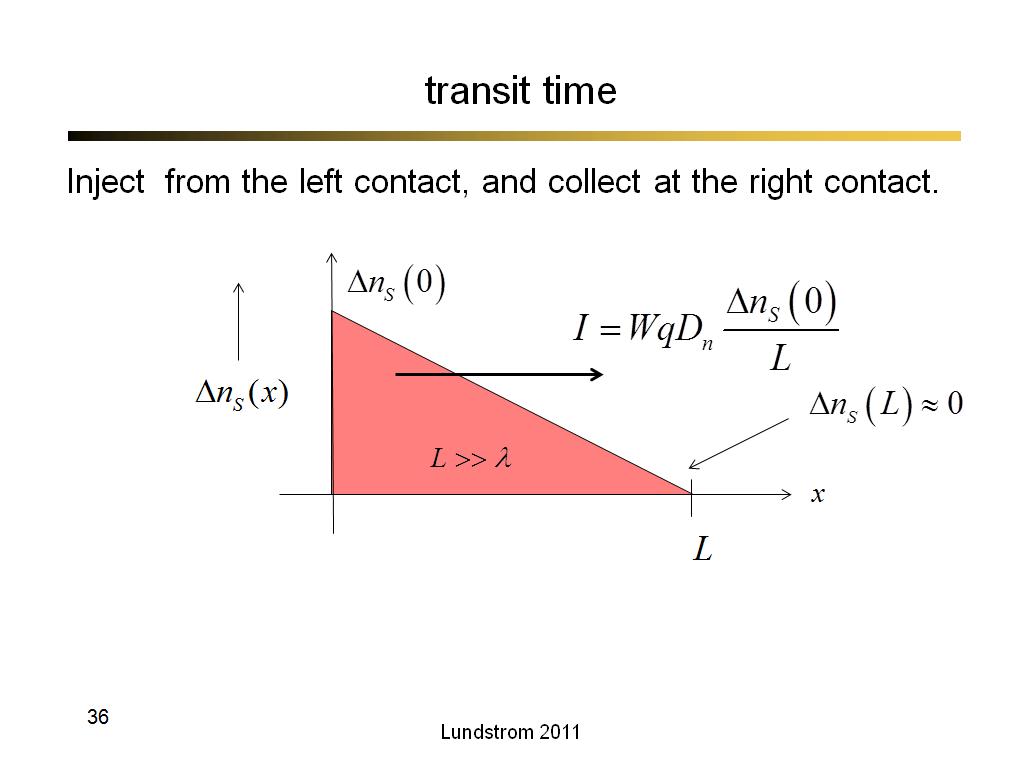
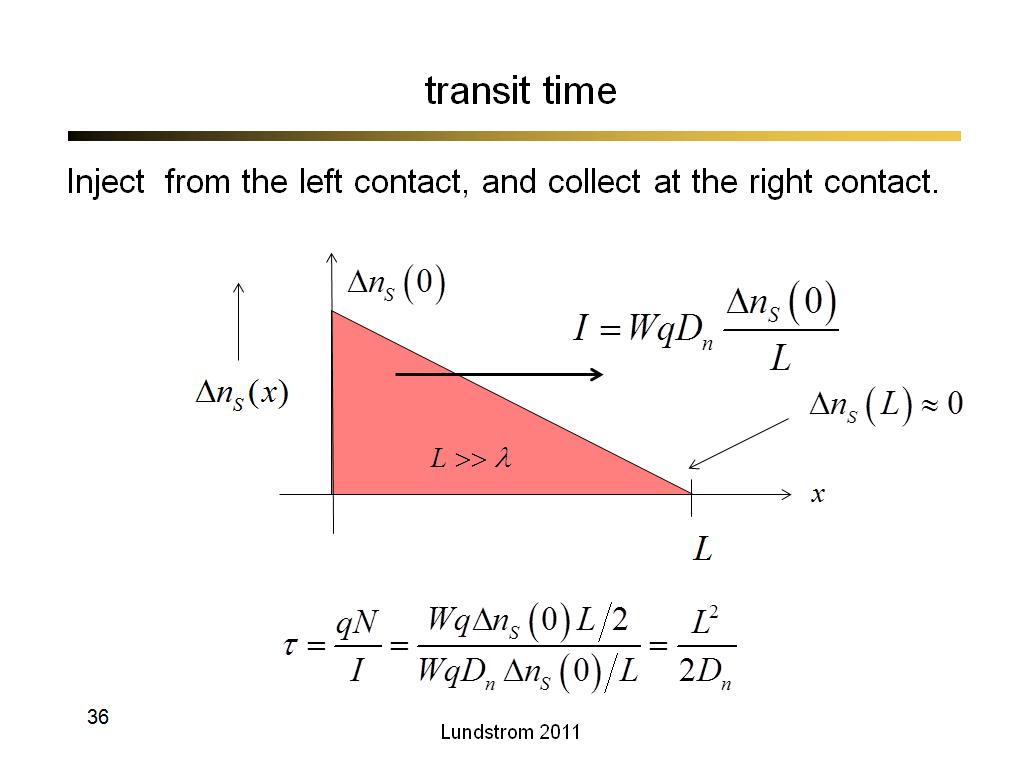
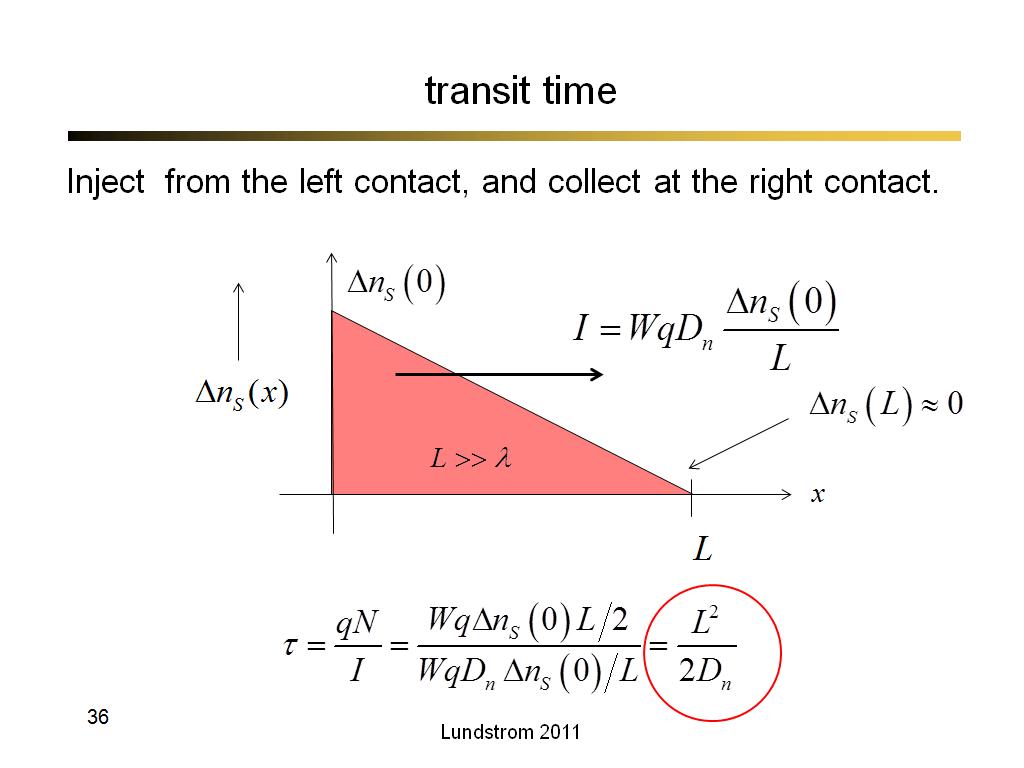
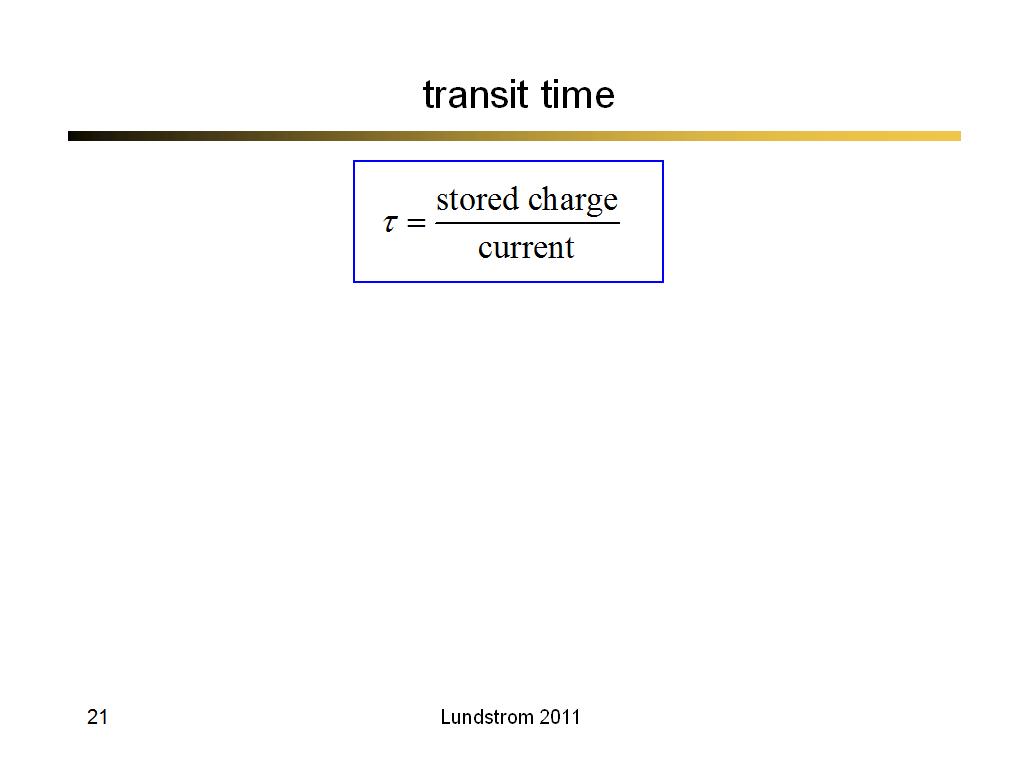 21. transit time
1467
00:00/00:00
21. transit time
1467
00:00/00:00 -
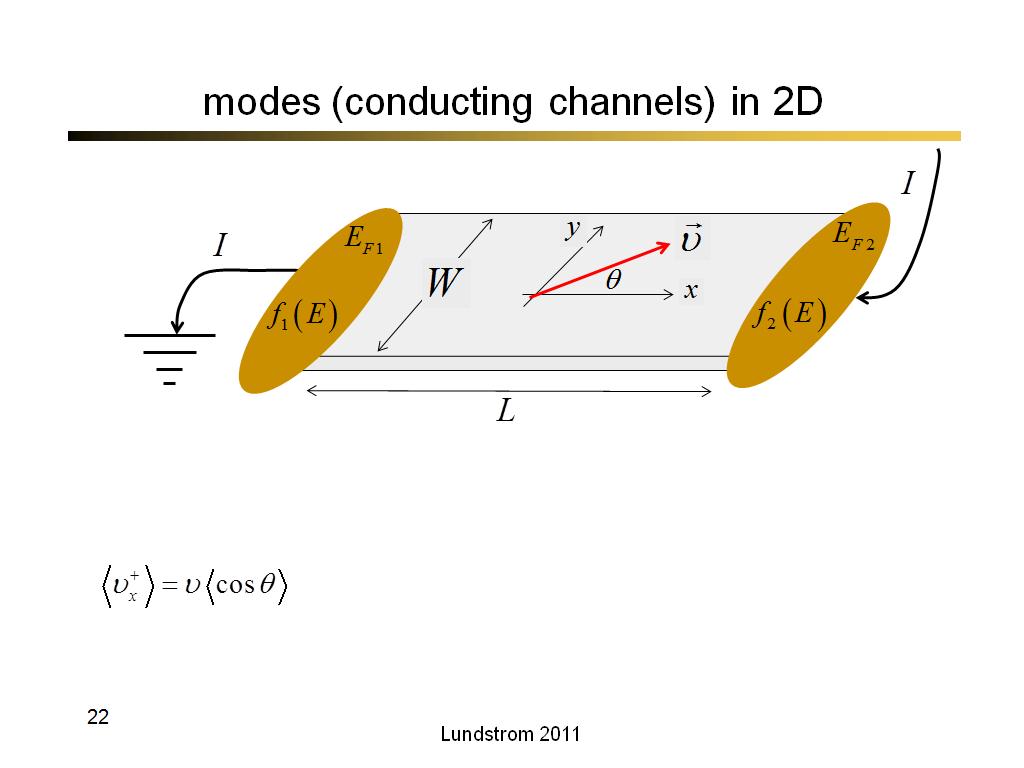
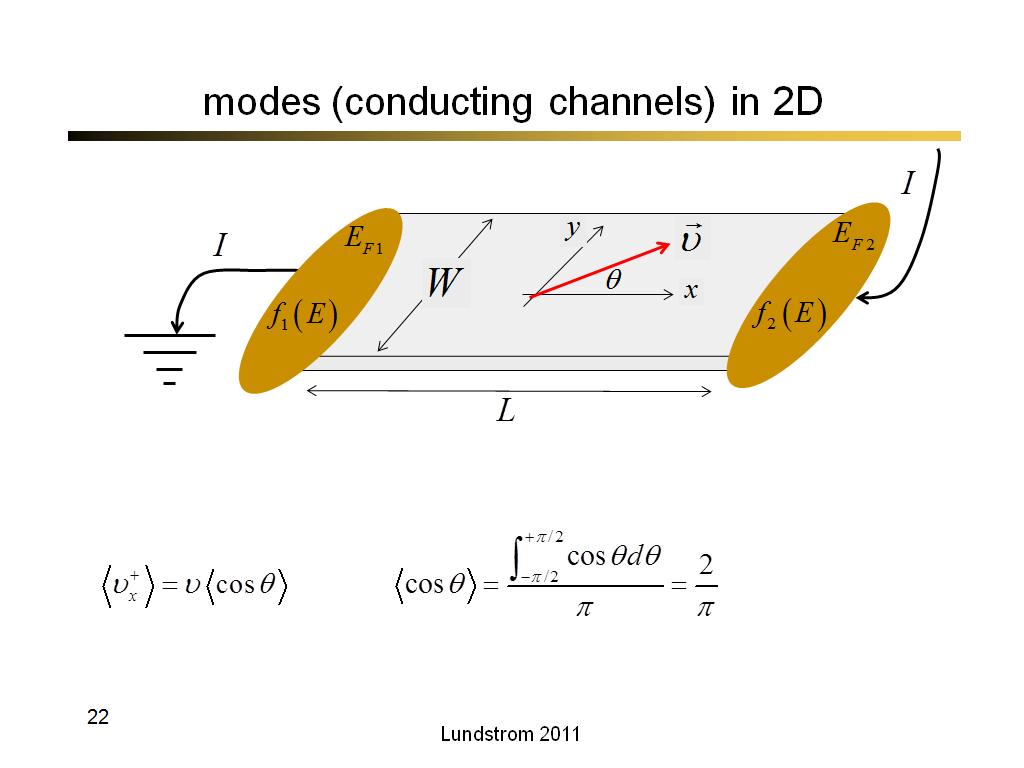
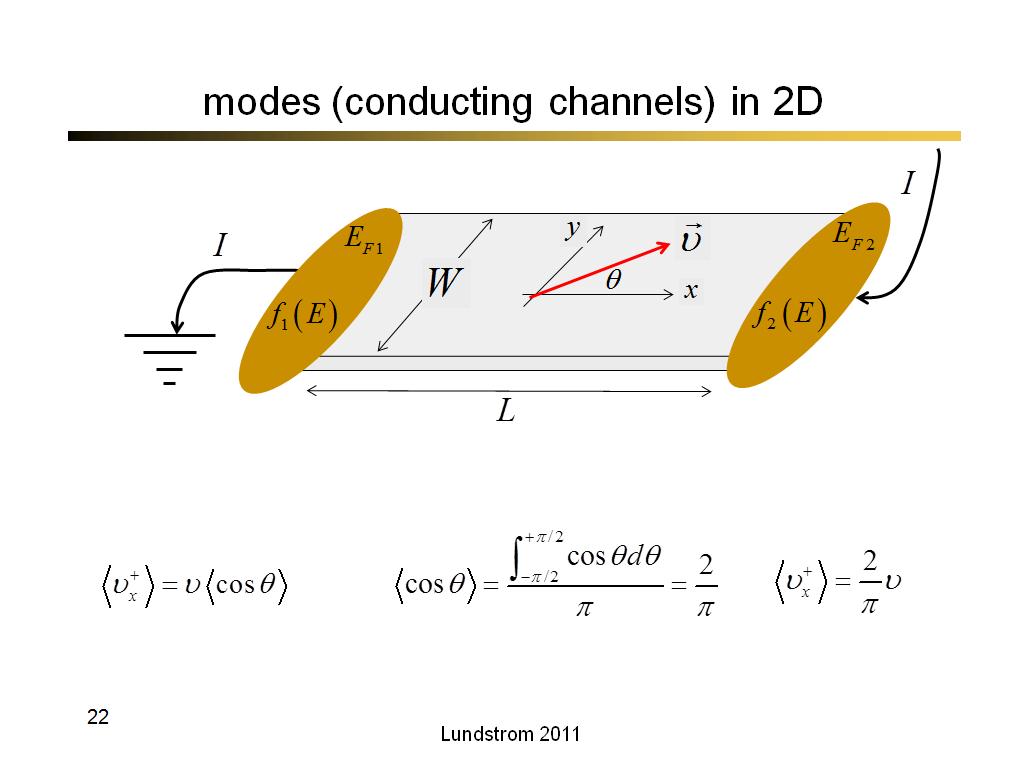
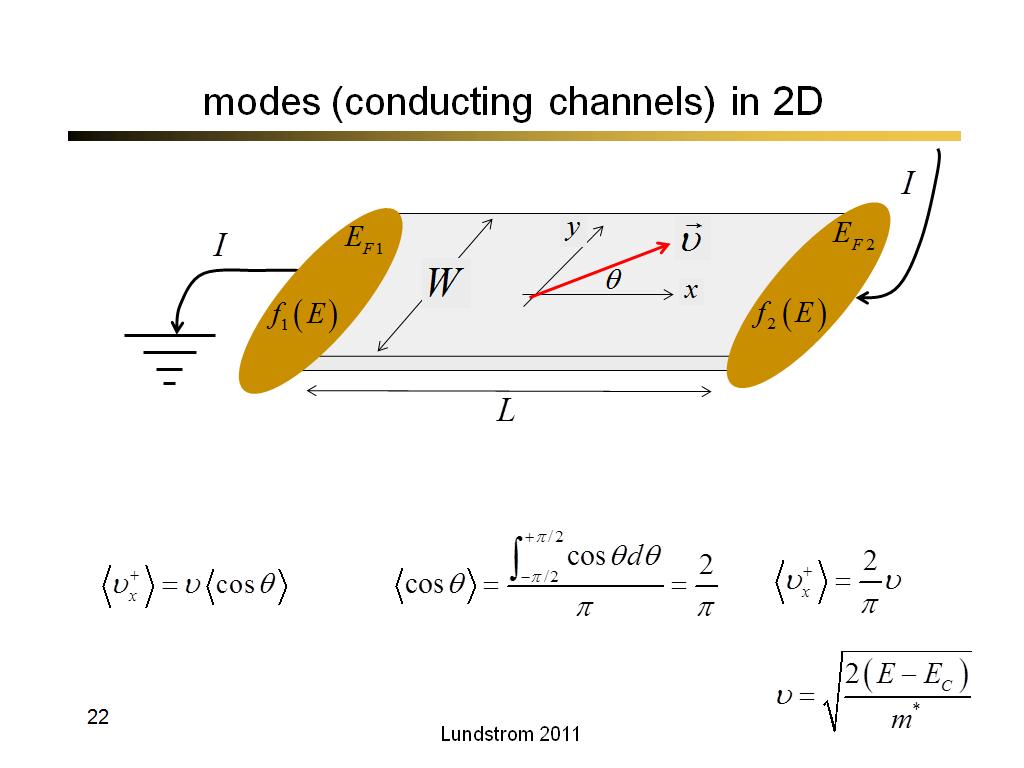
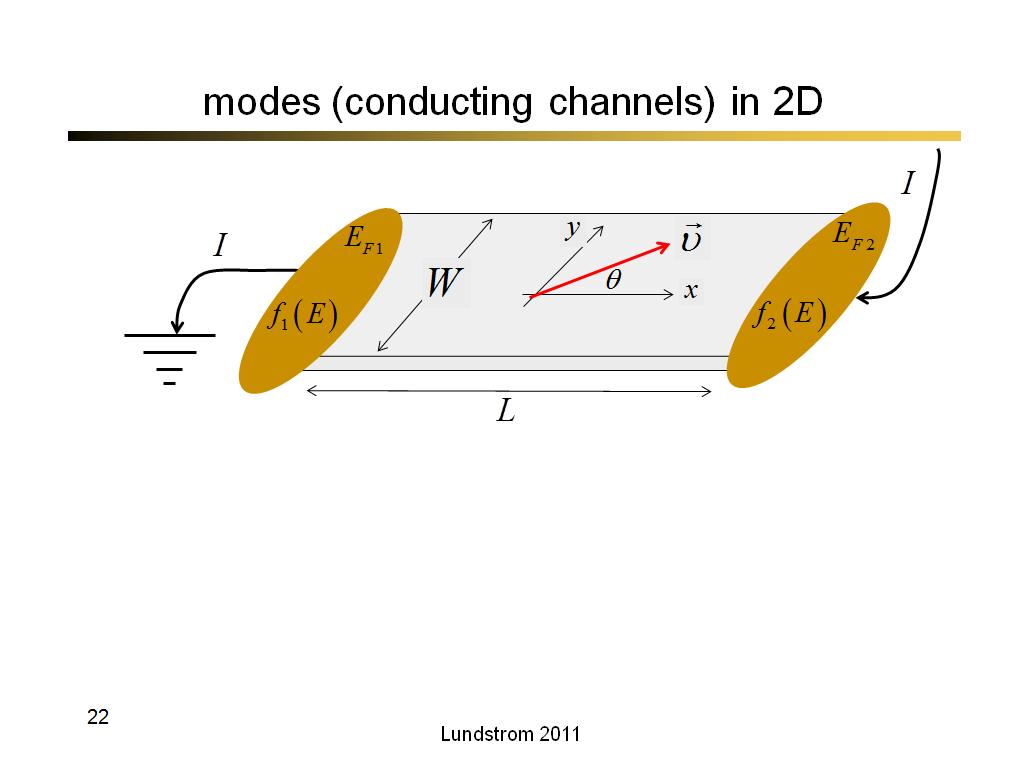 22. modes (conducting channels) in…
1579.5
00:00/00:00
22. modes (conducting channels) in…
1579.5
00:00/00:00 -
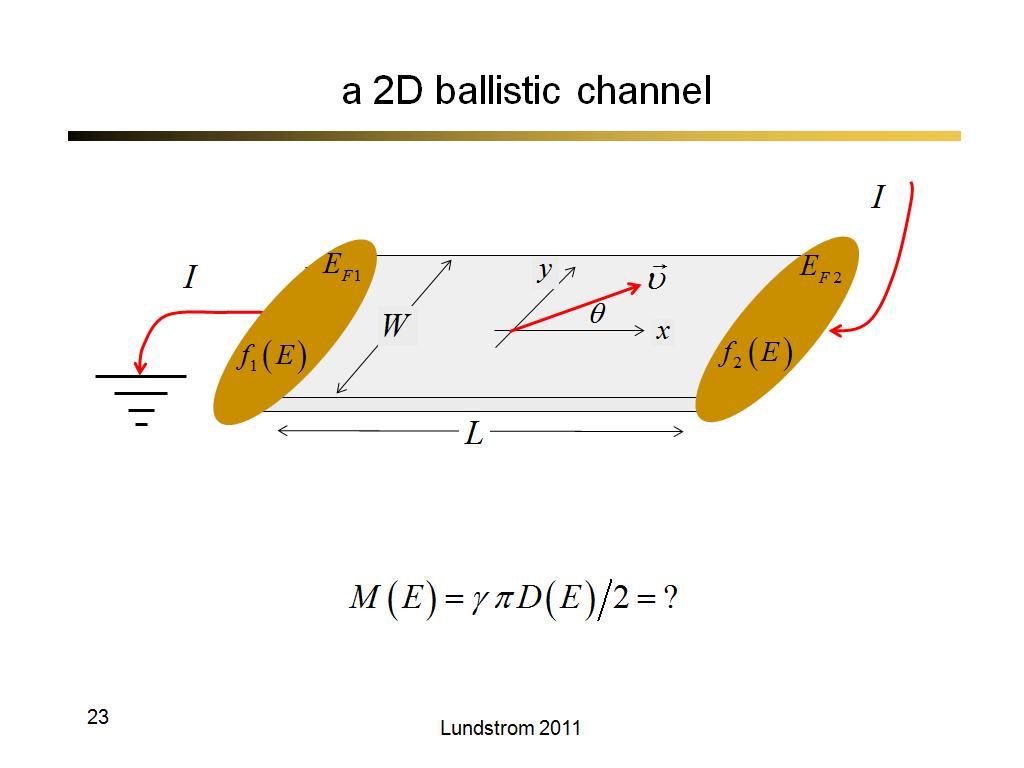 23. a 2D ballistic channel
1674.8666666666666
00:00/00:00
23. a 2D ballistic channel
1674.8666666666666
00:00/00:00 -
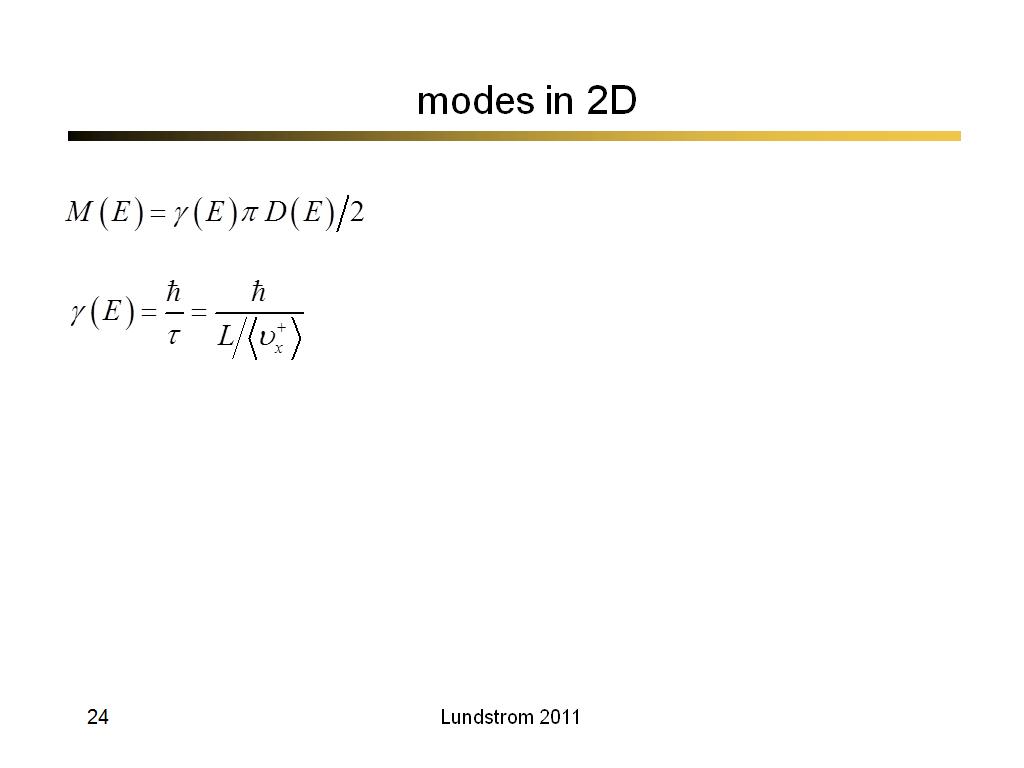
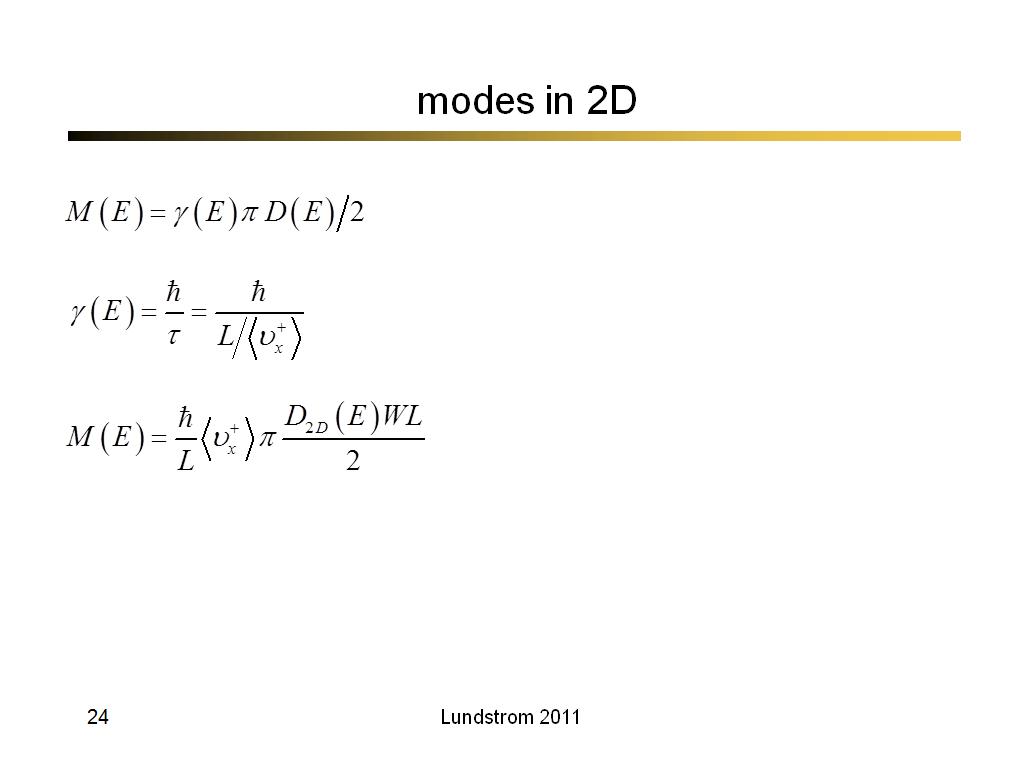
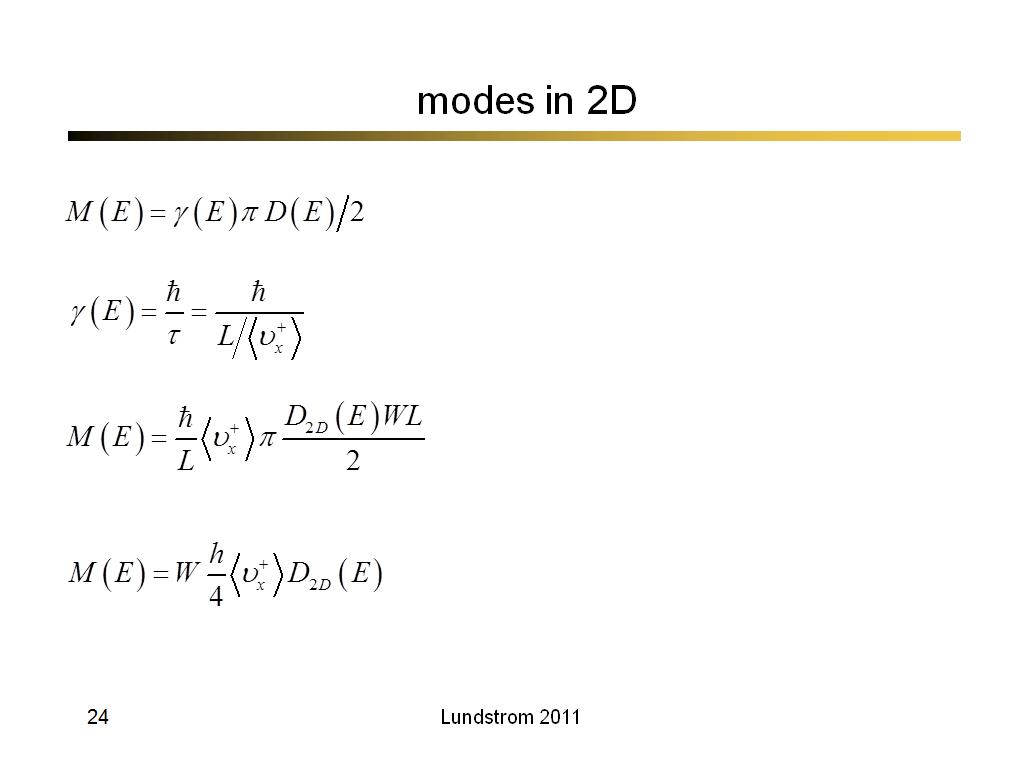
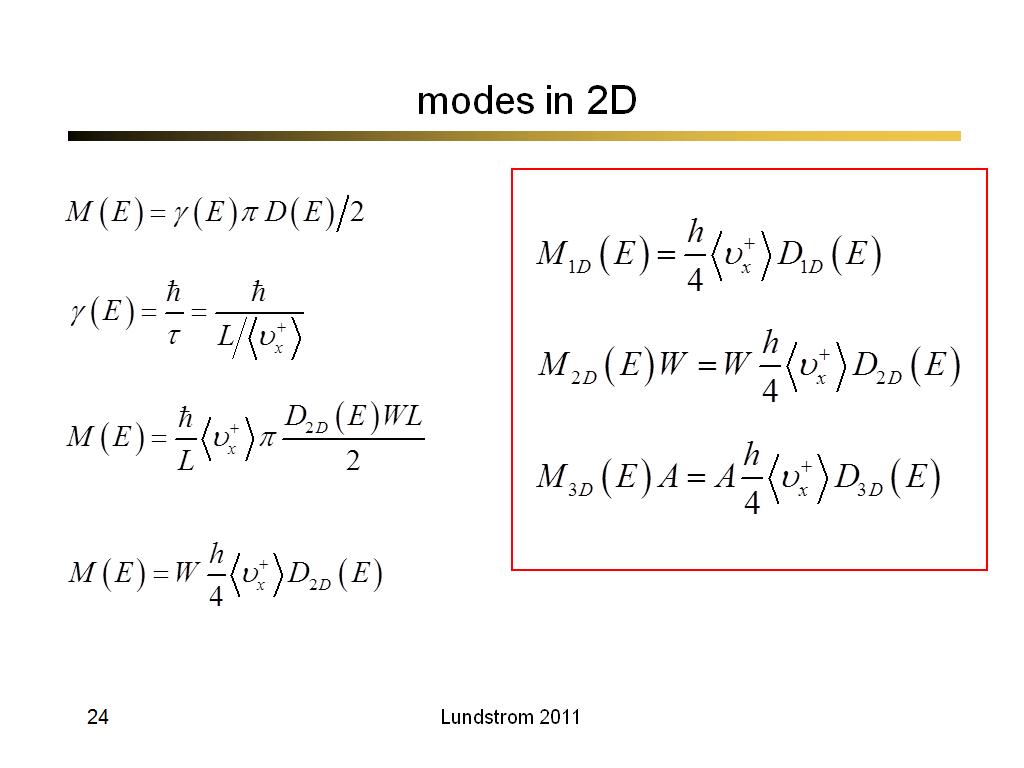
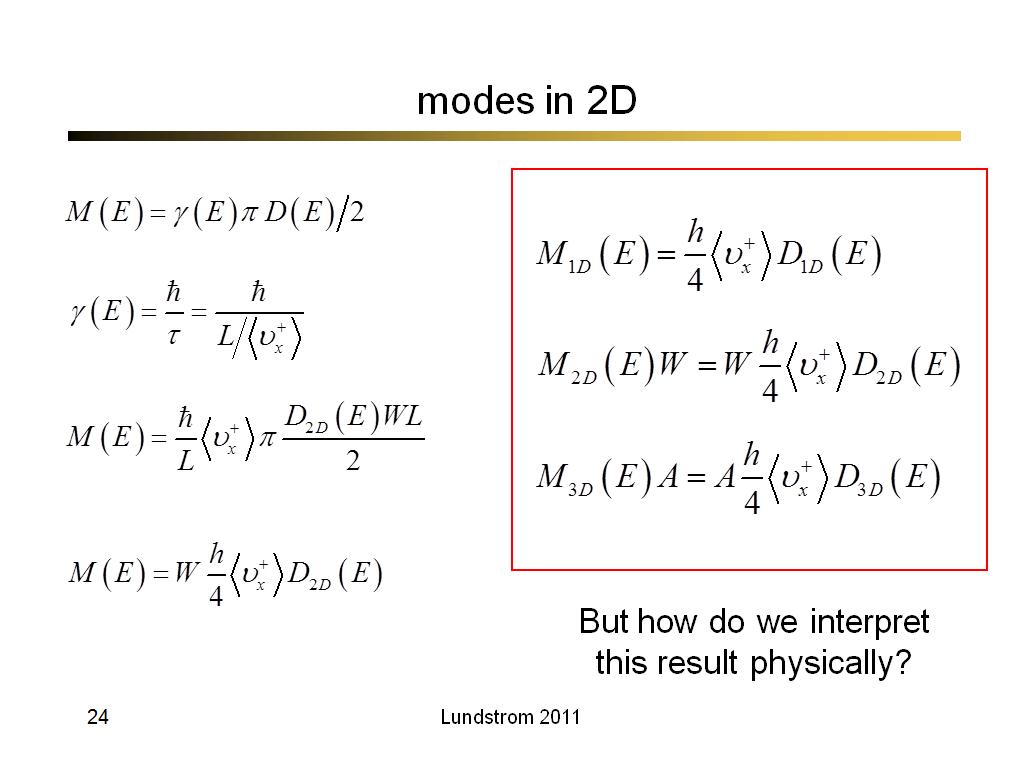
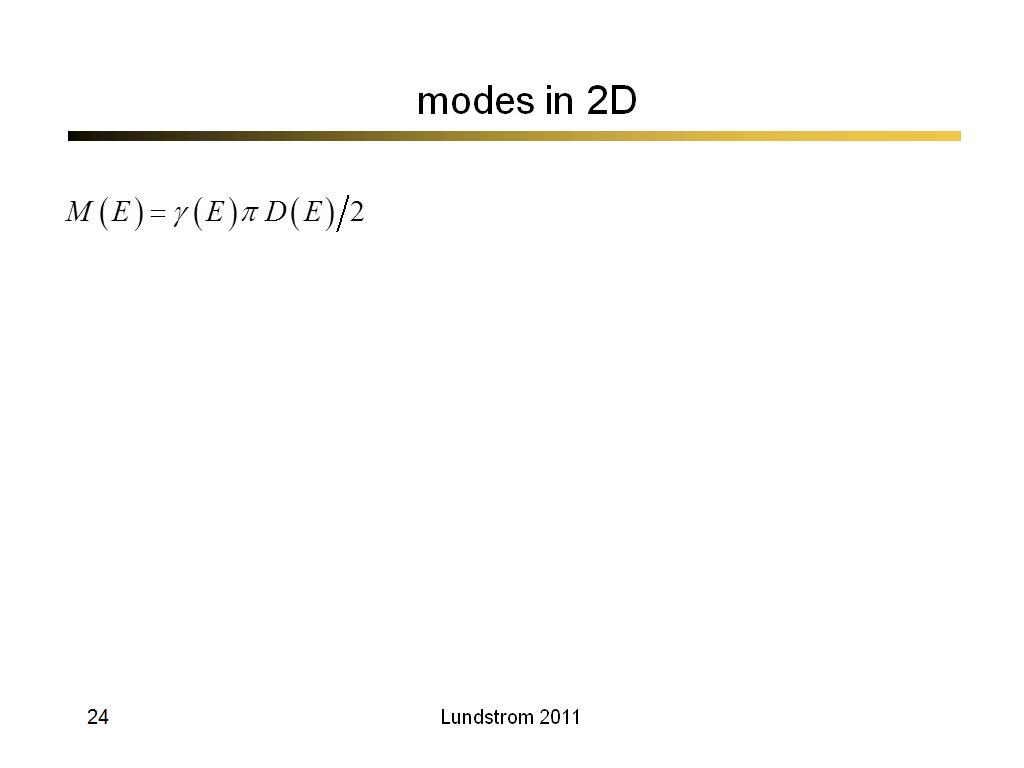 24. modes in 2D
1684.6333333333334
00:00/00:00
24. modes in 2D
1684.6333333333334
00:00/00:00 -
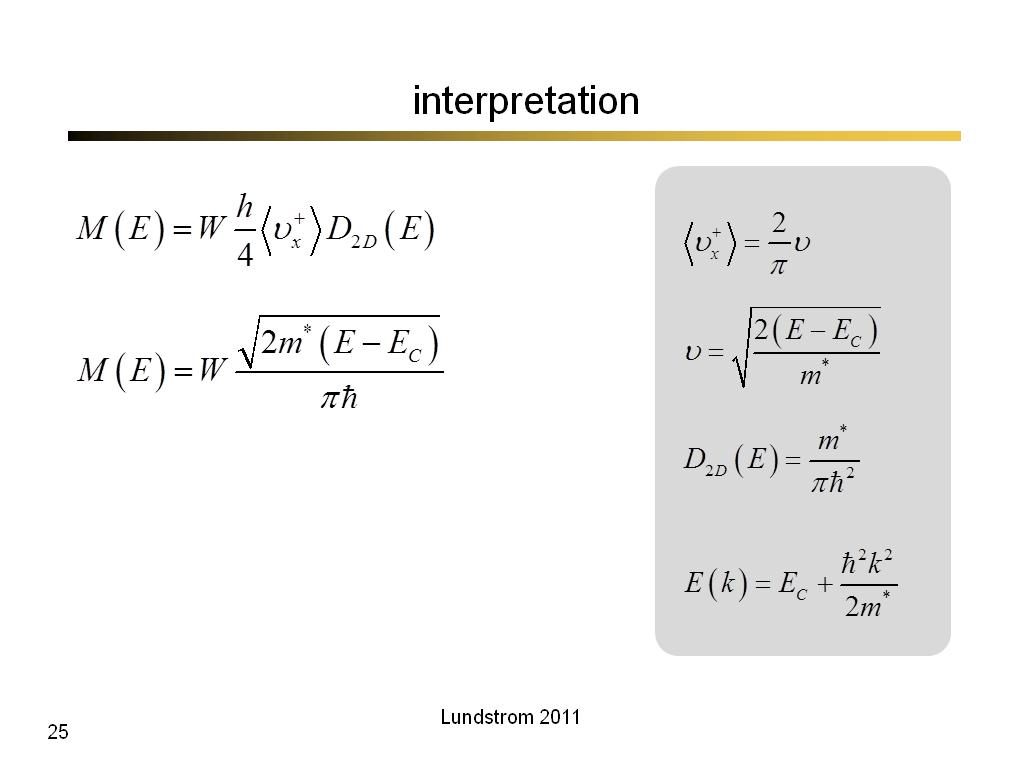
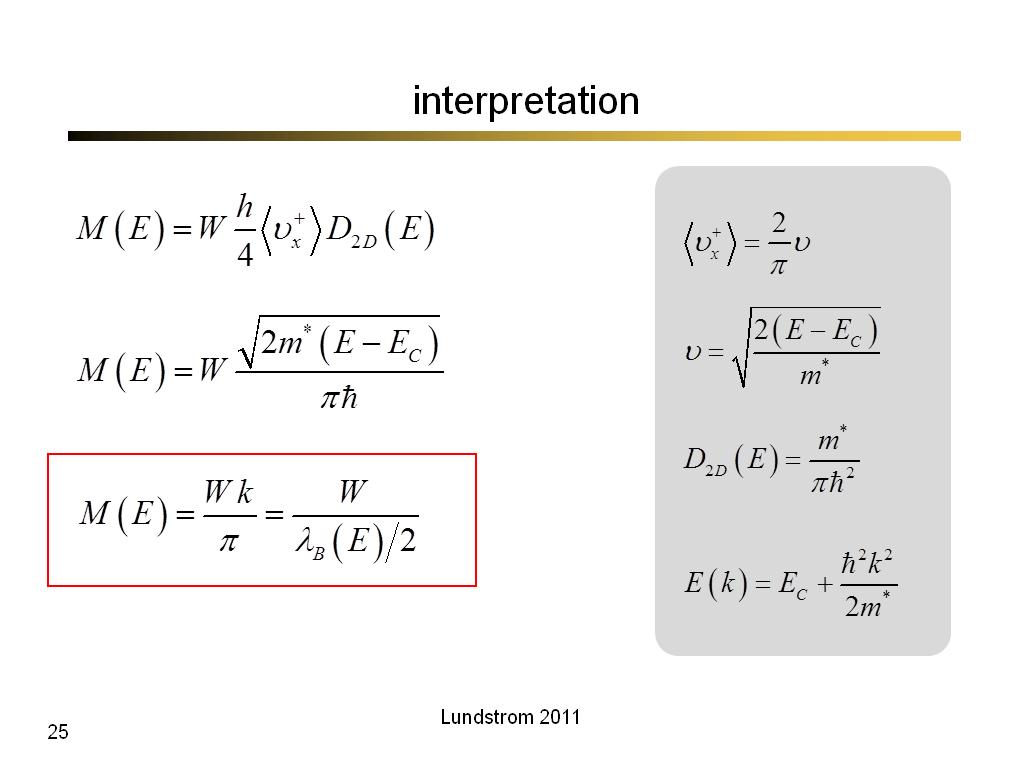
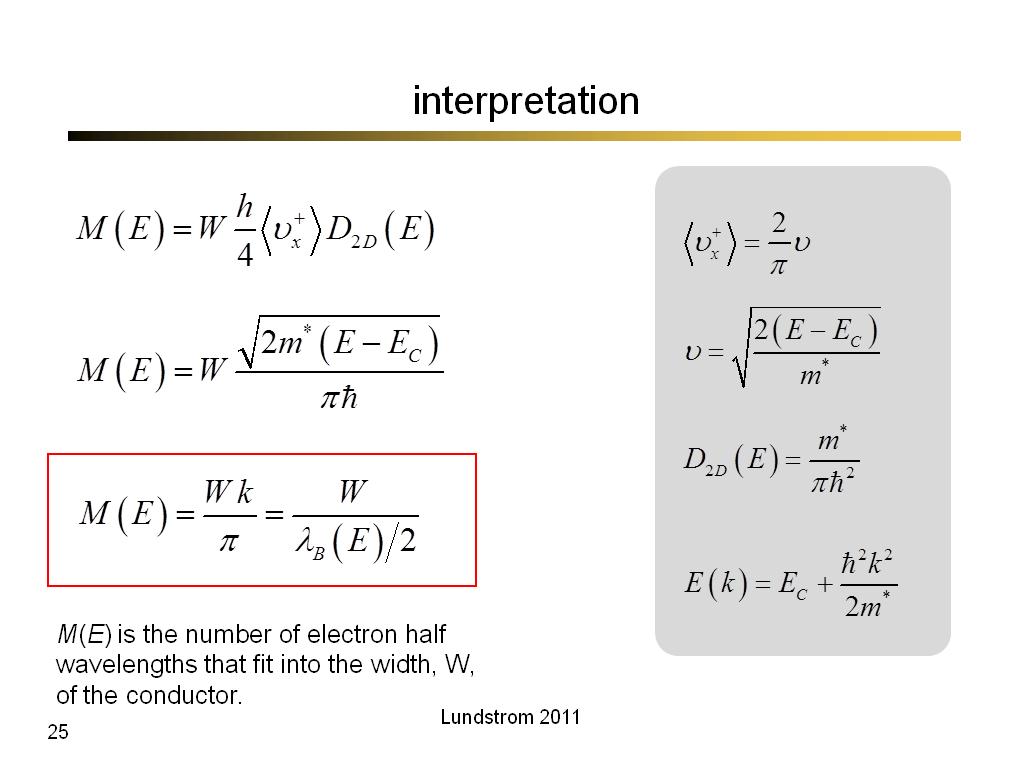
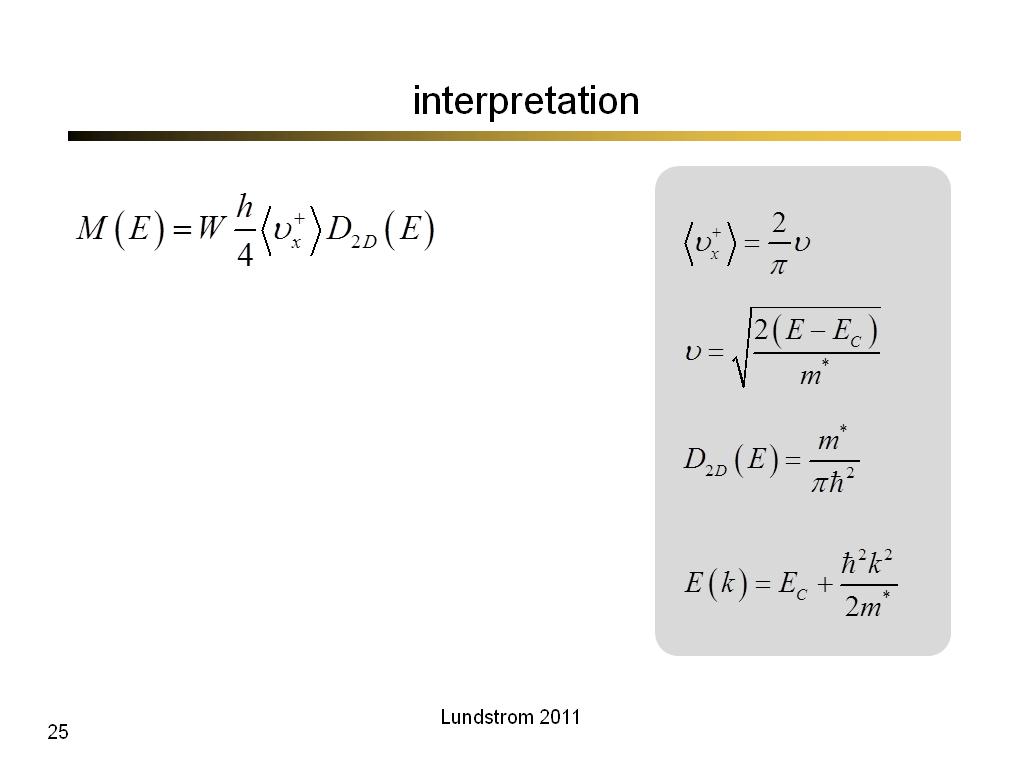 25. interpretation
1761.2333333333334
00:00/00:00
25. interpretation
1761.2333333333334
00:00/00:00 -
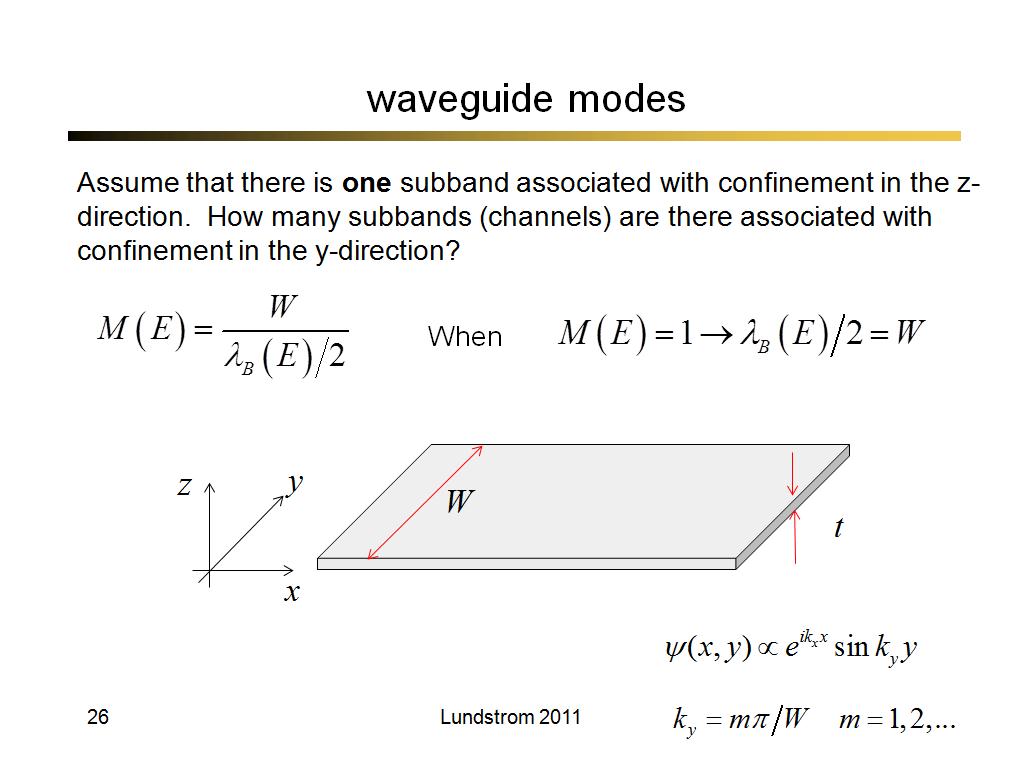
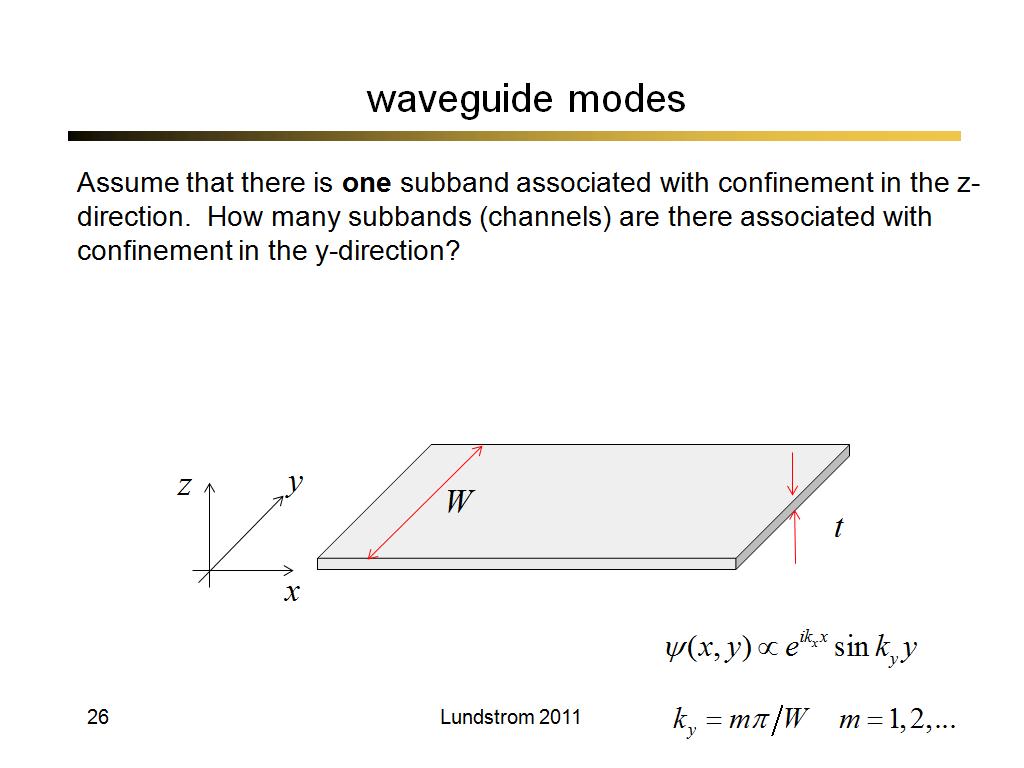 26. waveguide modes
1834.5
00:00/00:00
26. waveguide modes
1834.5
00:00/00:00 -
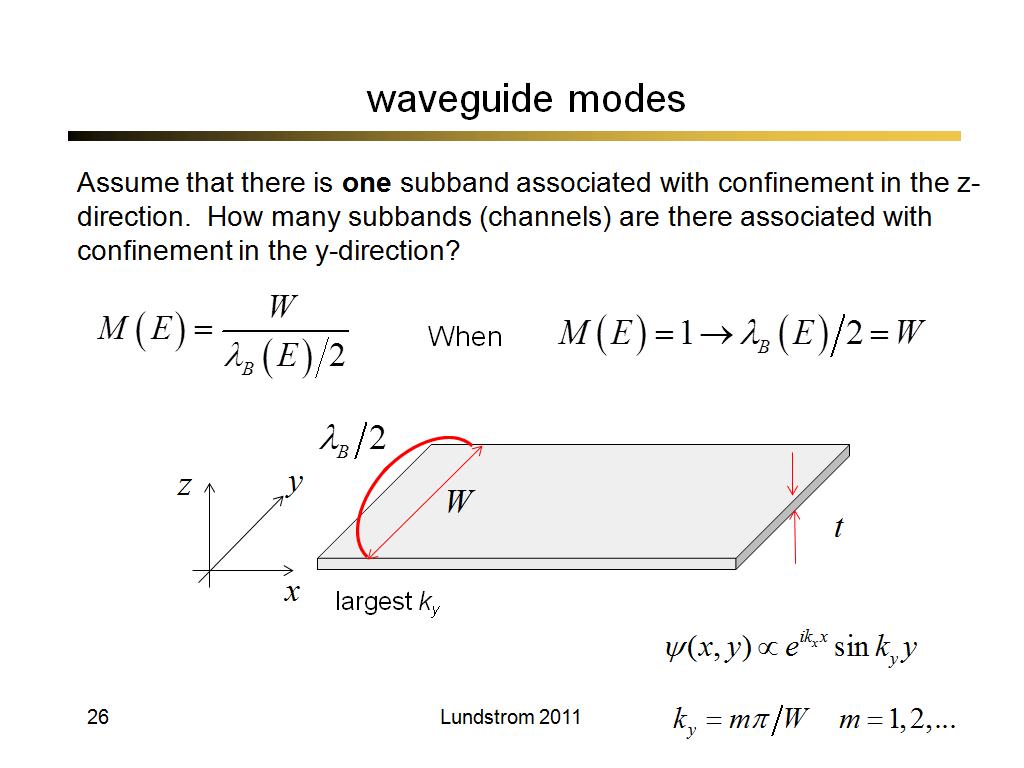
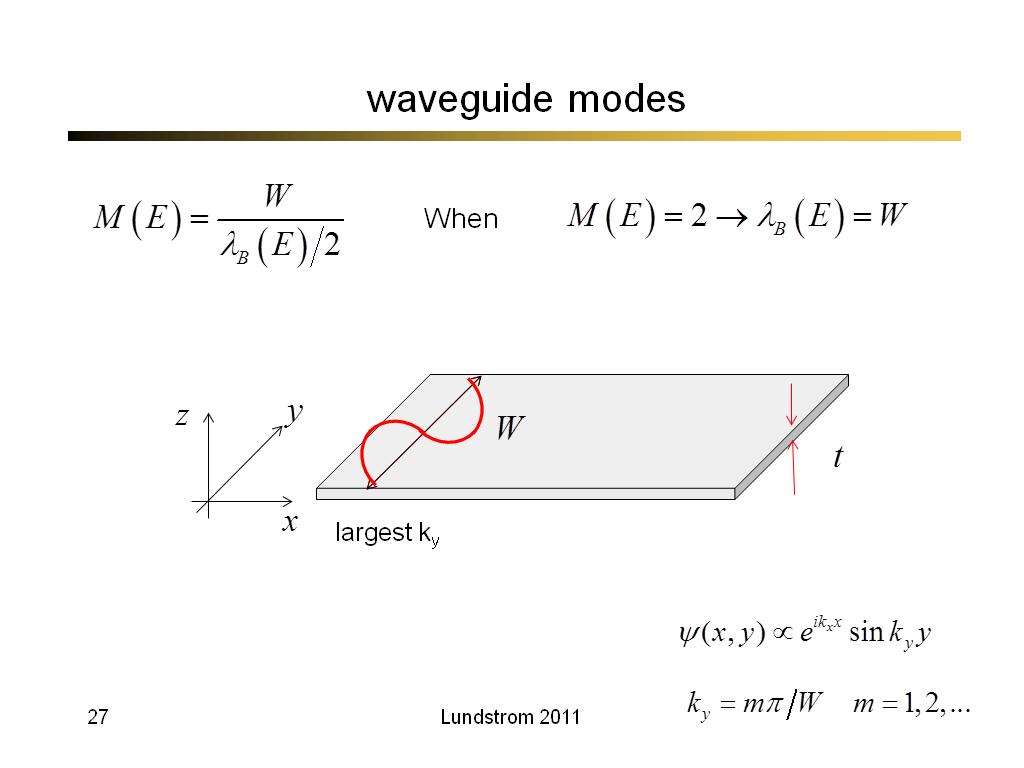
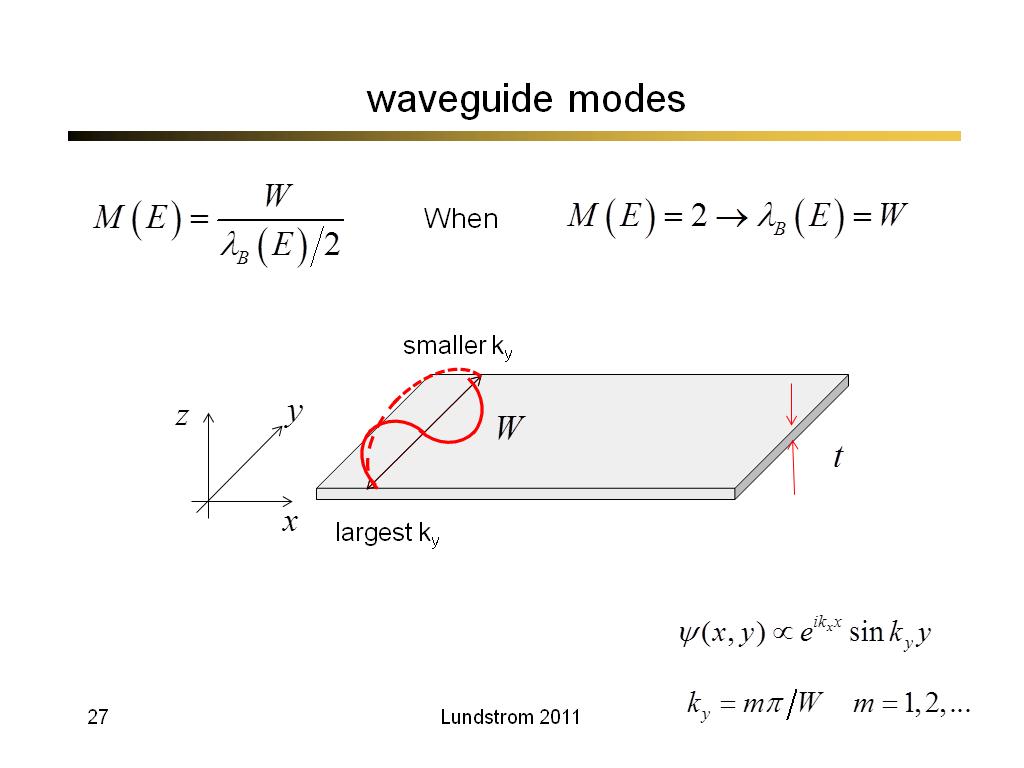
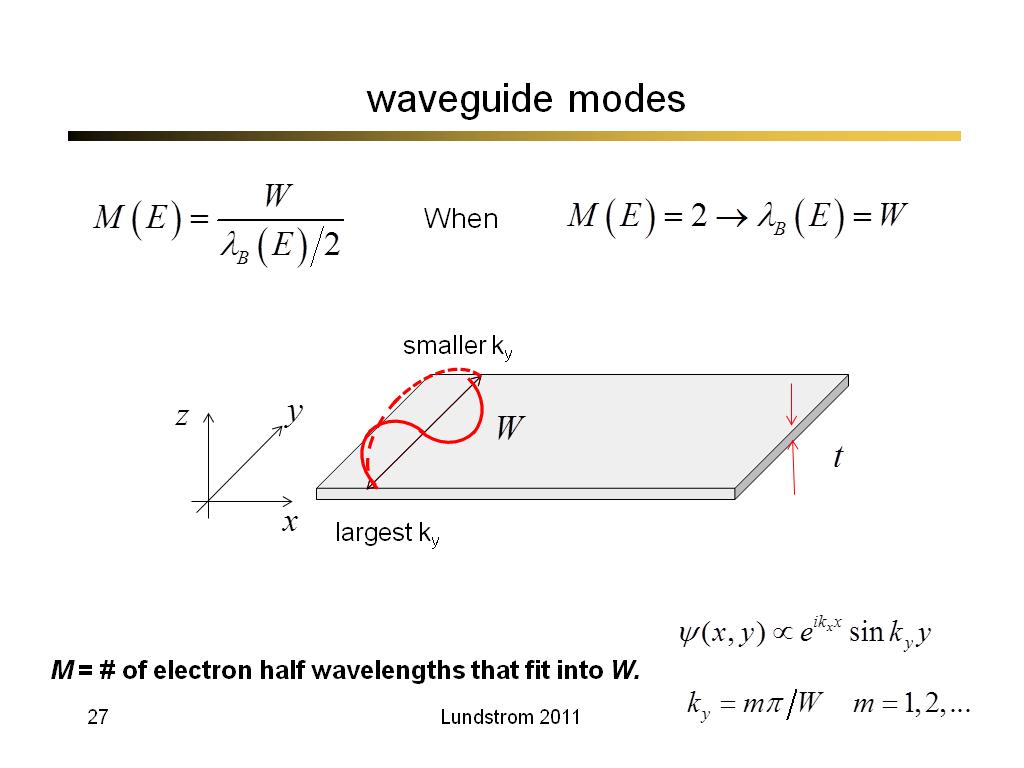
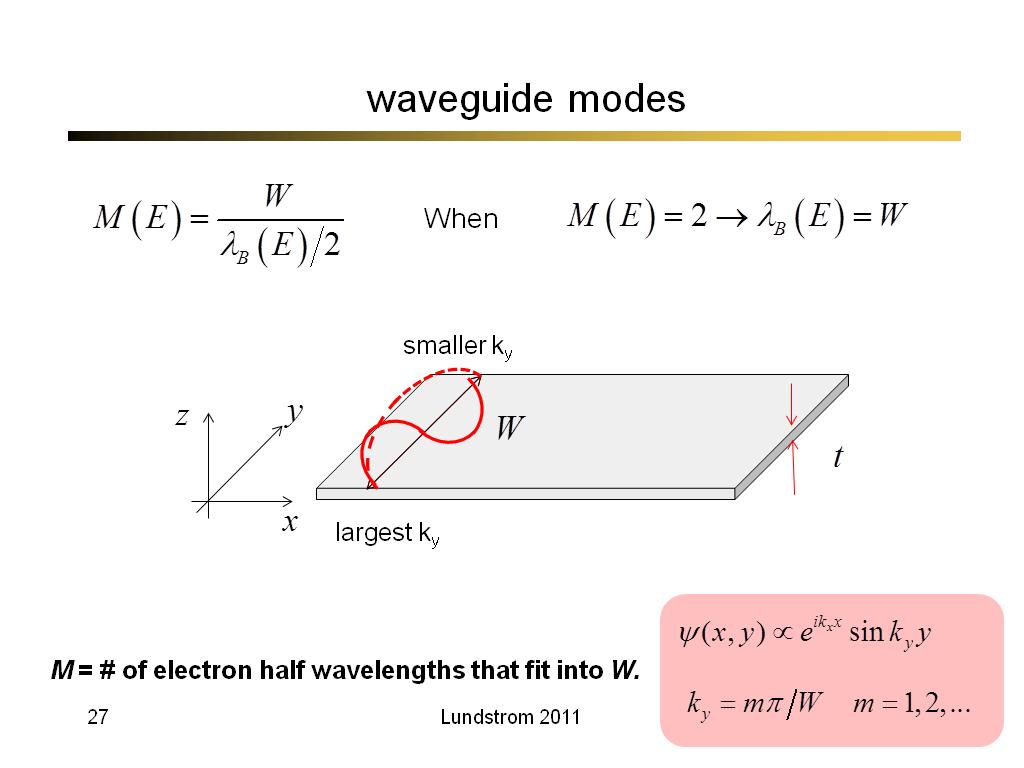
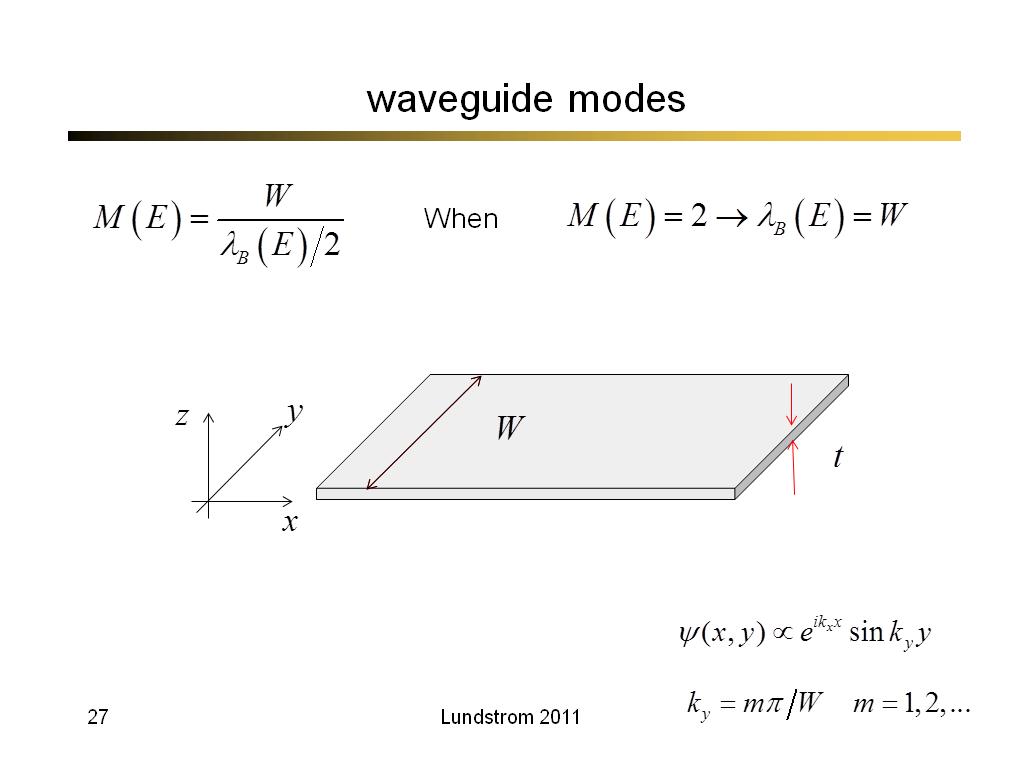 27. waveguide modes
1880.6666666666667
00:00/00:00
27. waveguide modes
1880.6666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
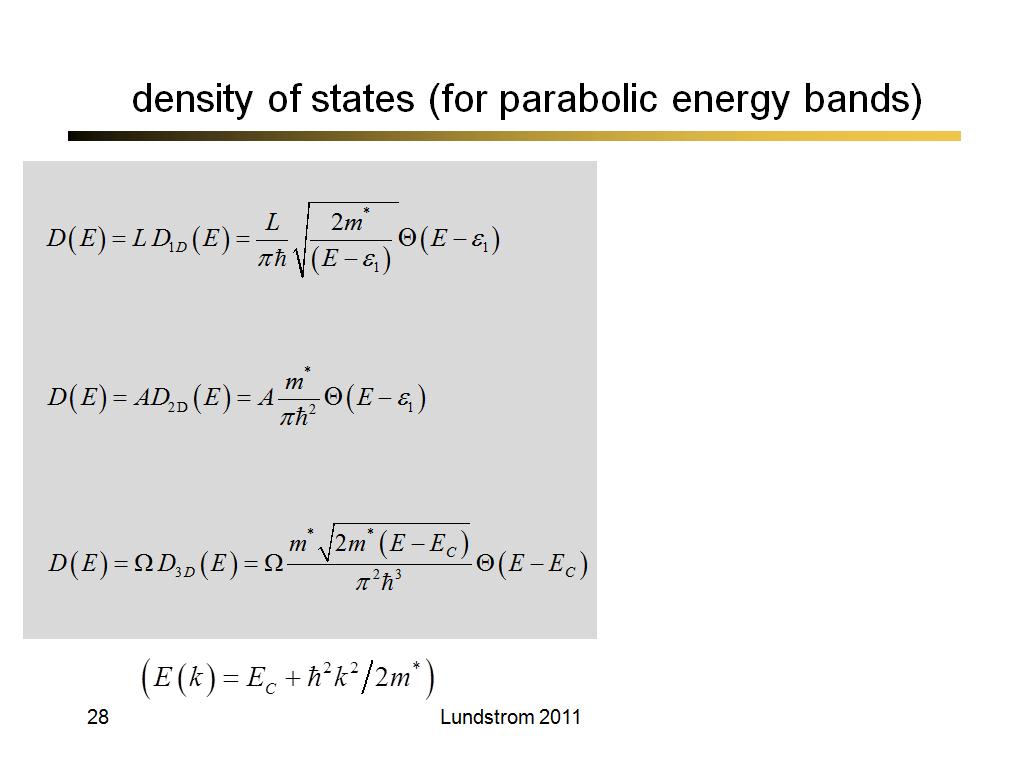
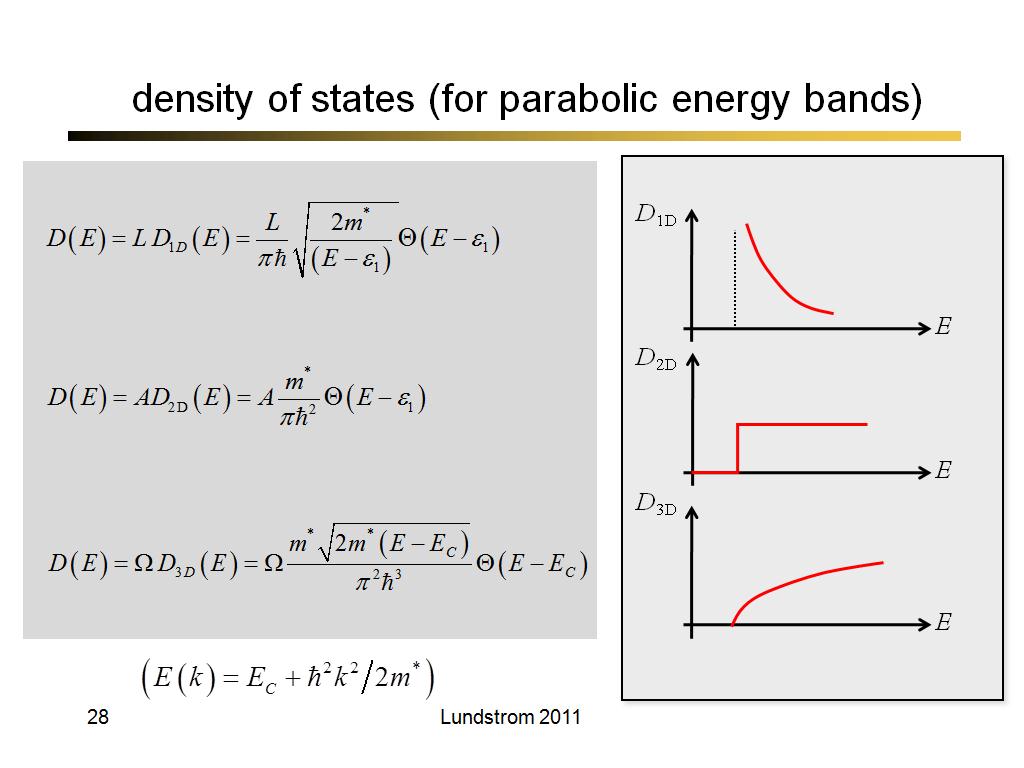
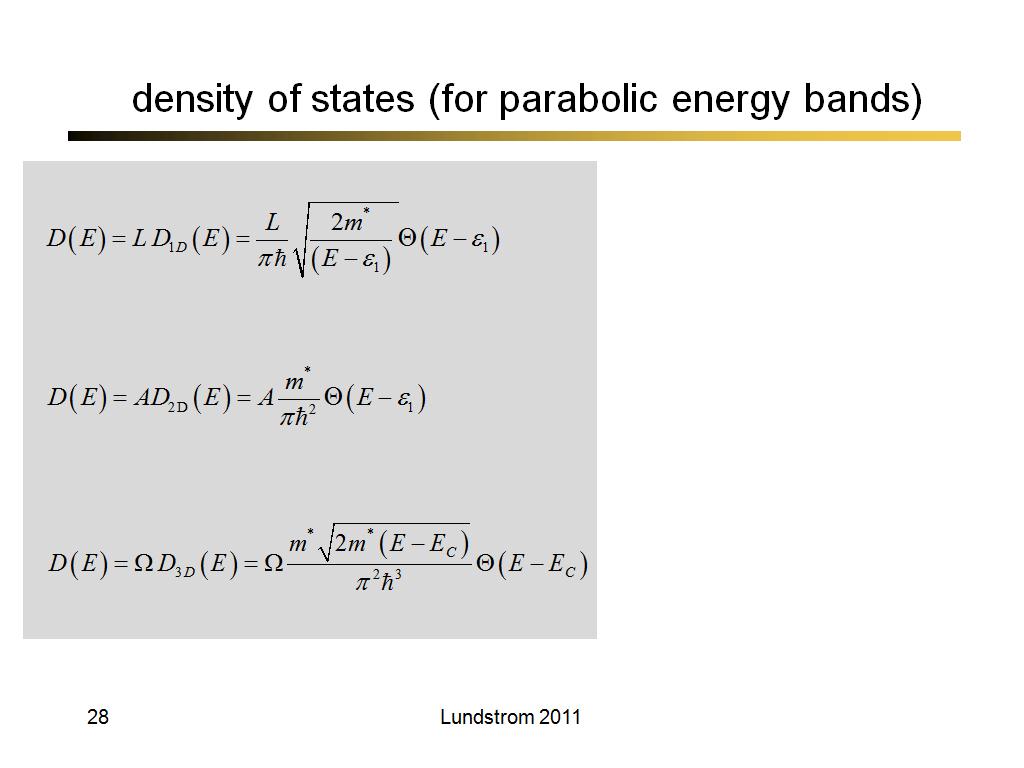 28. density of states (for parabol…
1952.8666666666666
00:00/00:00
28. density of states (for parabol…
1952.8666666666666
00:00/00:00 -
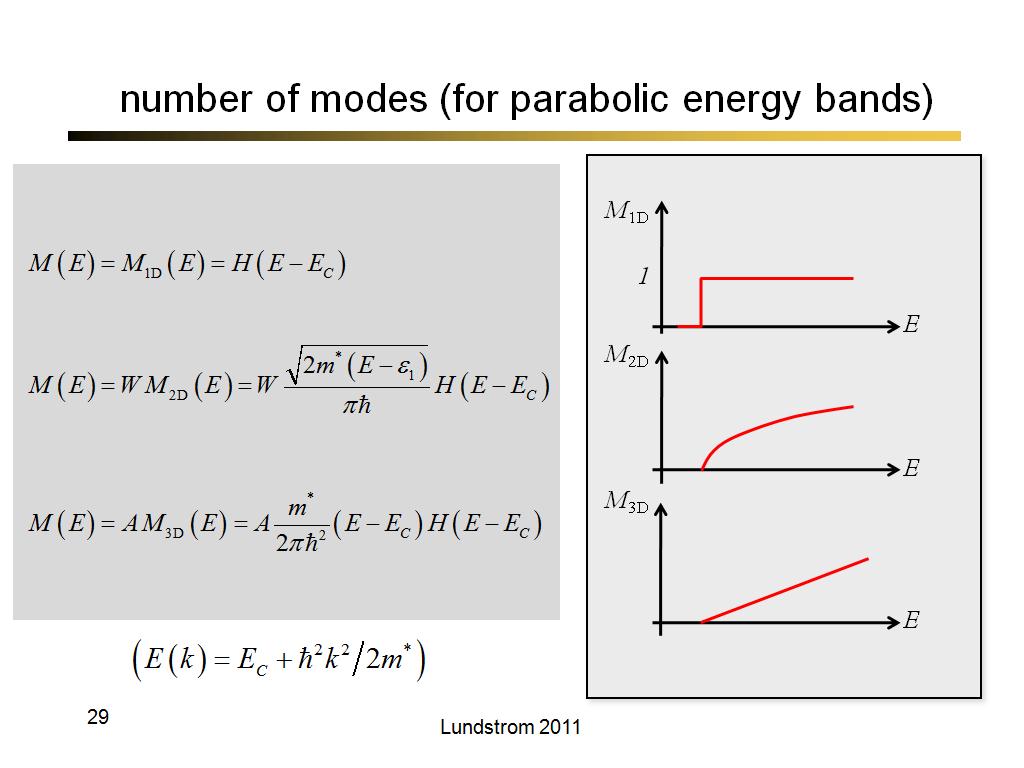
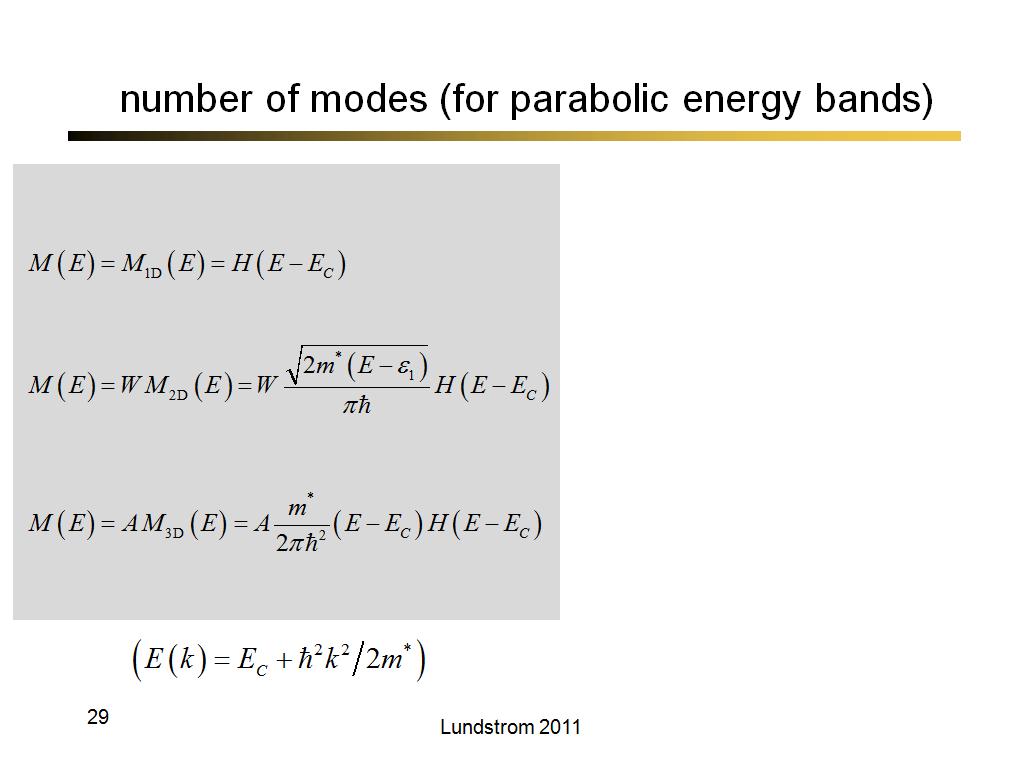 29. number of modes (for parabolic…
1982.5
00:00/00:00
29. number of modes (for parabolic…
1982.5
00:00/00:00 -
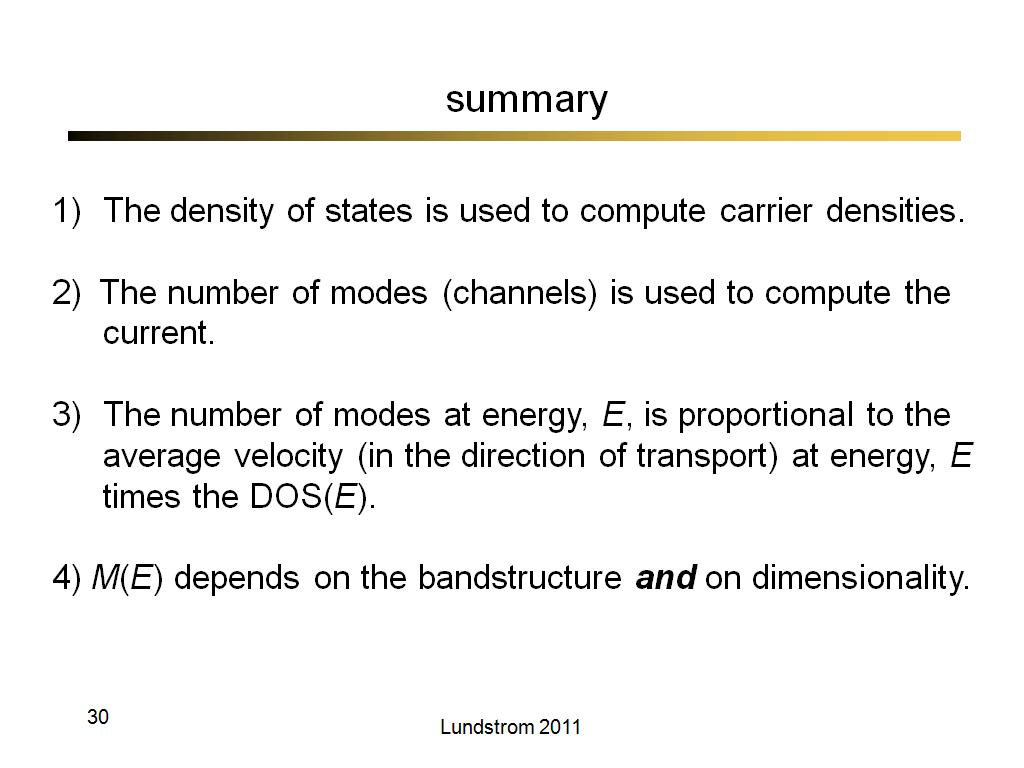 30. summary
2017.5
00:00/00:00
30. summary
2017.5
00:00/00:00 -
 31. outline
2080.9333333333334
00:00/00:00
31. outline
2080.9333333333334
00:00/00:00 -
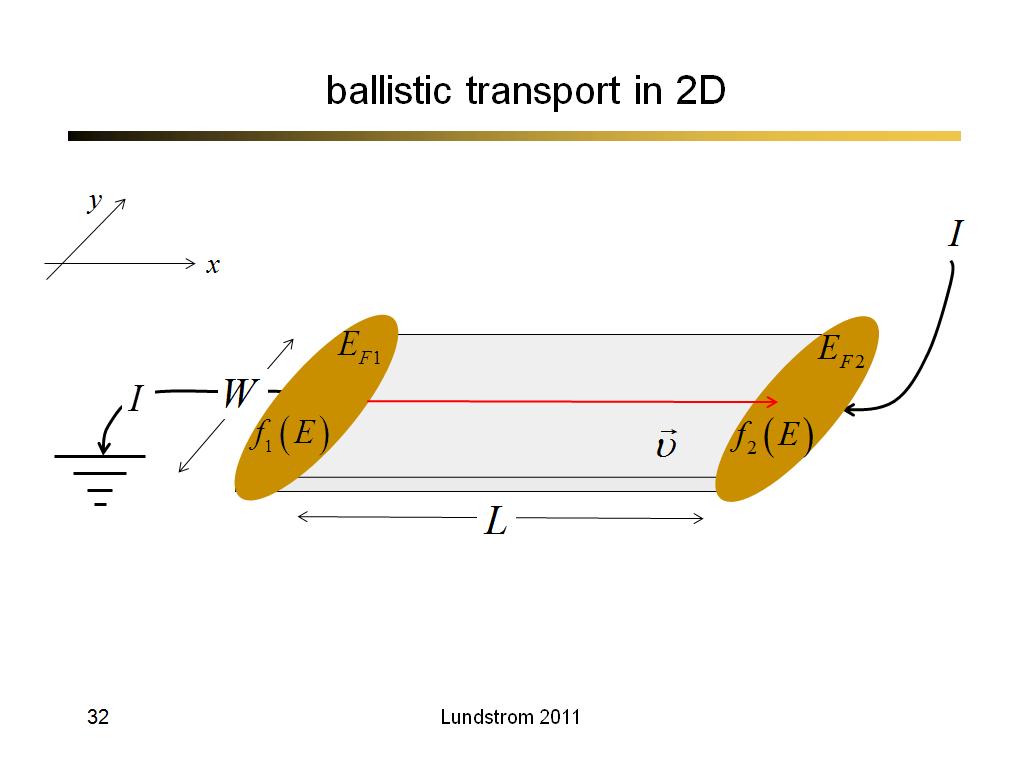
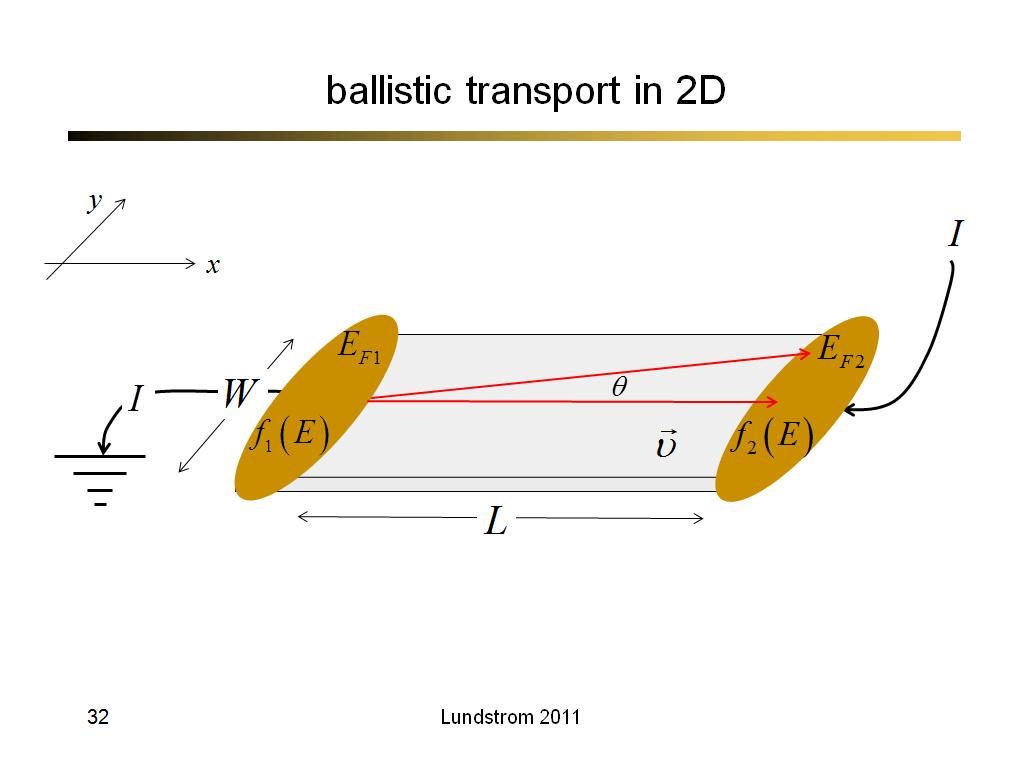
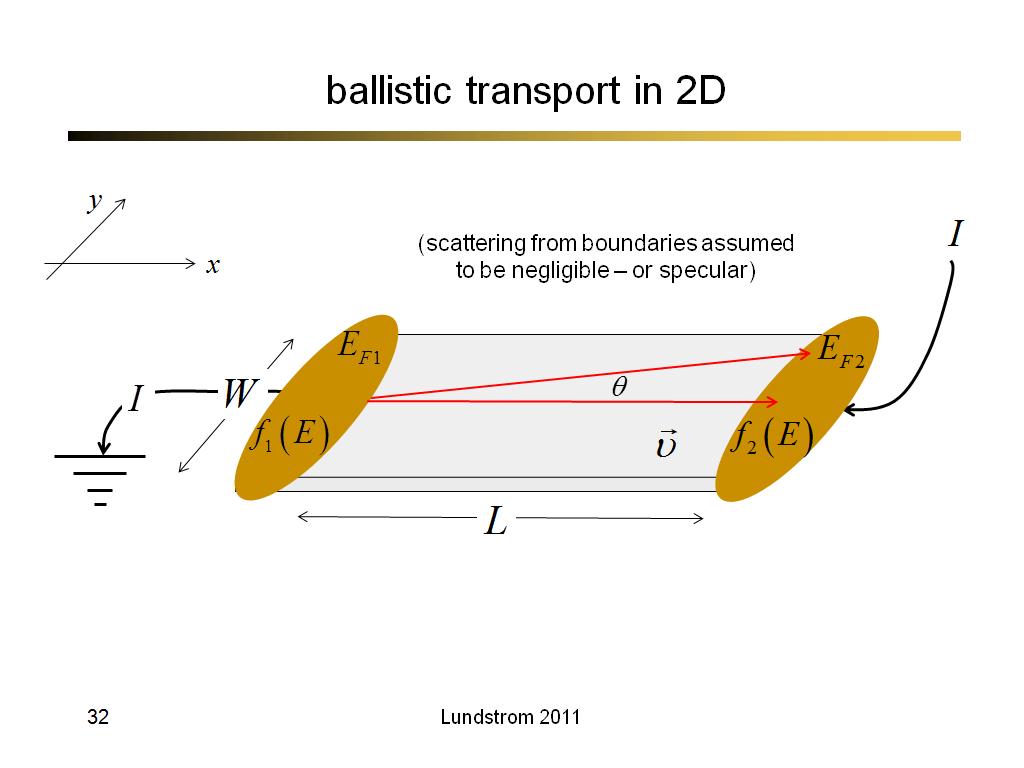
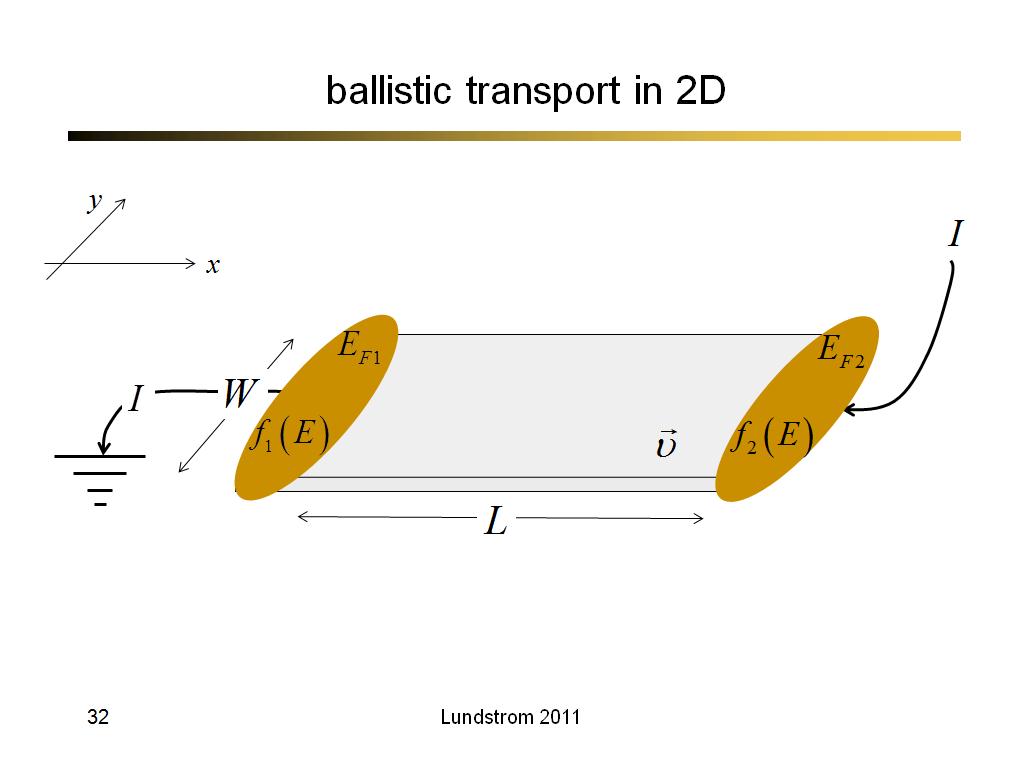 32. ballistic transport in 2D
2099.4
00:00/00:00
32. ballistic transport in 2D
2099.4
00:00/00:00 -
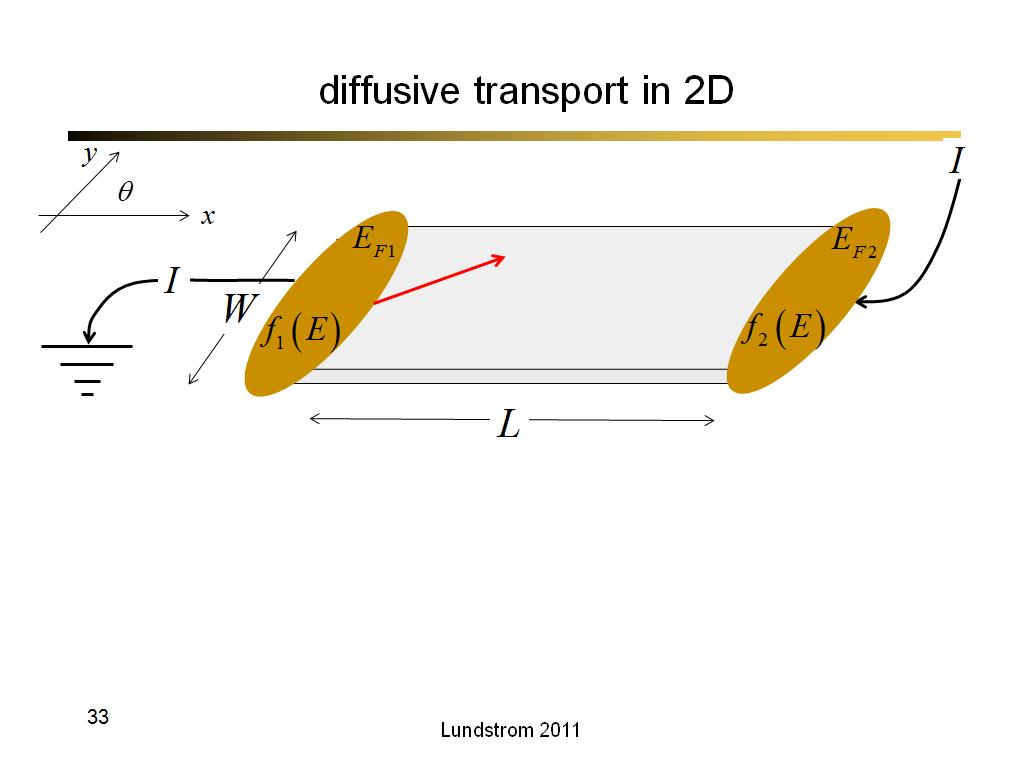
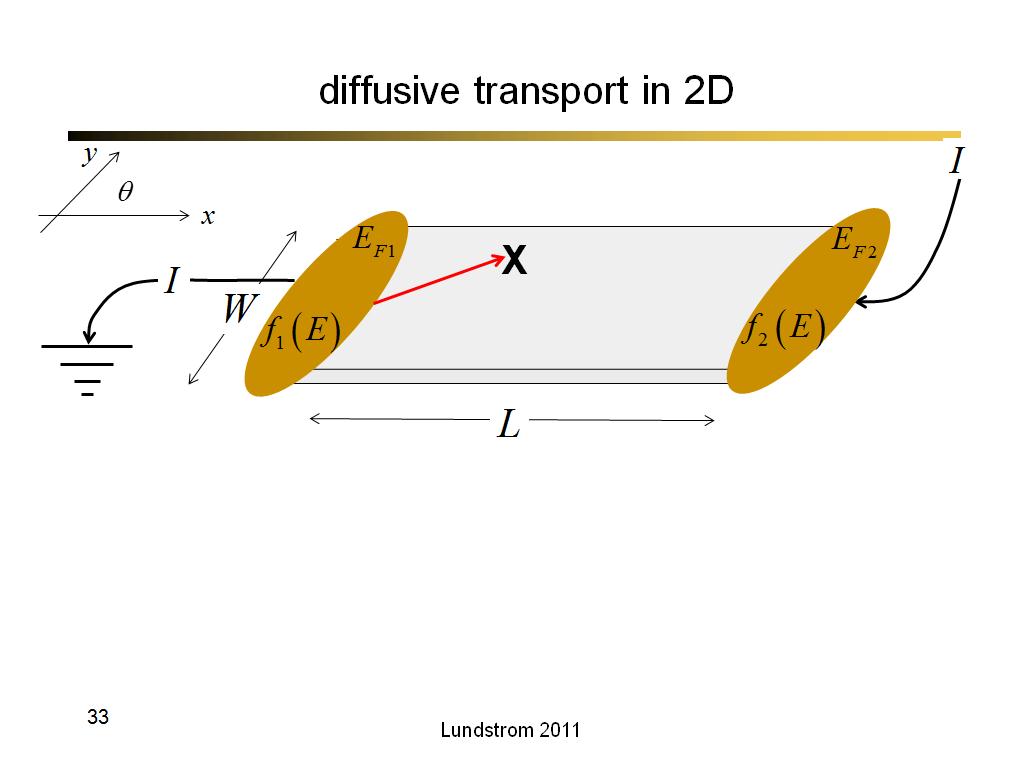
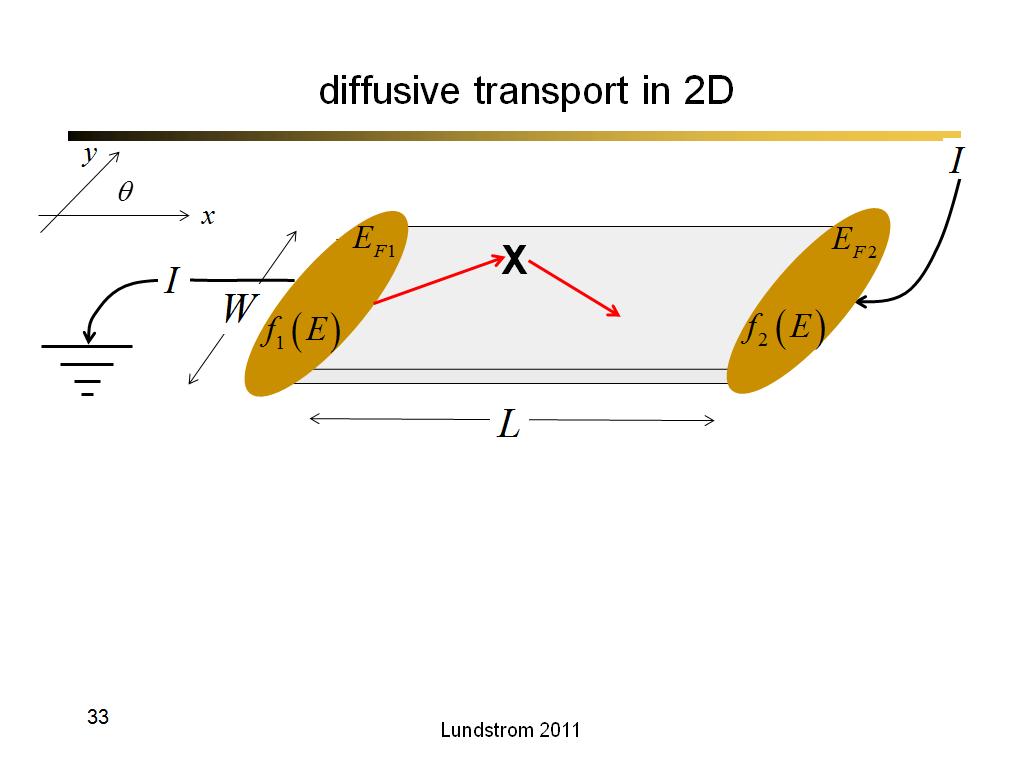
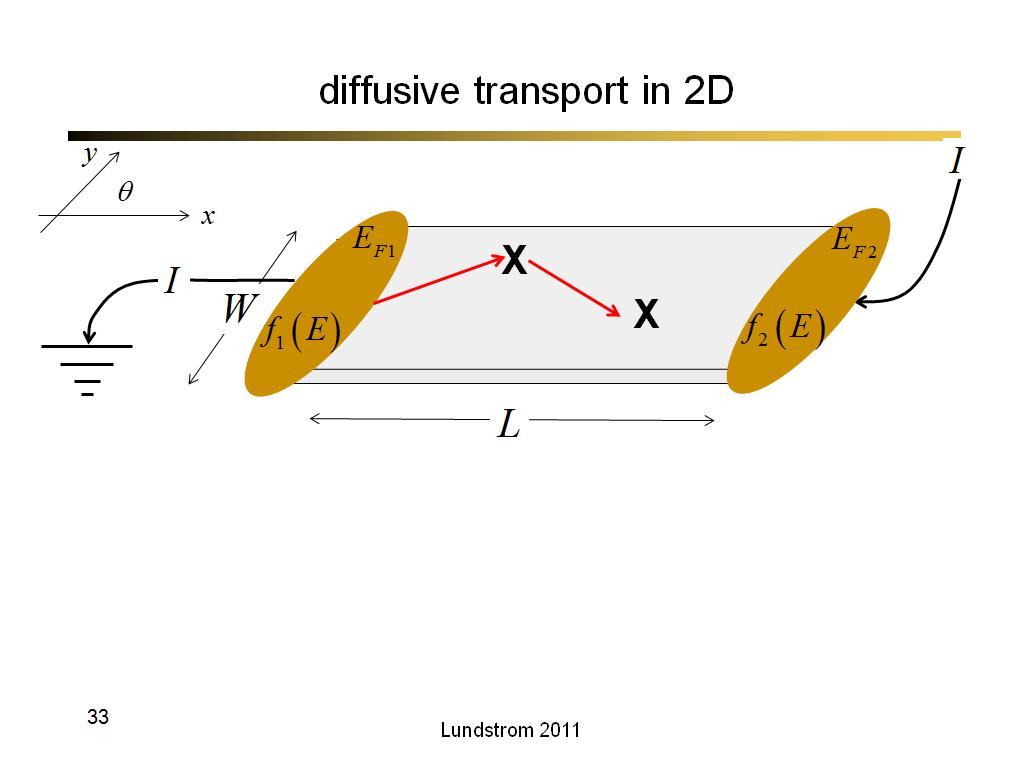
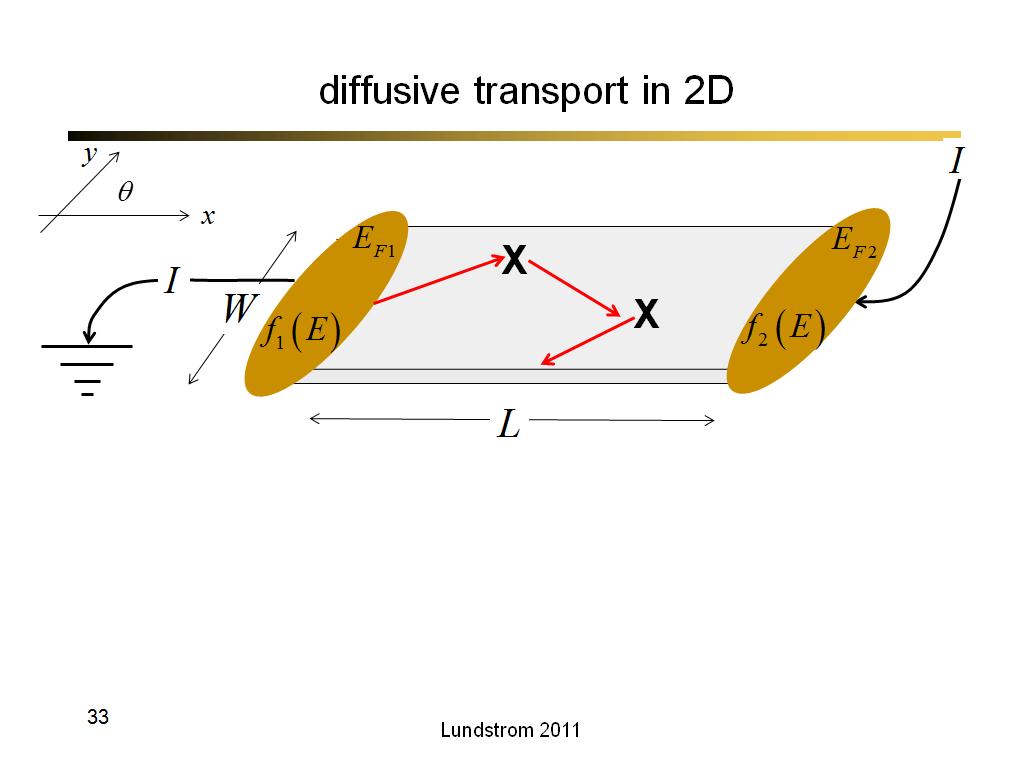
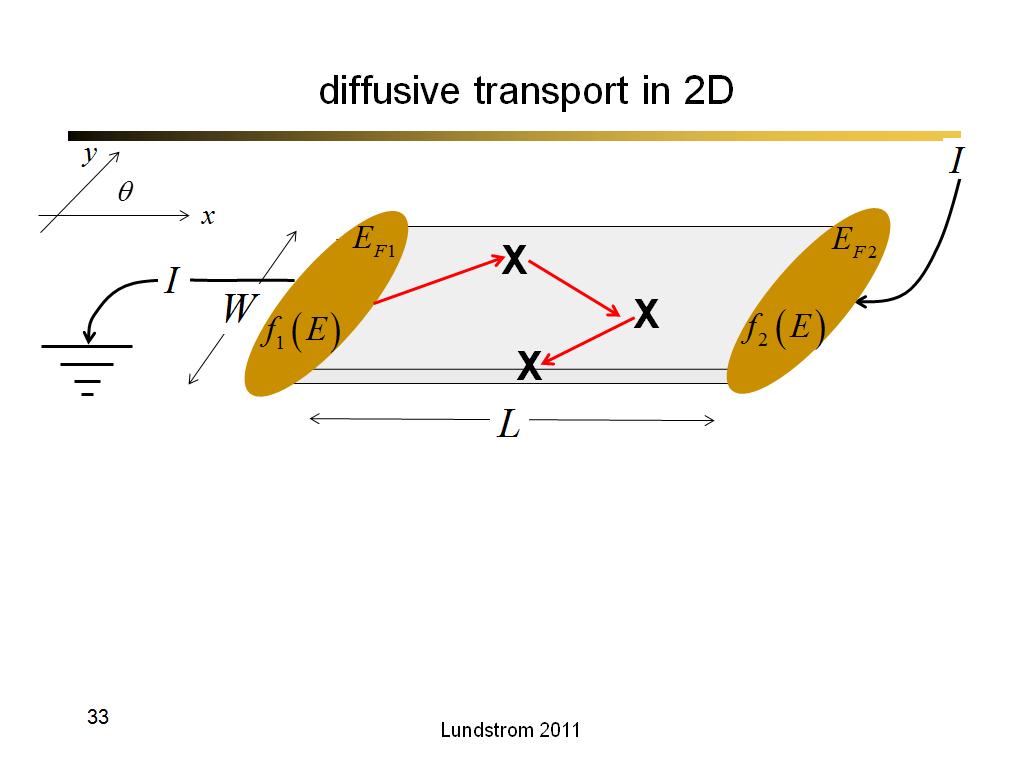
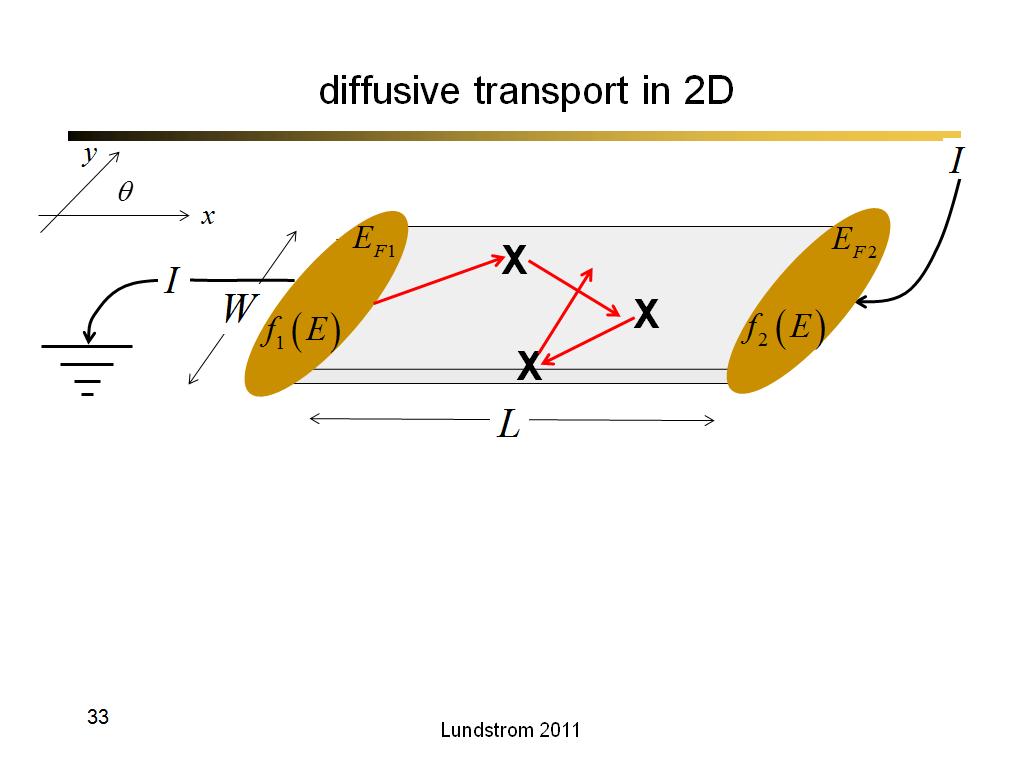
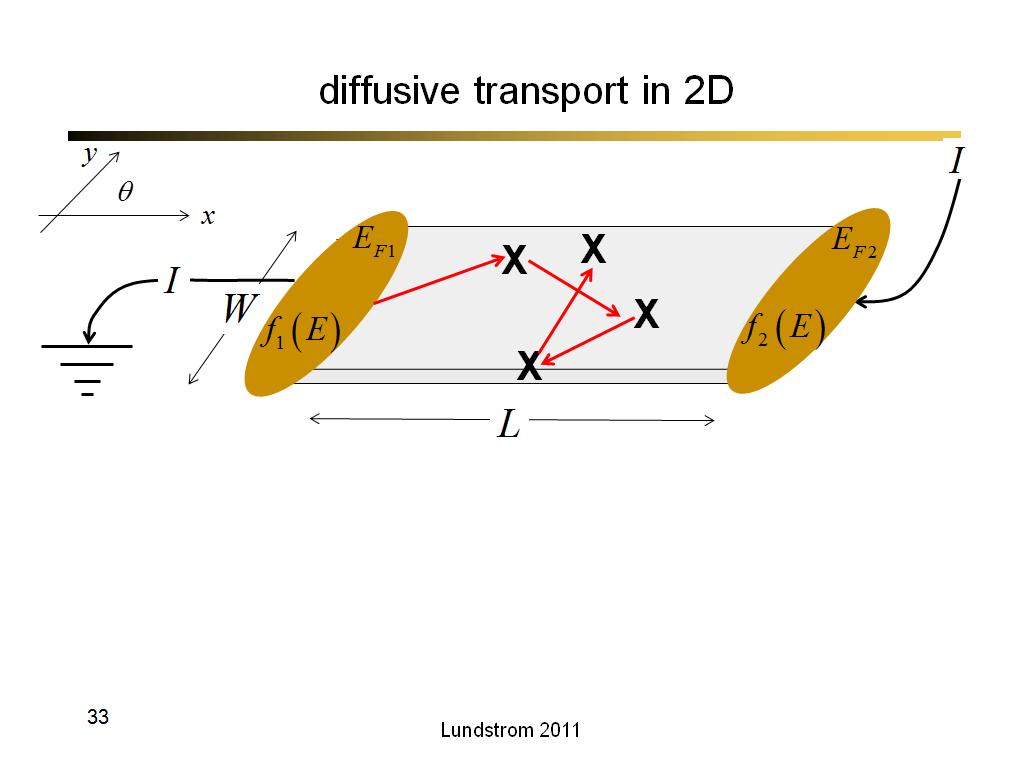
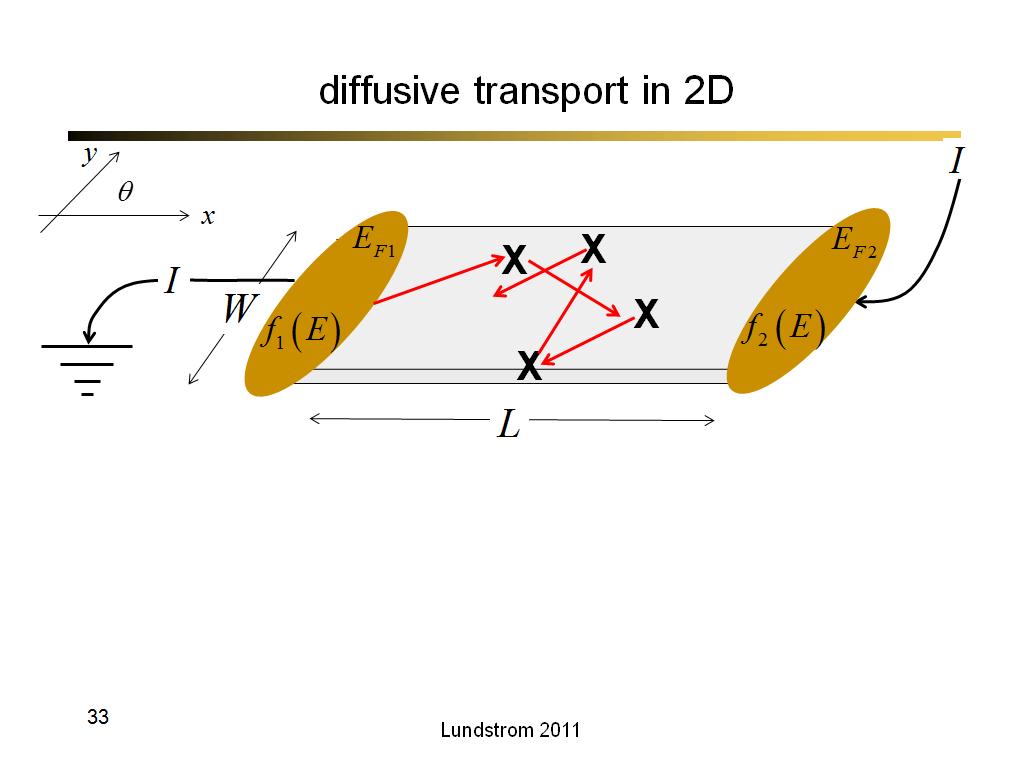
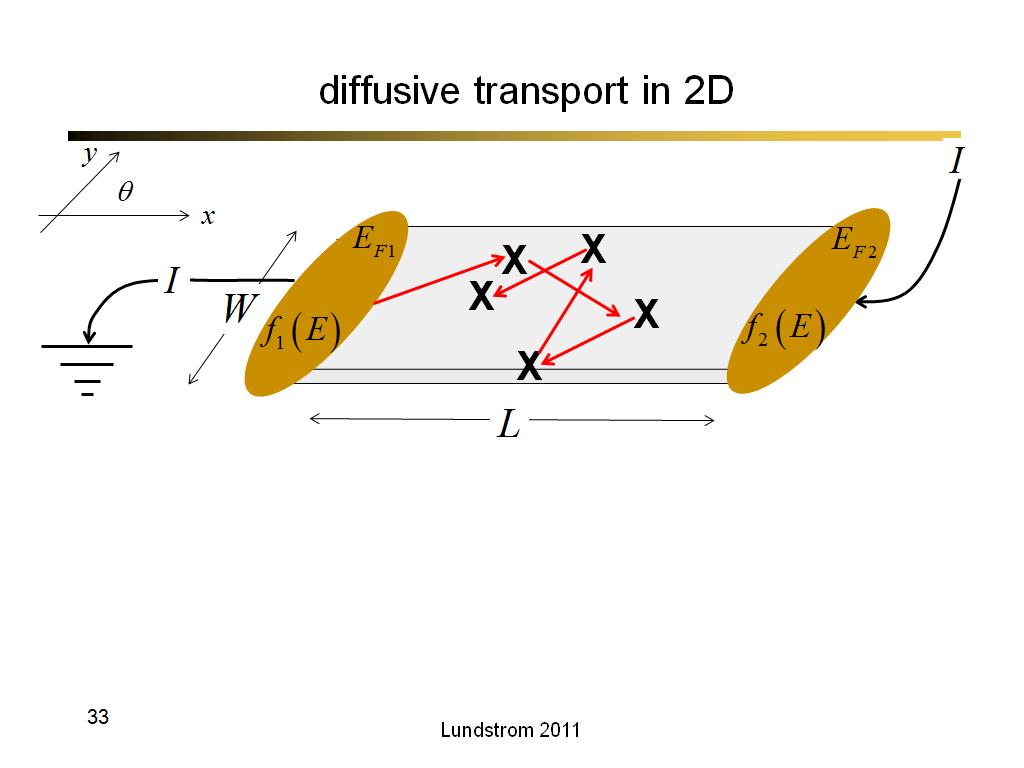
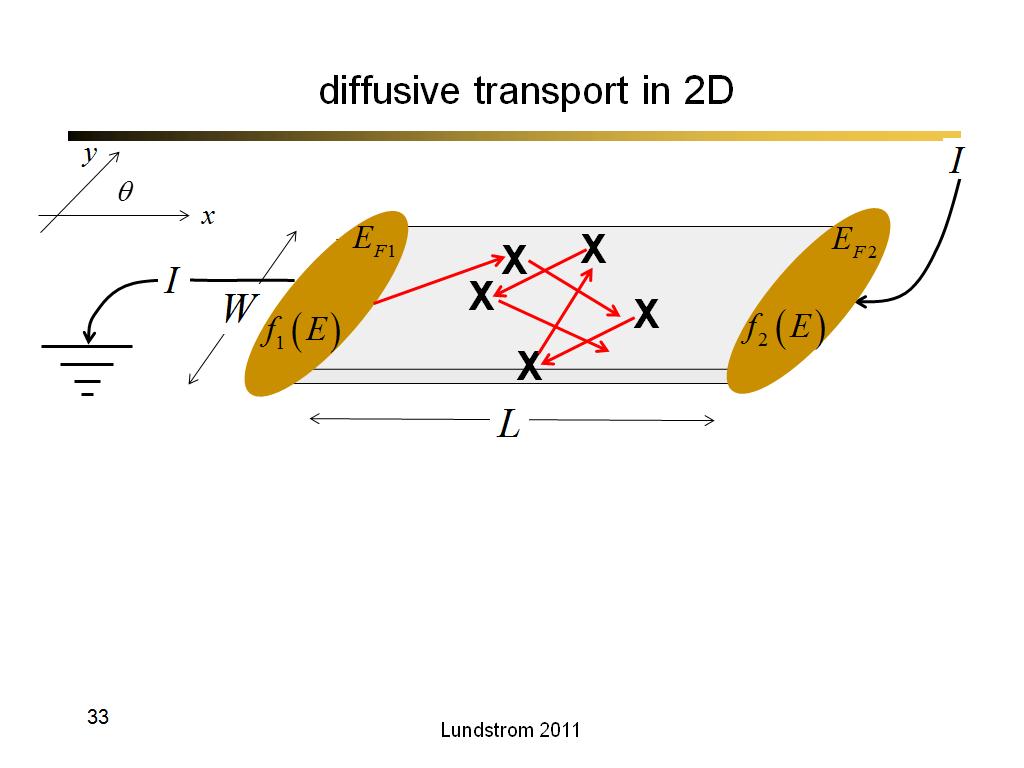
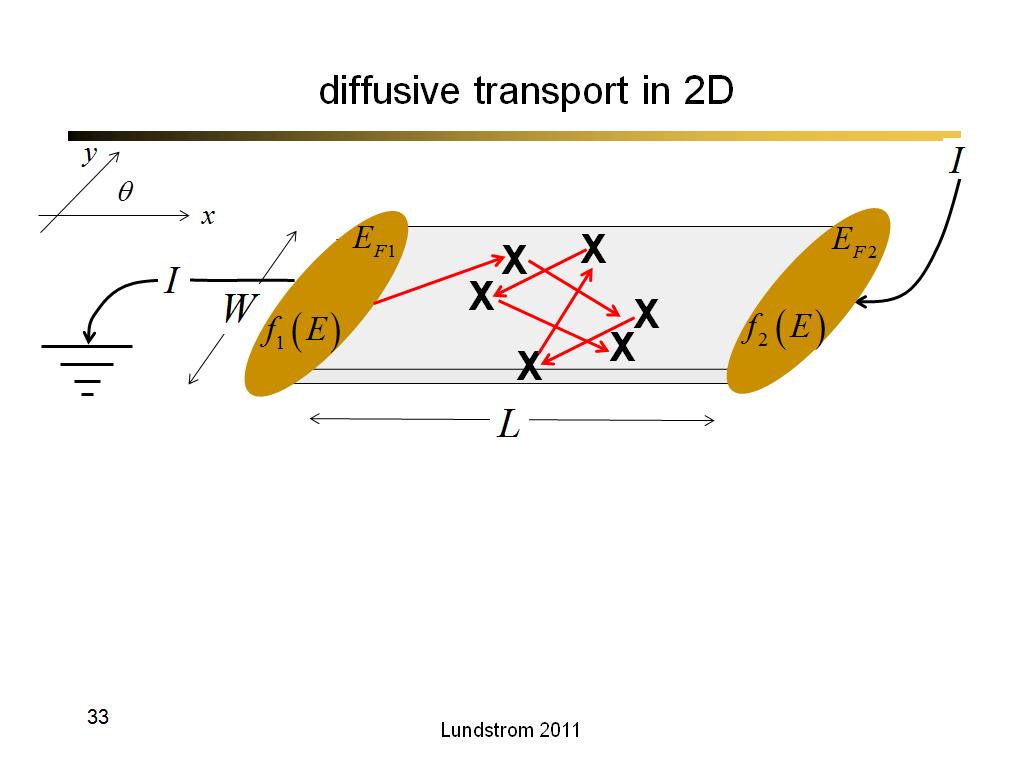
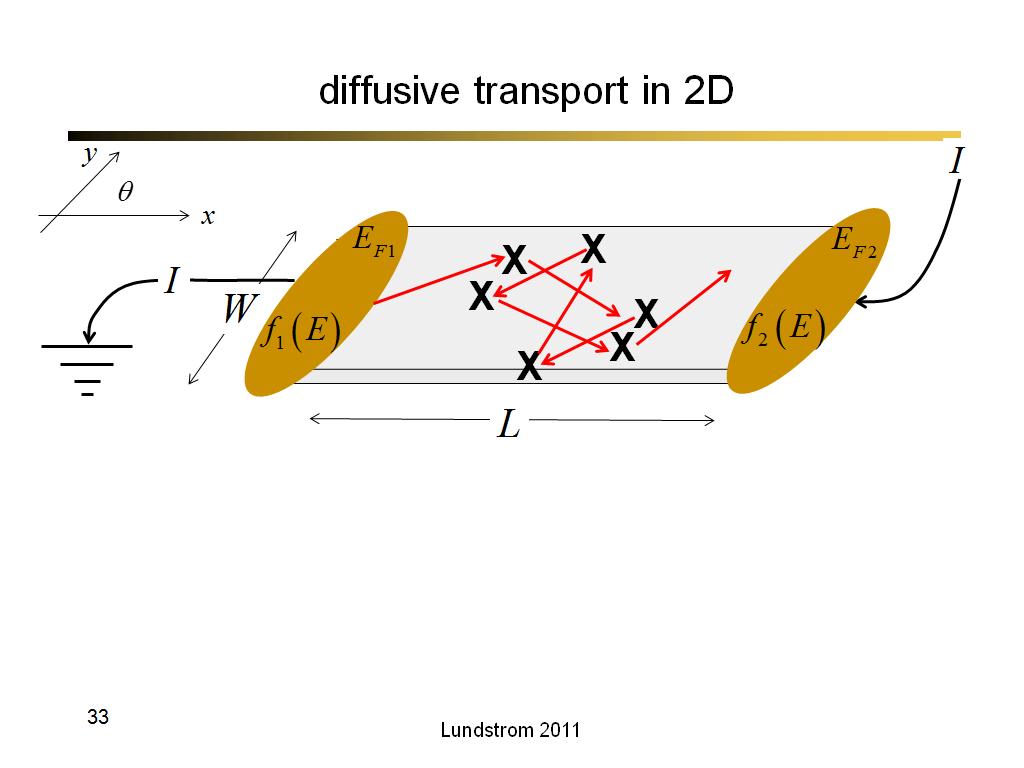
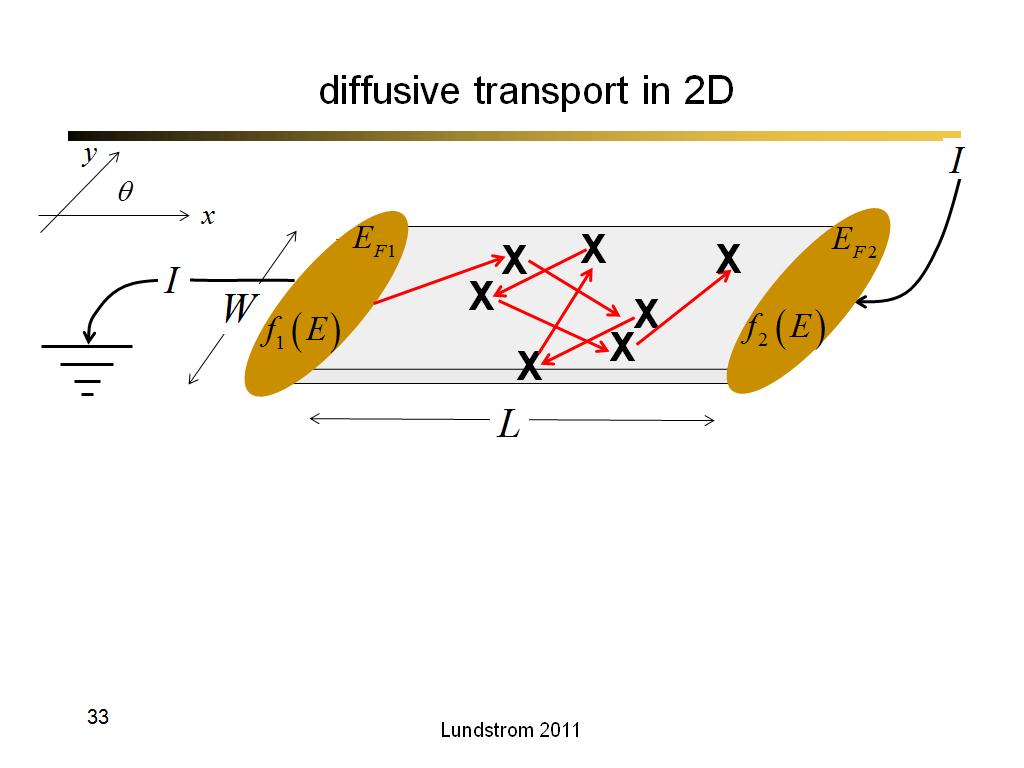
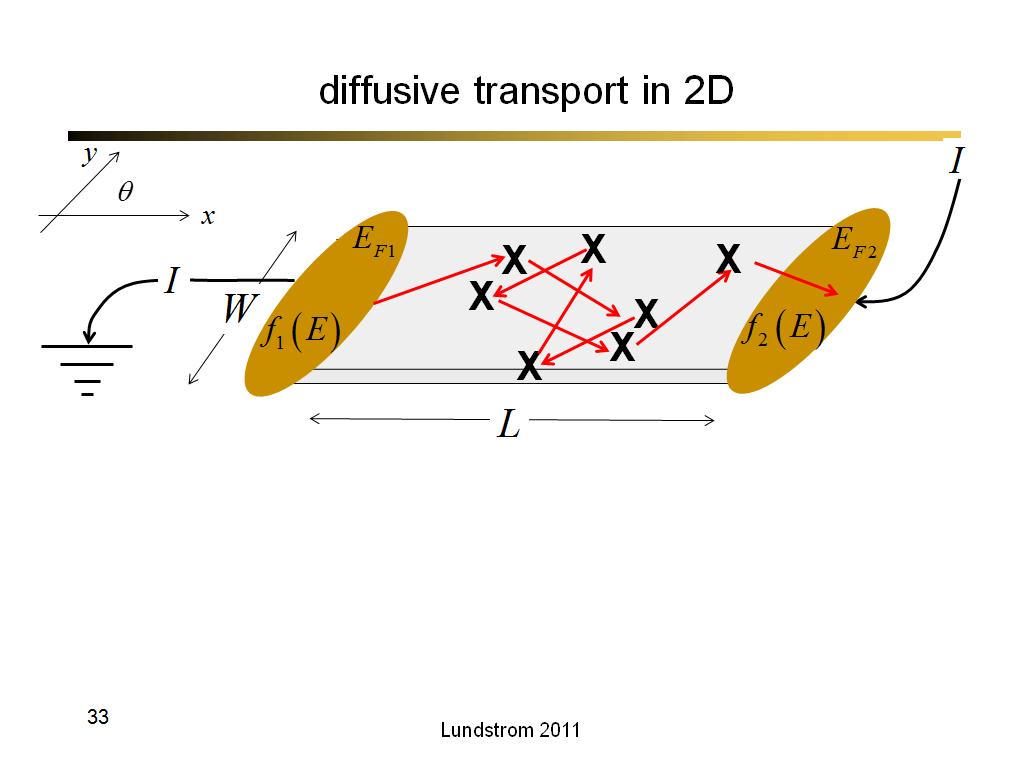
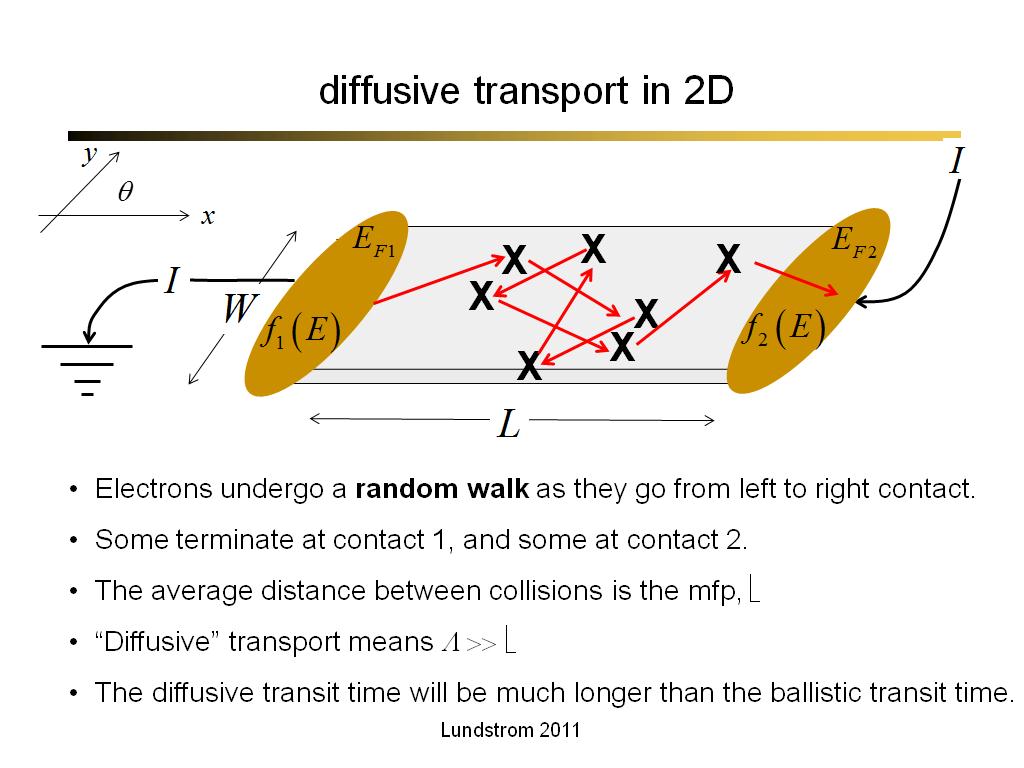
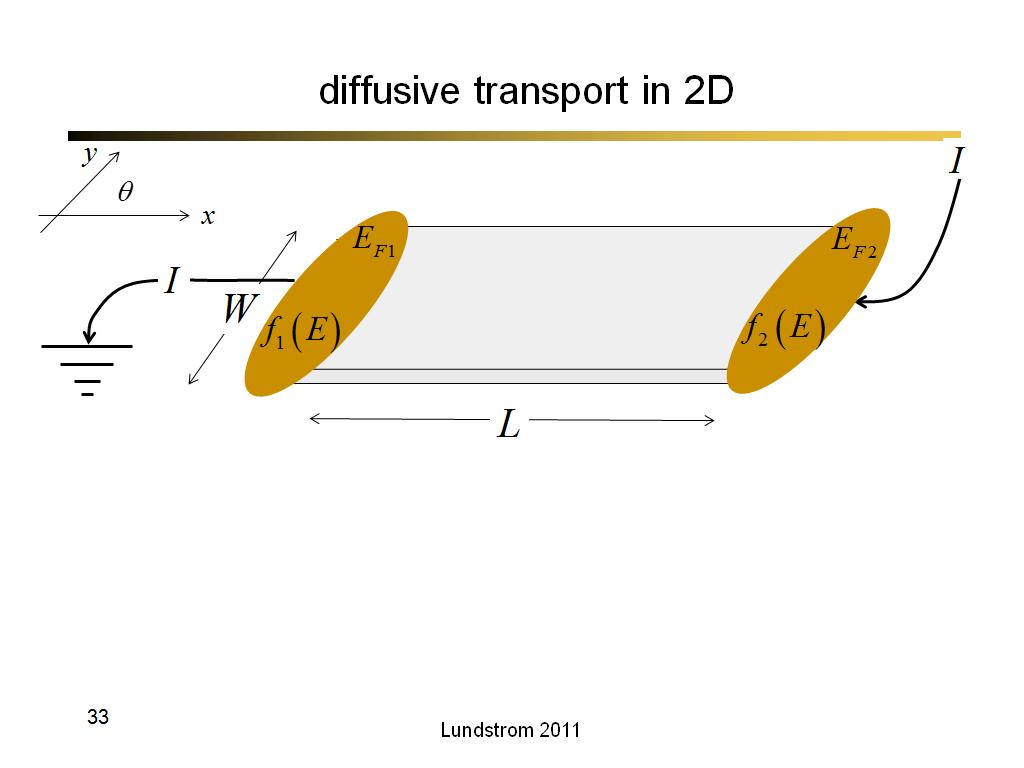 33. diffusive transport in 2D
2146.7666666666669
00:00/00:00
33. diffusive transport in 2D
2146.7666666666669
00:00/00:00 -
 34. ballistic vs. diffusive transp…
2260.1
00:00/00:00
34. ballistic vs. diffusive transp…
2260.1
00:00/00:00 -
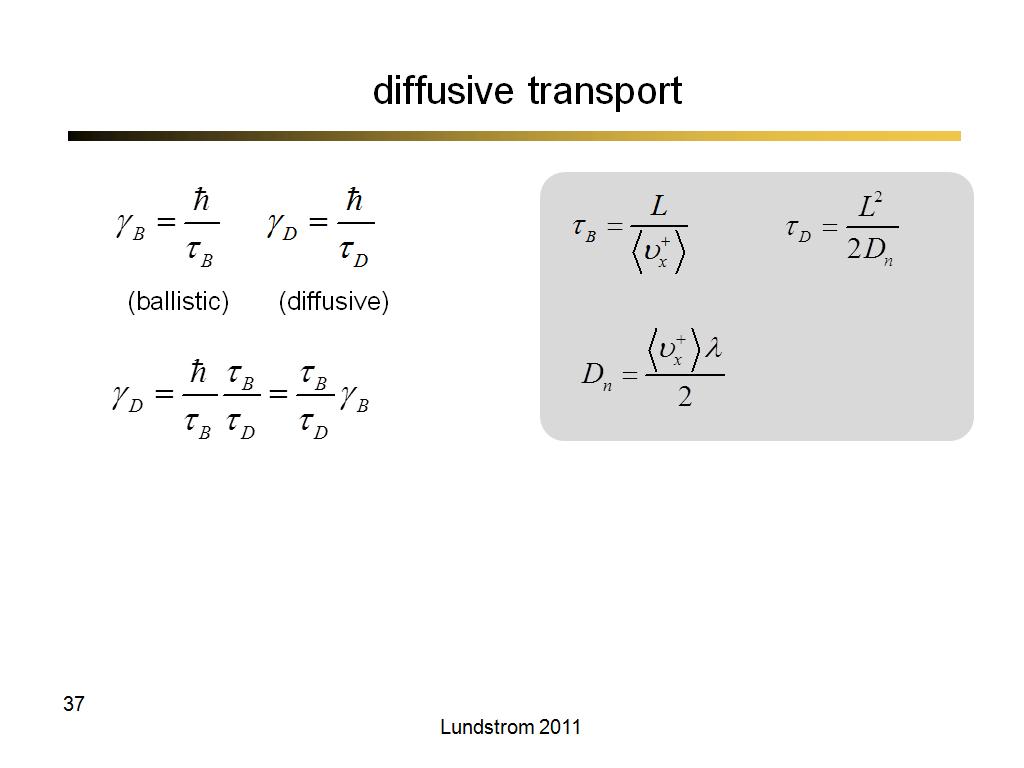
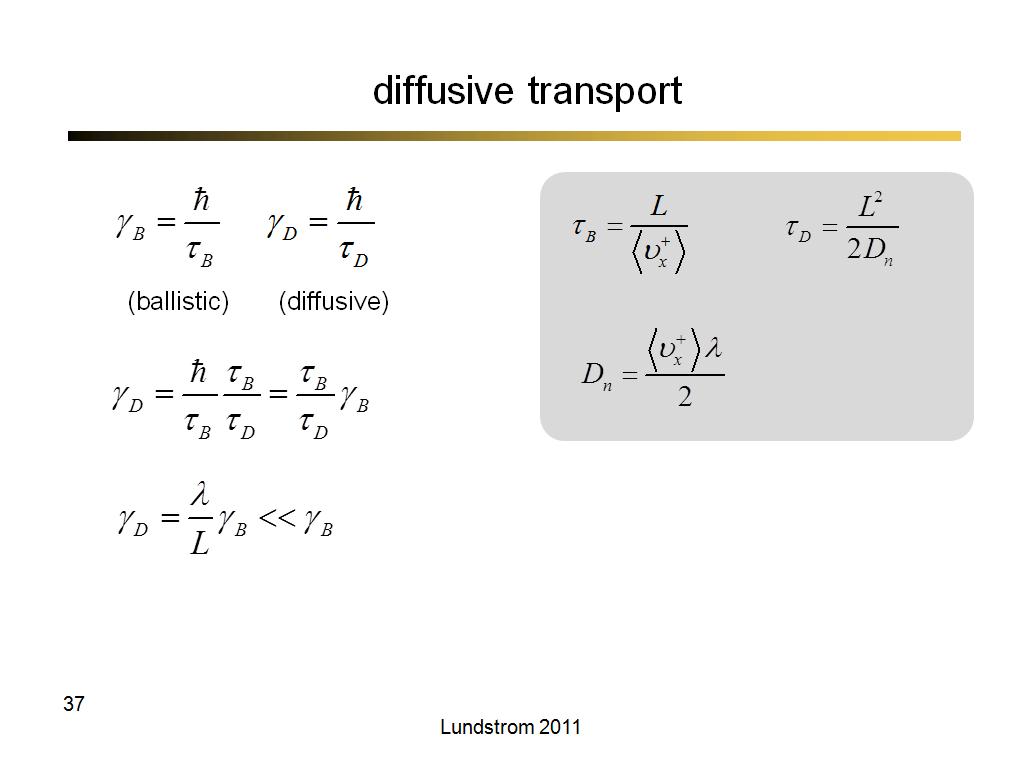
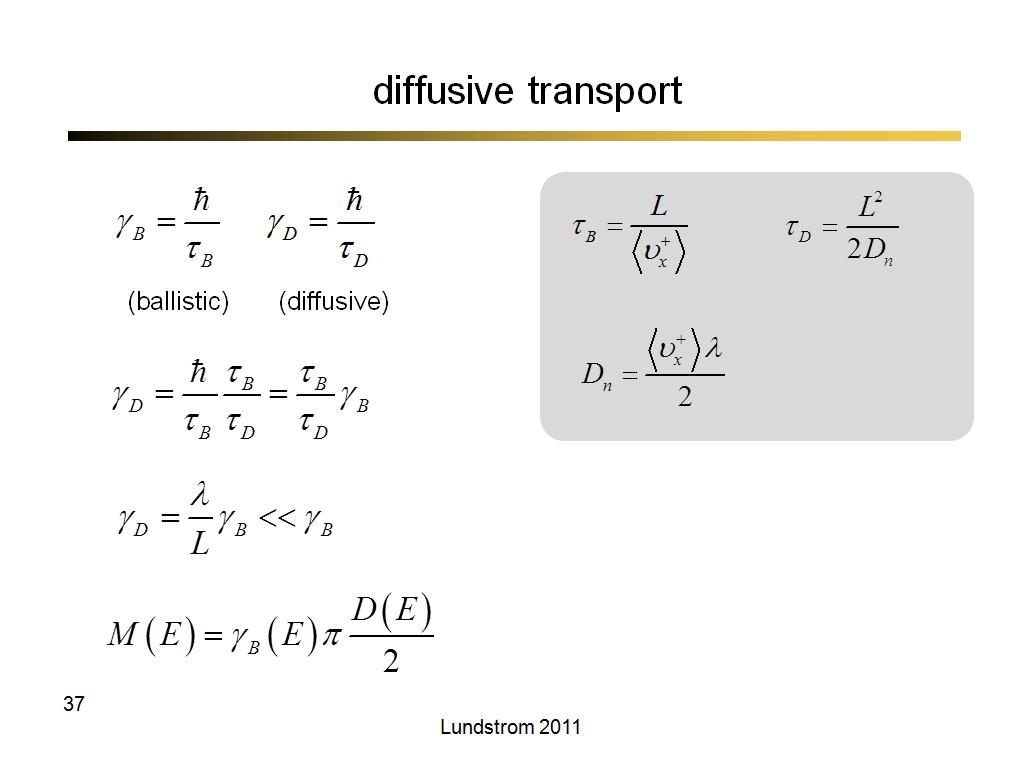
 35. diffusive transport
2280.2
00:00/00:00
35. diffusive transport
2280.2
00:00/00:00 -
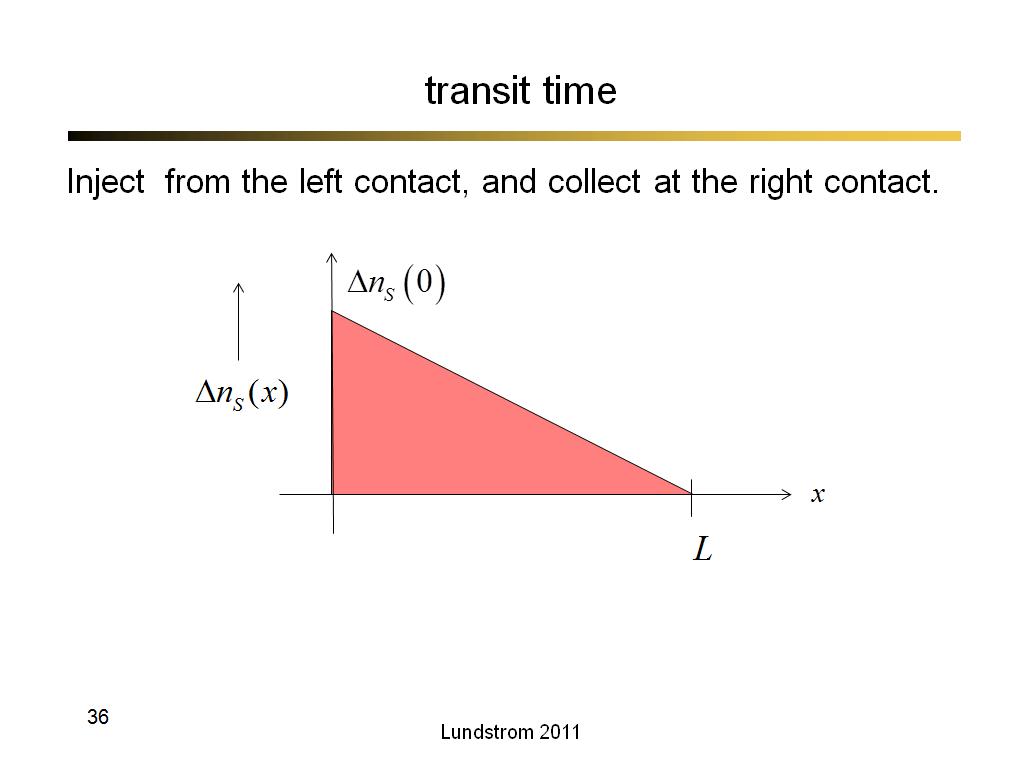
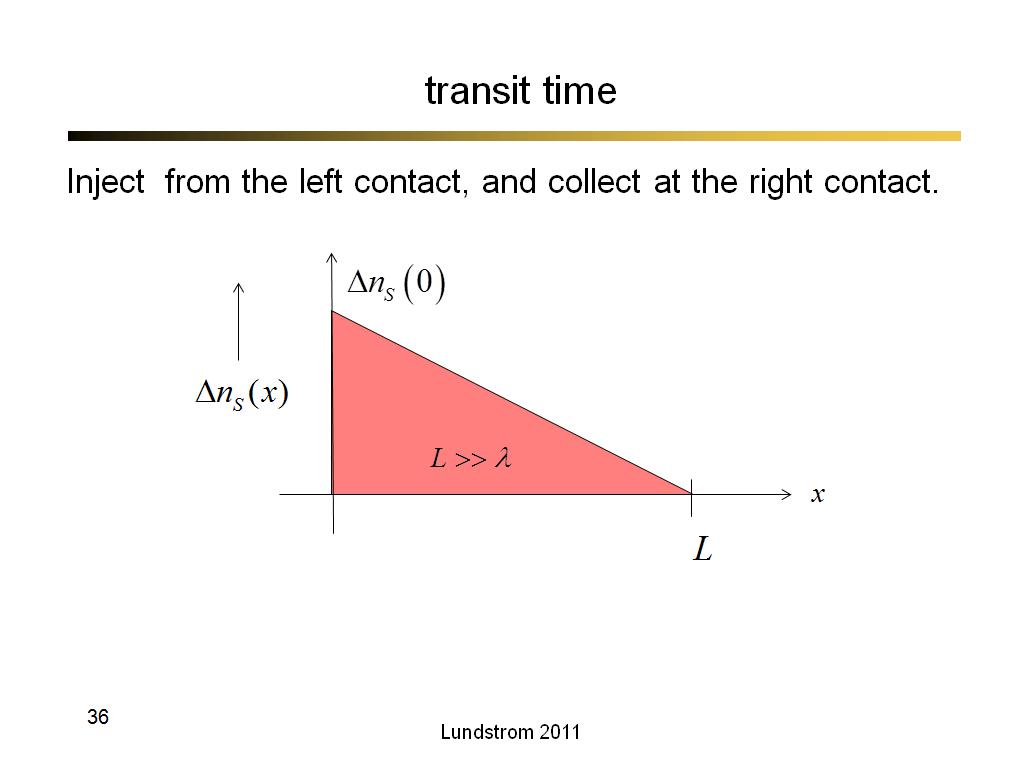
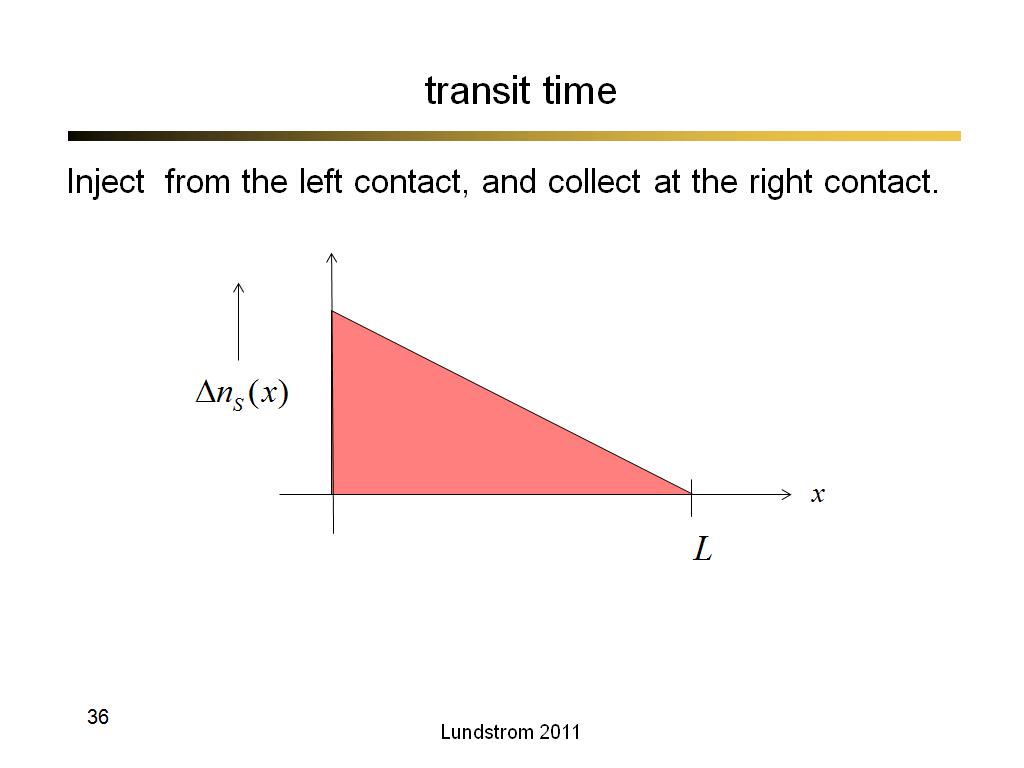 36. transit time
2320.3333333333335
00:00/00:00
36. transit time
2320.3333333333335
00:00/00:00 -
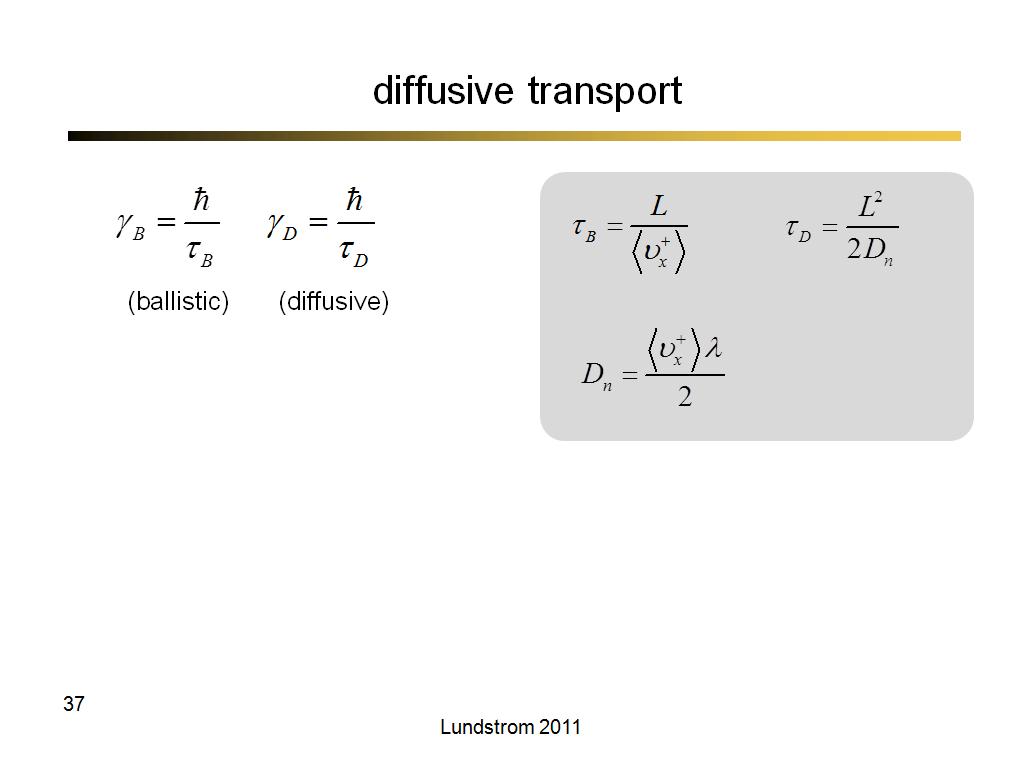 37. diffusive transport
2444.6
00:00/00:00
37. diffusive transport
2444.6
00:00/00:00 -
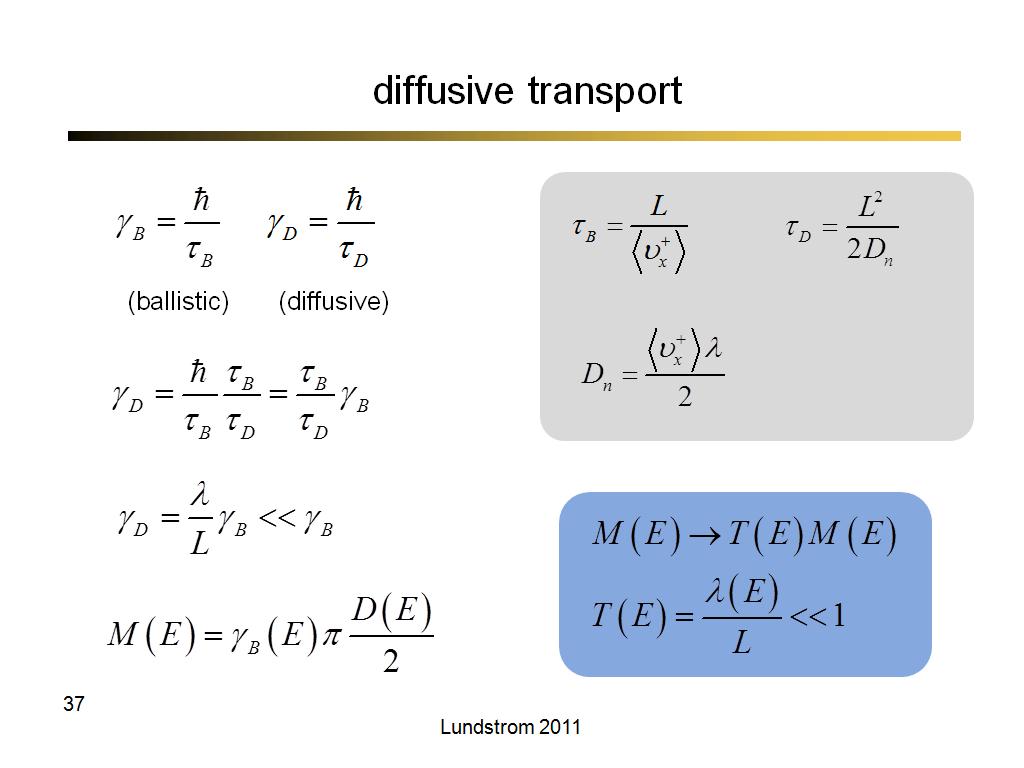
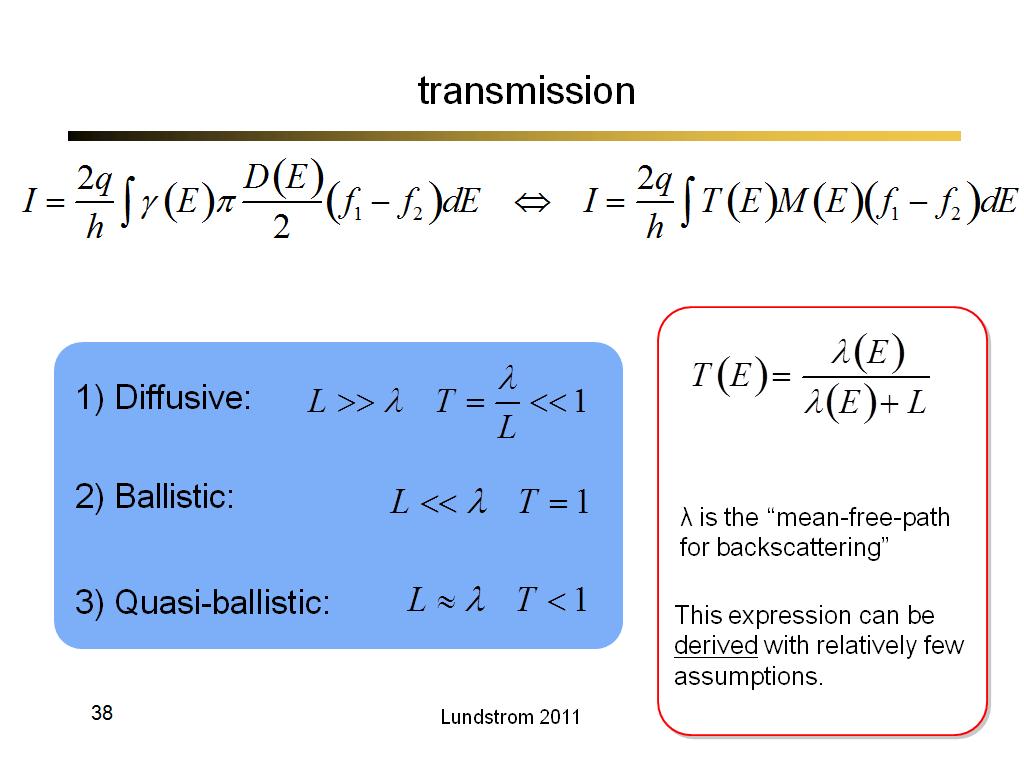
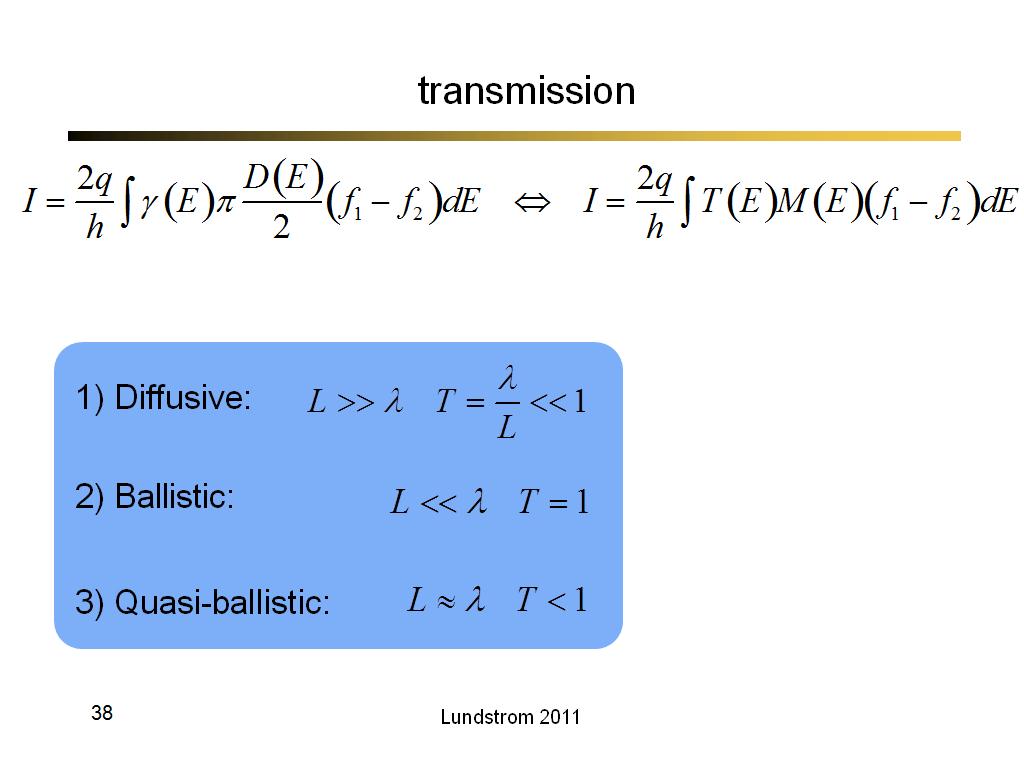 38. transmission
2651.9
00:00/00:00
38. transmission
2651.9
00:00/00:00 -
 39. outline
2826.6333333333332
00:00/00:00
39. outline
2826.6333333333332
00:00/00:00 -
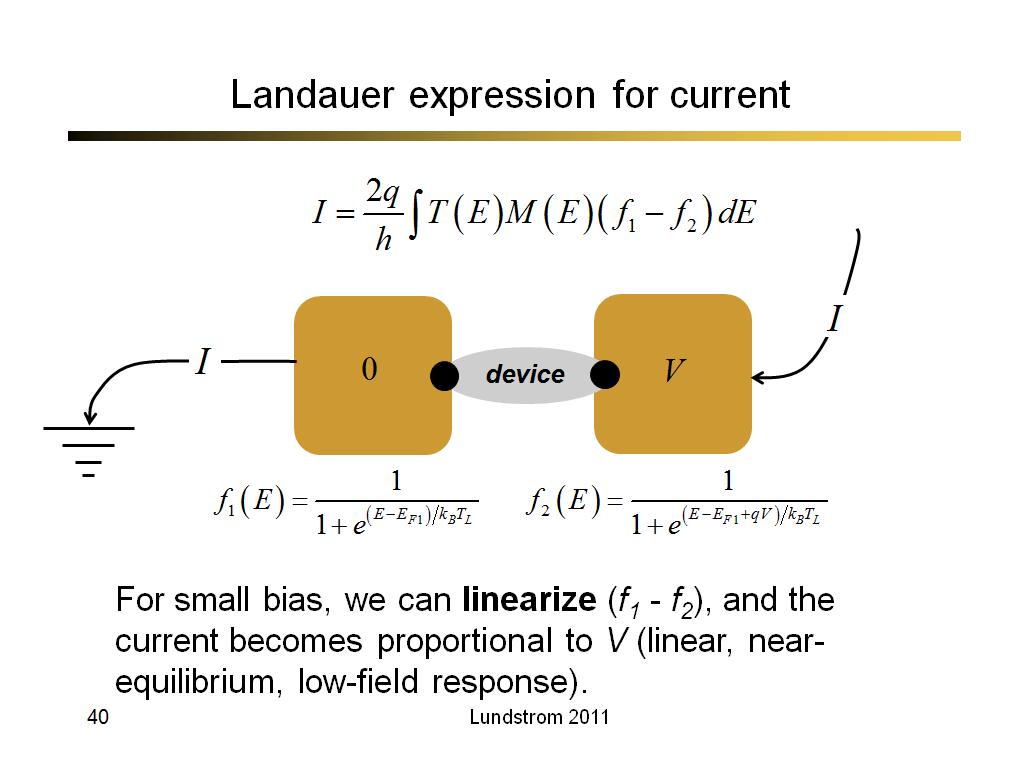
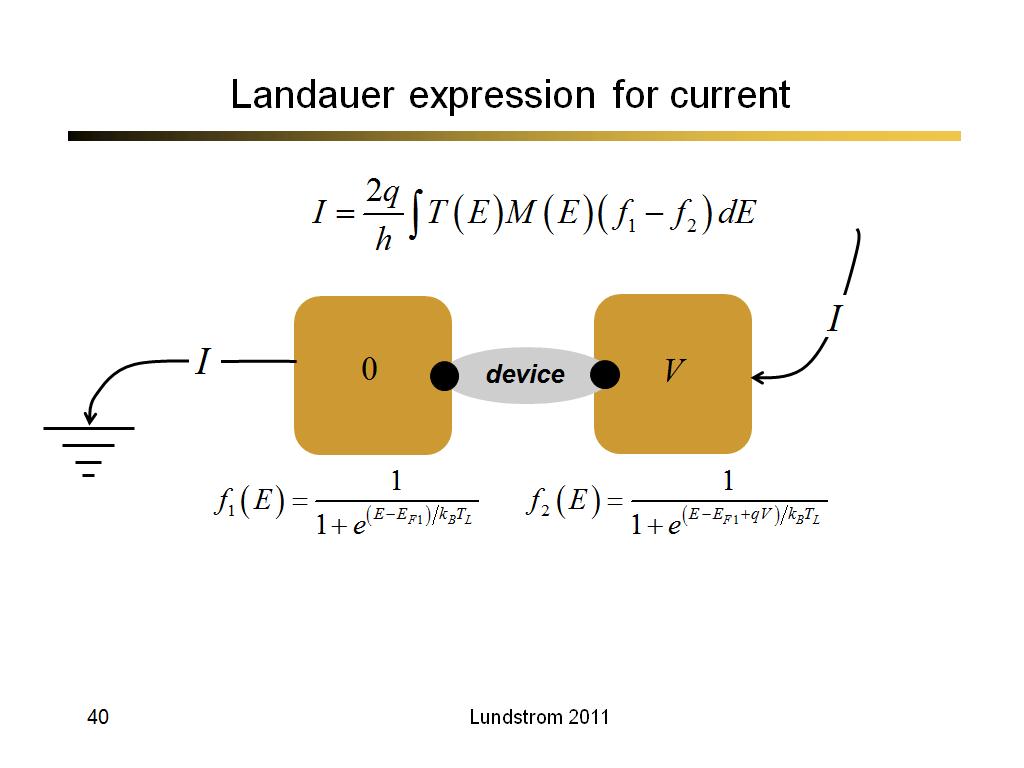 40. Landauer expression for curren…
2835.6666666666665
00:00/00:00
40. Landauer expression for curren…
2835.6666666666665
00:00/00:00 -
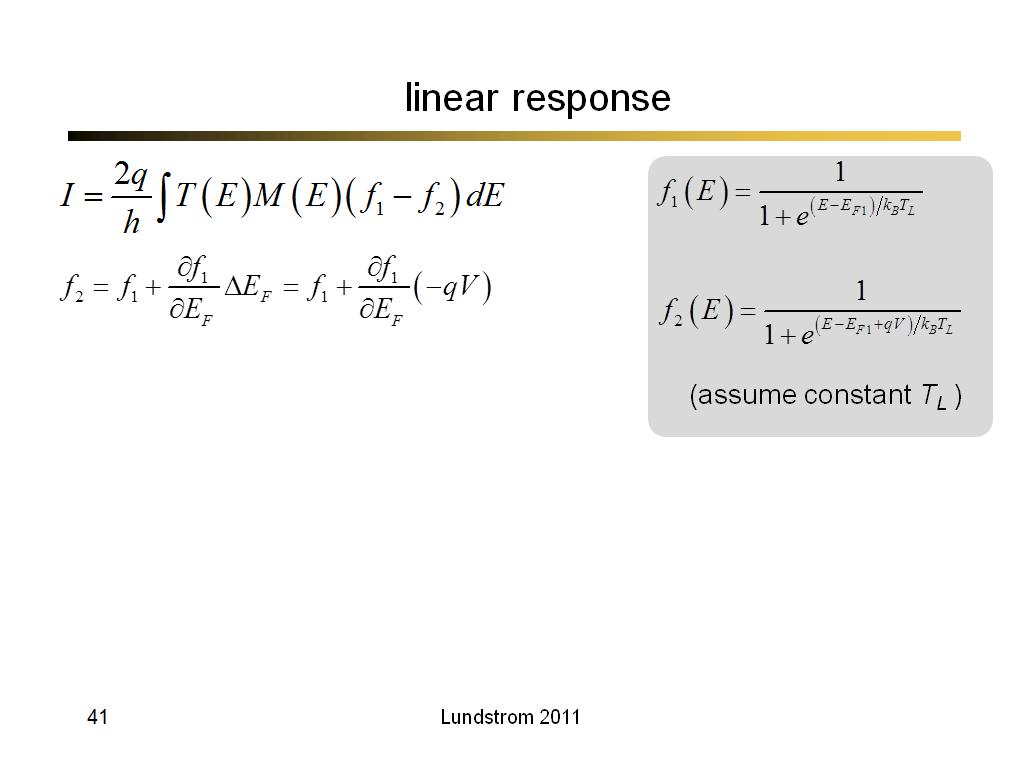
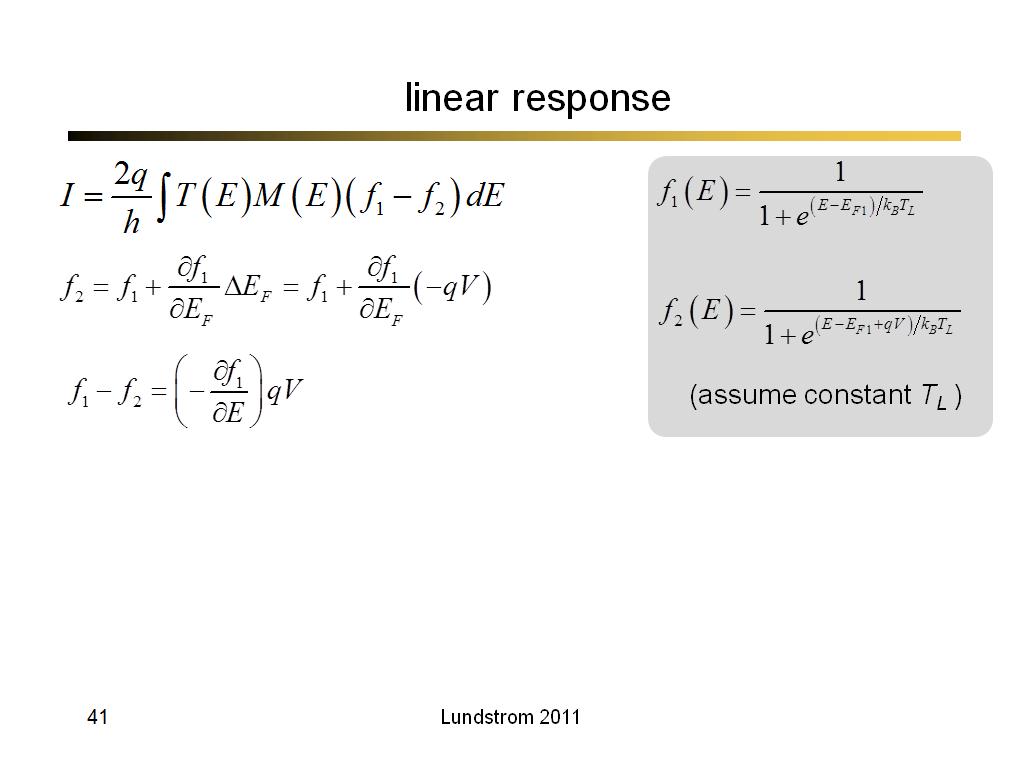
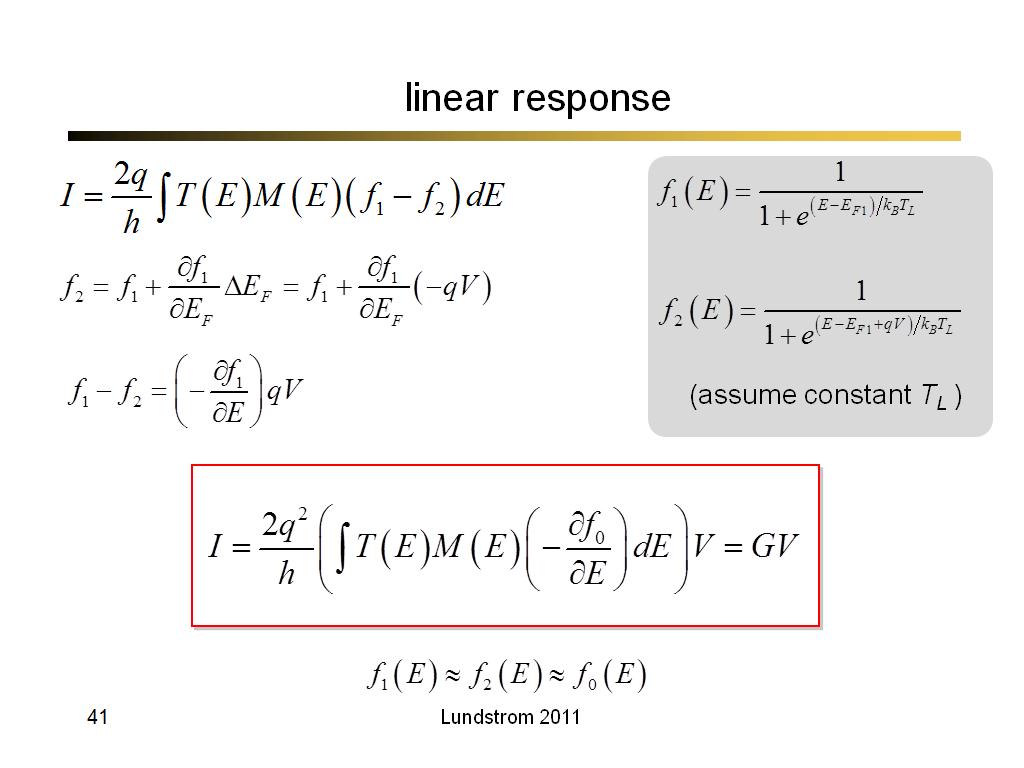
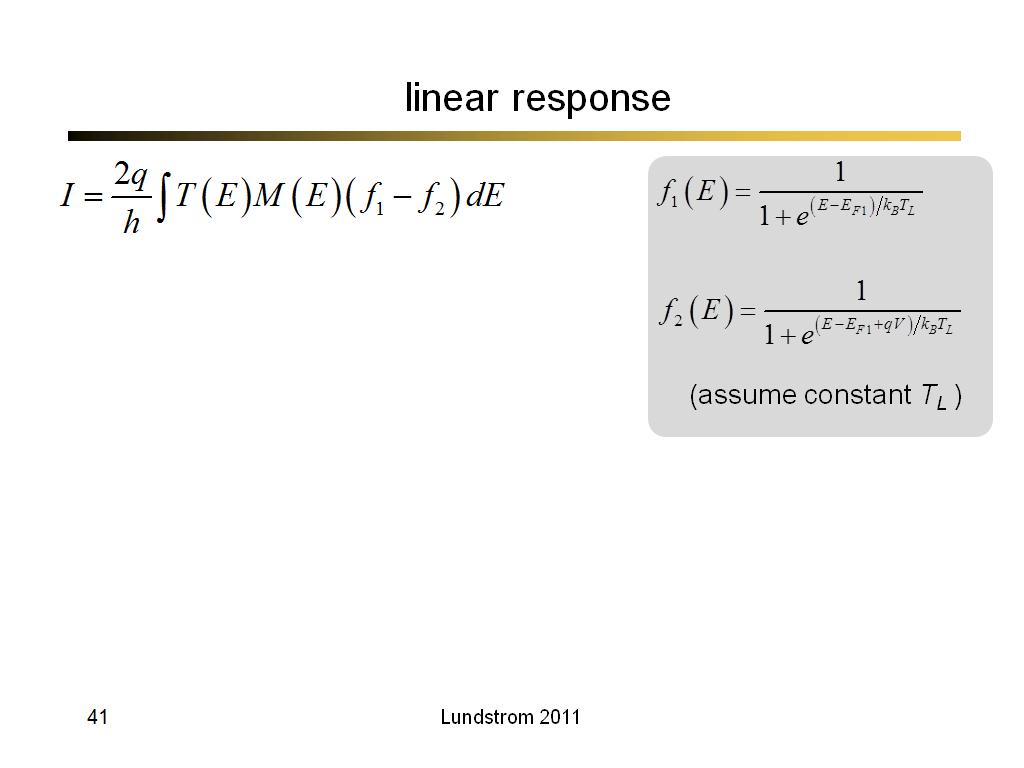 41. linear response
2879
00:00/00:00
41. linear response
2879
00:00/00:00 -
 42. outline
3003.5333333333333
00:00/00:00
42. outline
3003.5333333333333
00:00/00:00 -
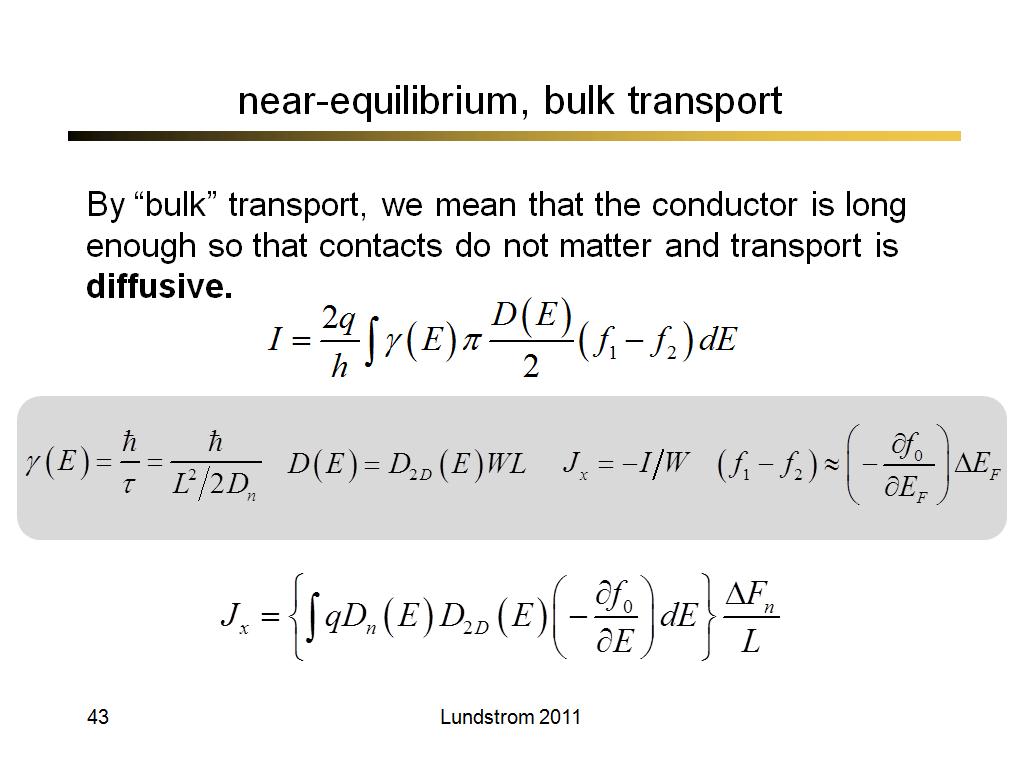
 43. near-equilibrium, bulk transpo…
3012.8
00:00/00:00
43. near-equilibrium, bulk transpo…
3012.8
00:00/00:00 -
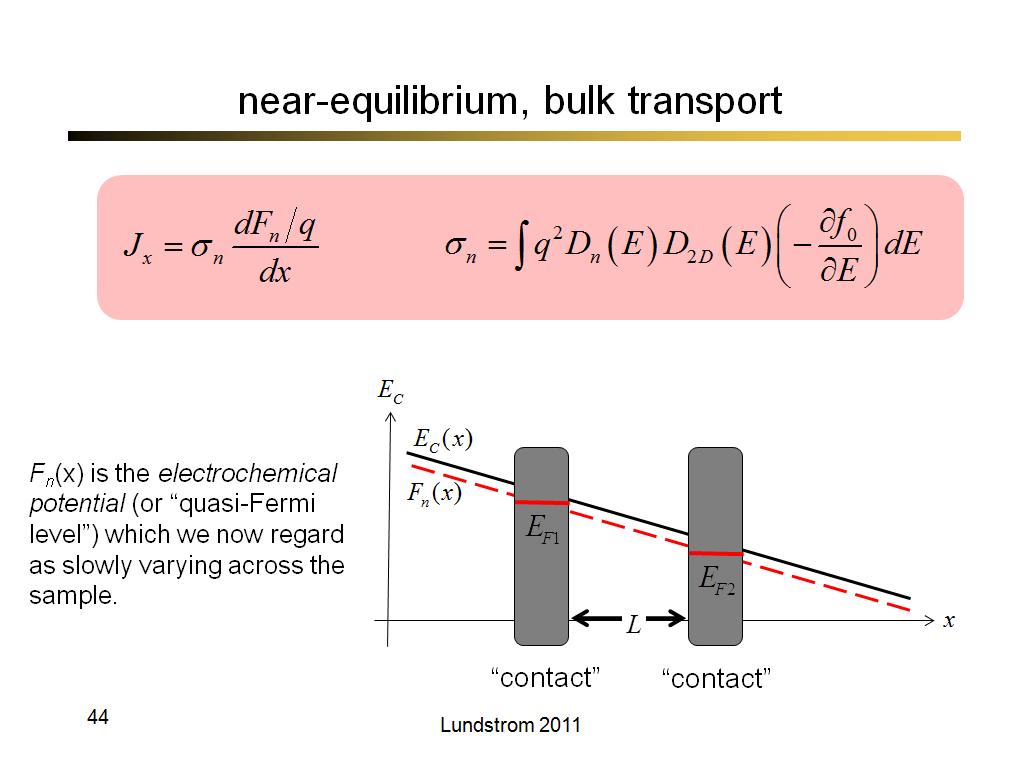
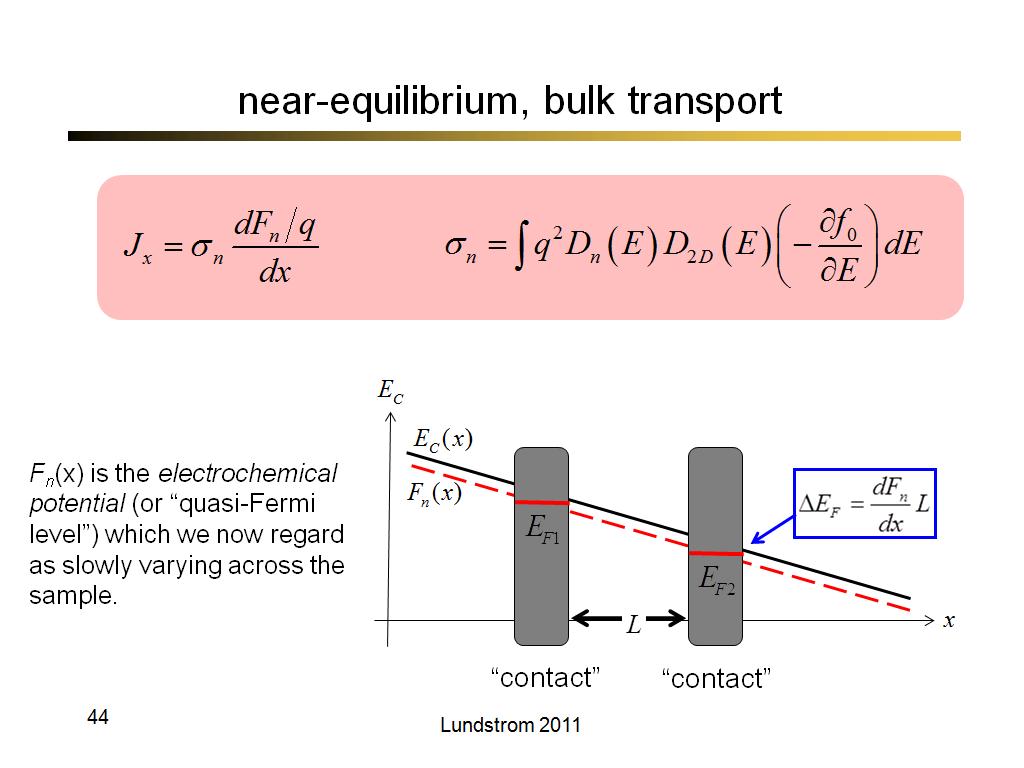
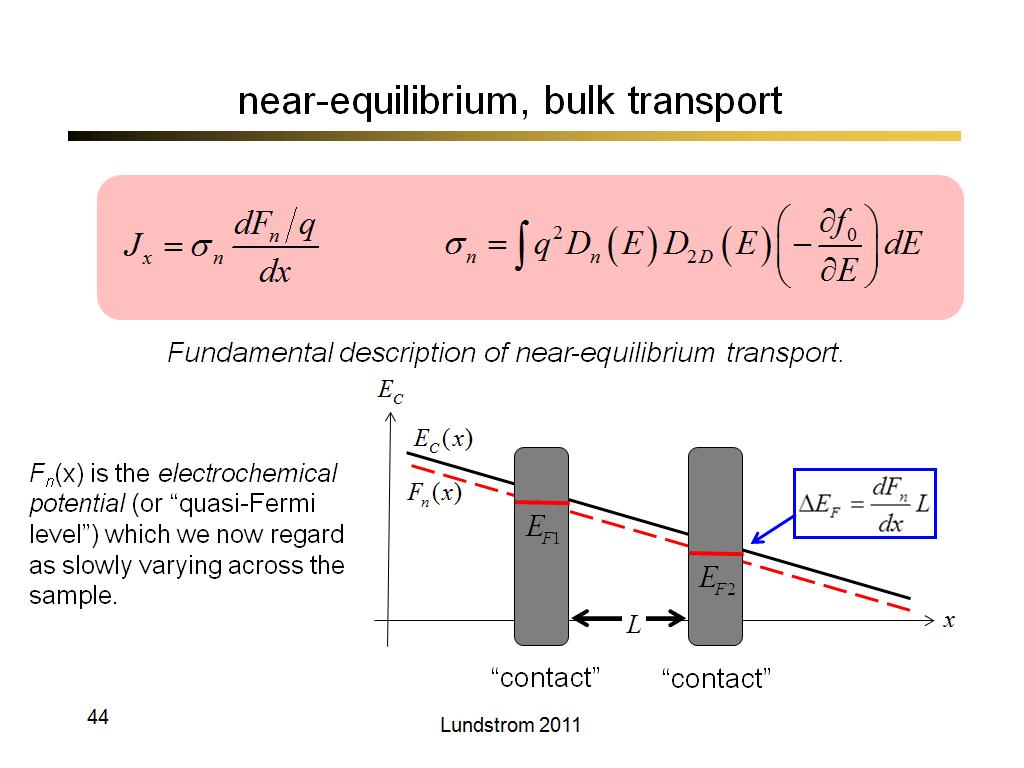
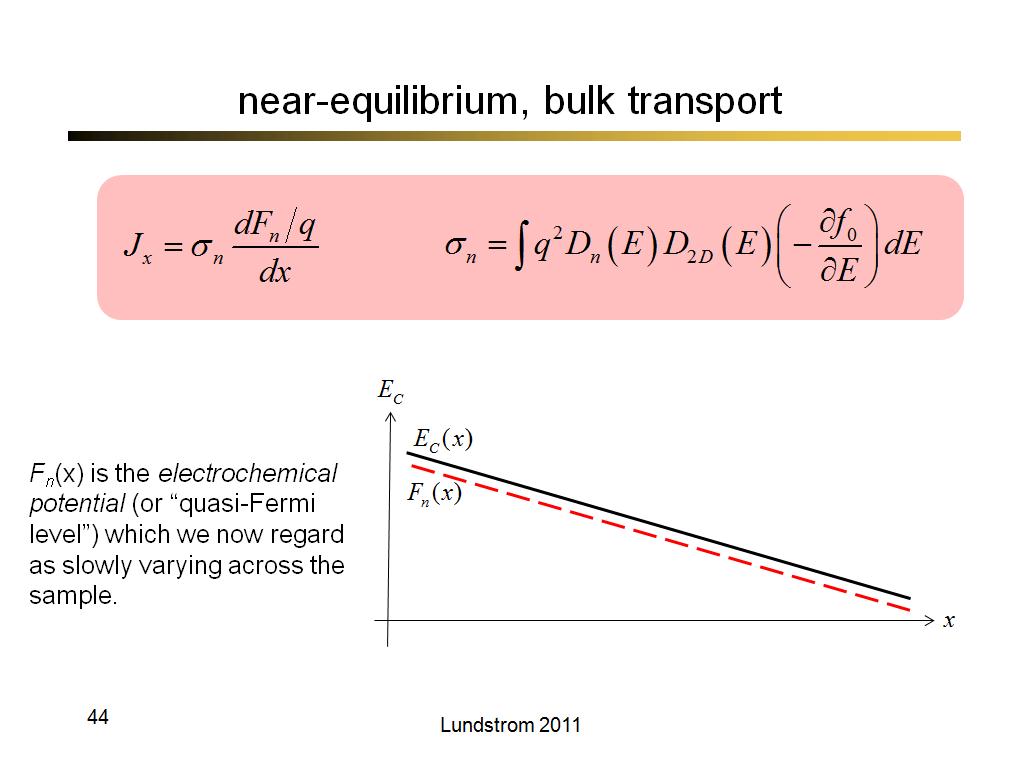 44. near-equilibrium, bulk transpo…
3157.7333333333331
00:00/00:00
44. near-equilibrium, bulk transpo…
3157.7333333333331
00:00/00:00 -
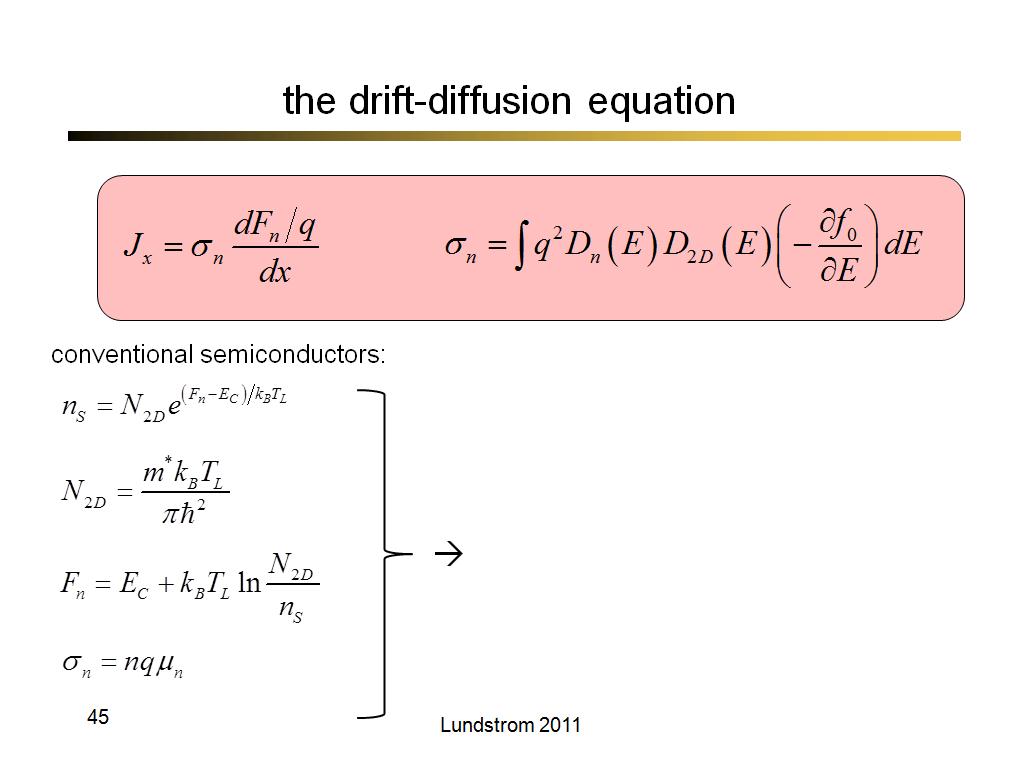
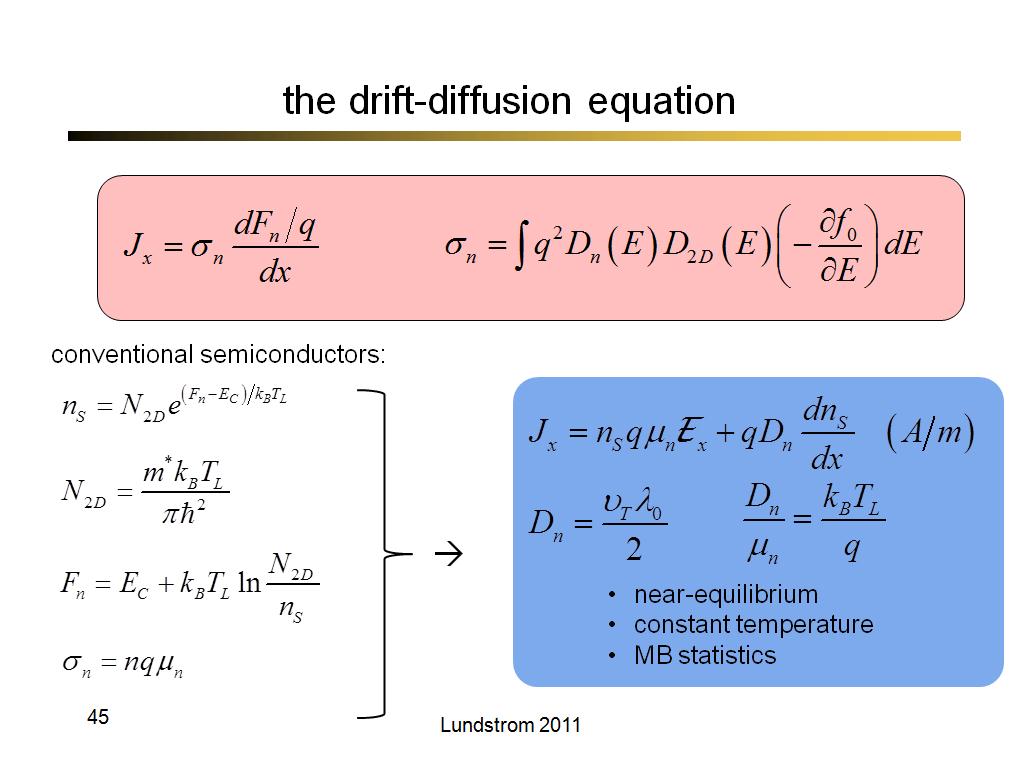
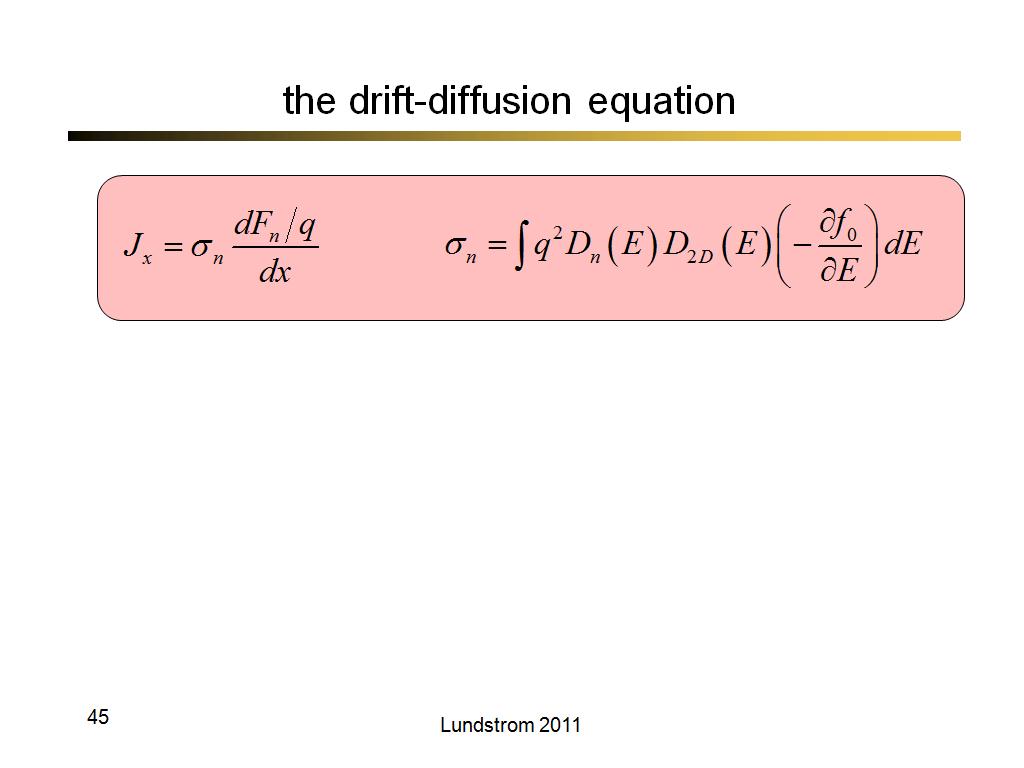 45. the drift-diffusion equation
3329.1333333333332
00:00/00:00
45. the drift-diffusion equation
3329.1333333333332
00:00/00:00 -
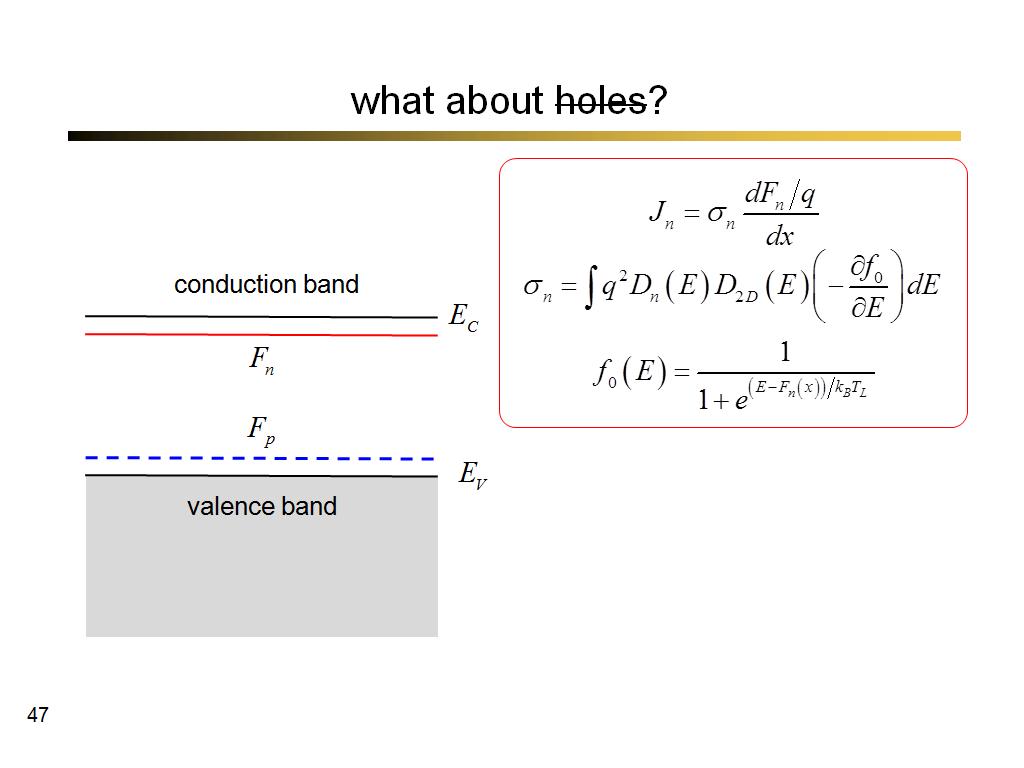
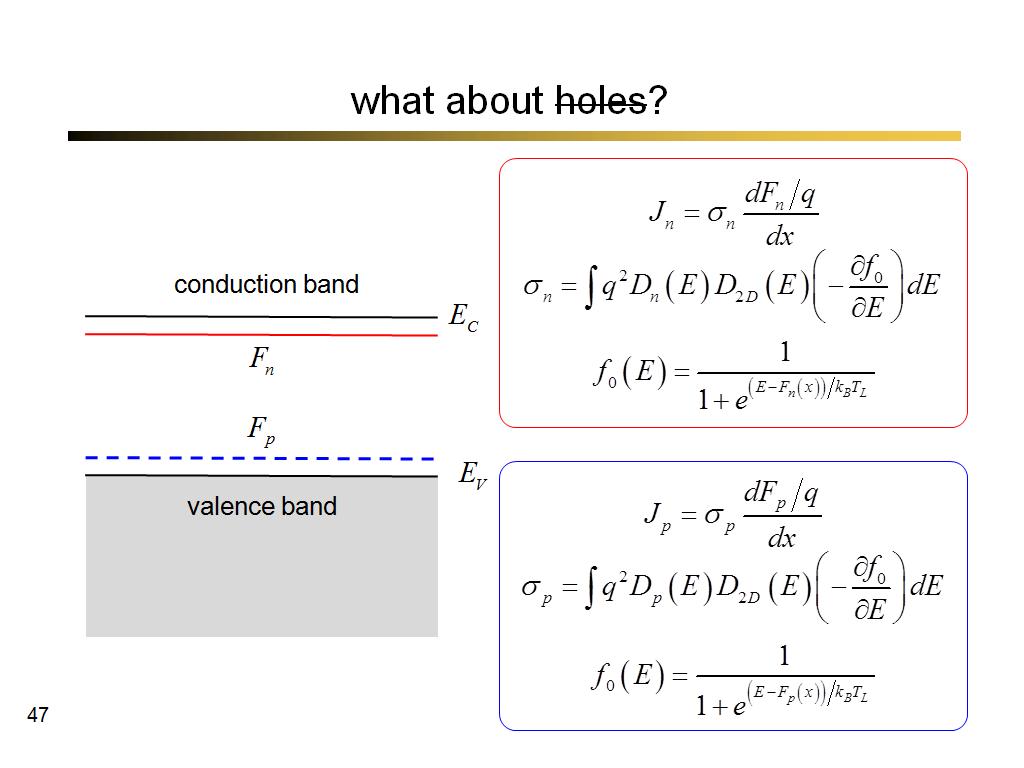
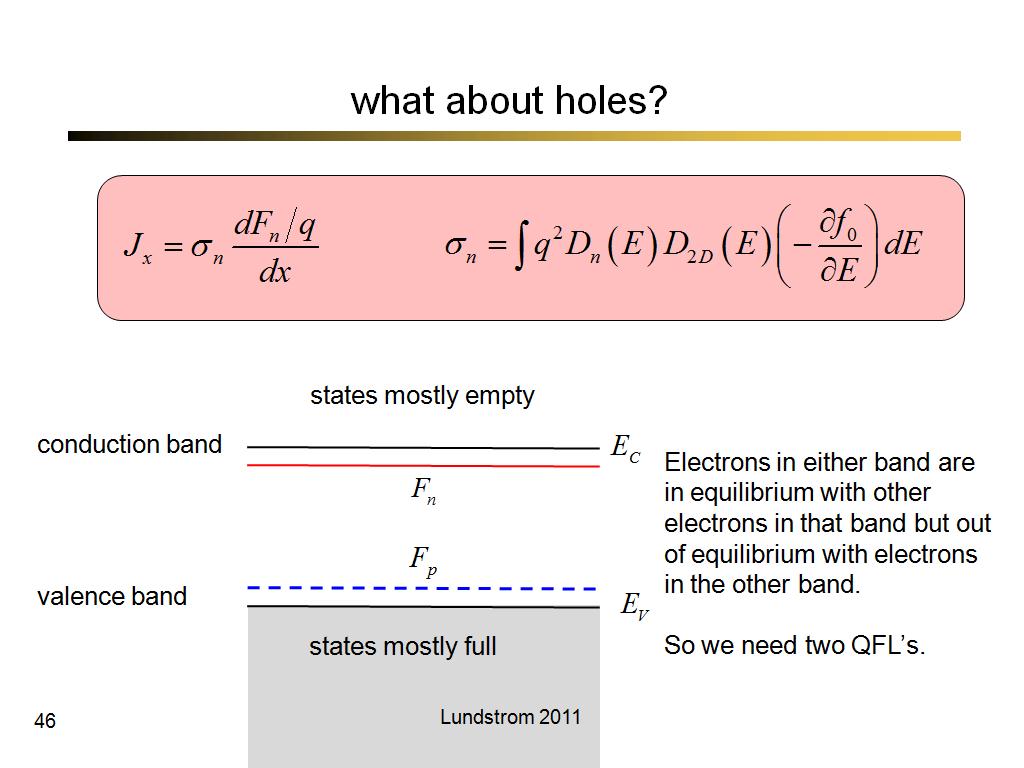 46. what about holes?
3470.9666666666667
00:00/00:00
46. what about holes?
3470.9666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
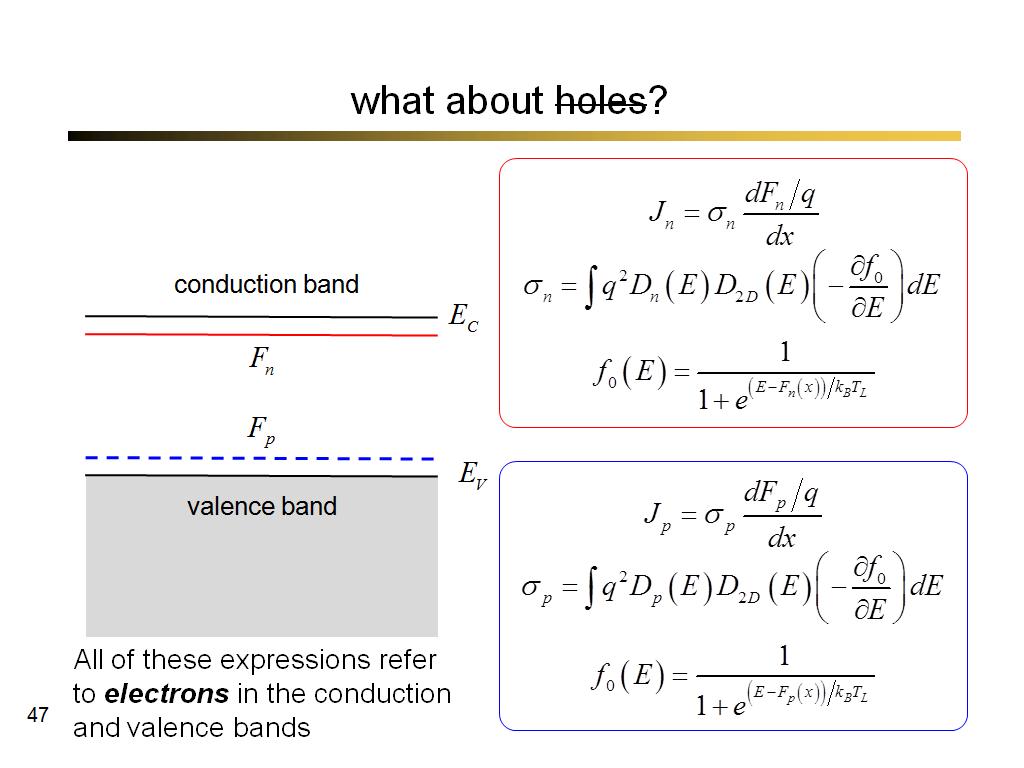
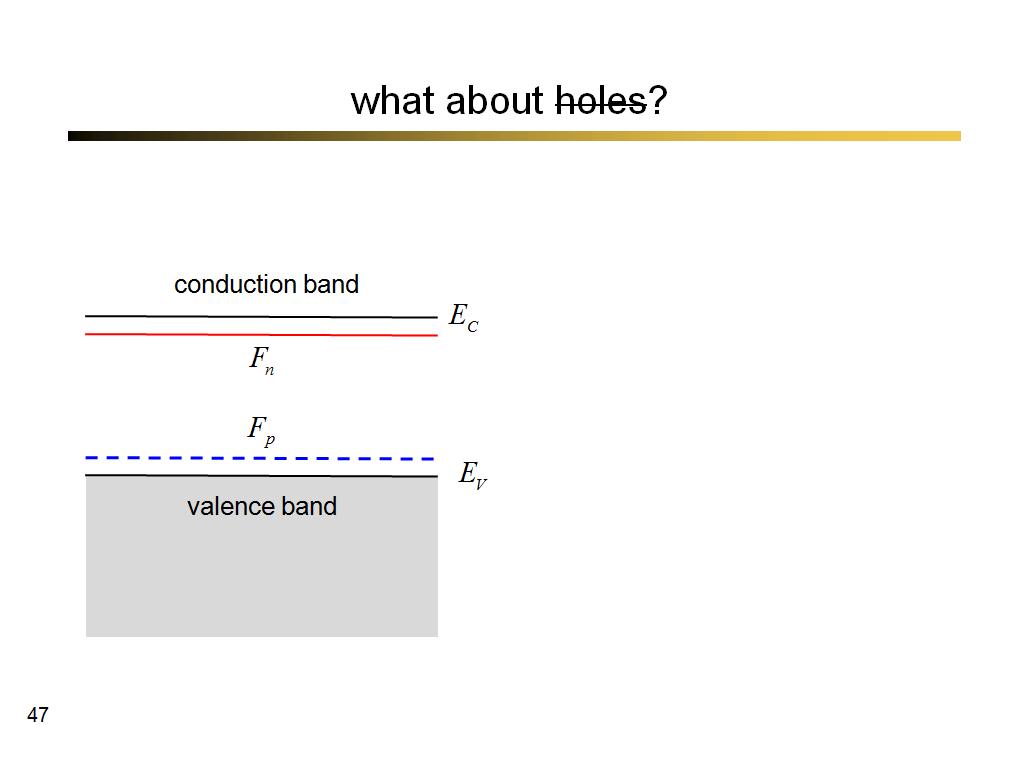 47. what about holes?
3553.5
00:00/00:00
47. what about holes?
3553.5
00:00/00:00 -
 48. outline
3665.8
00:00/00:00
48. outline
3665.8
00:00/00:00 -
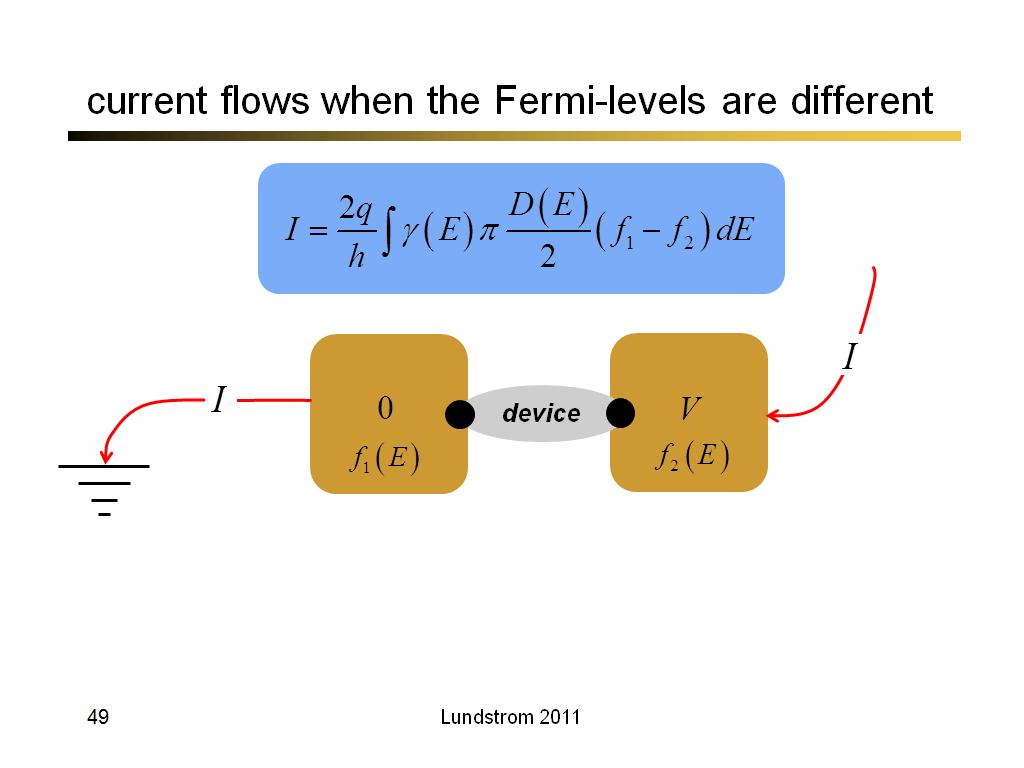
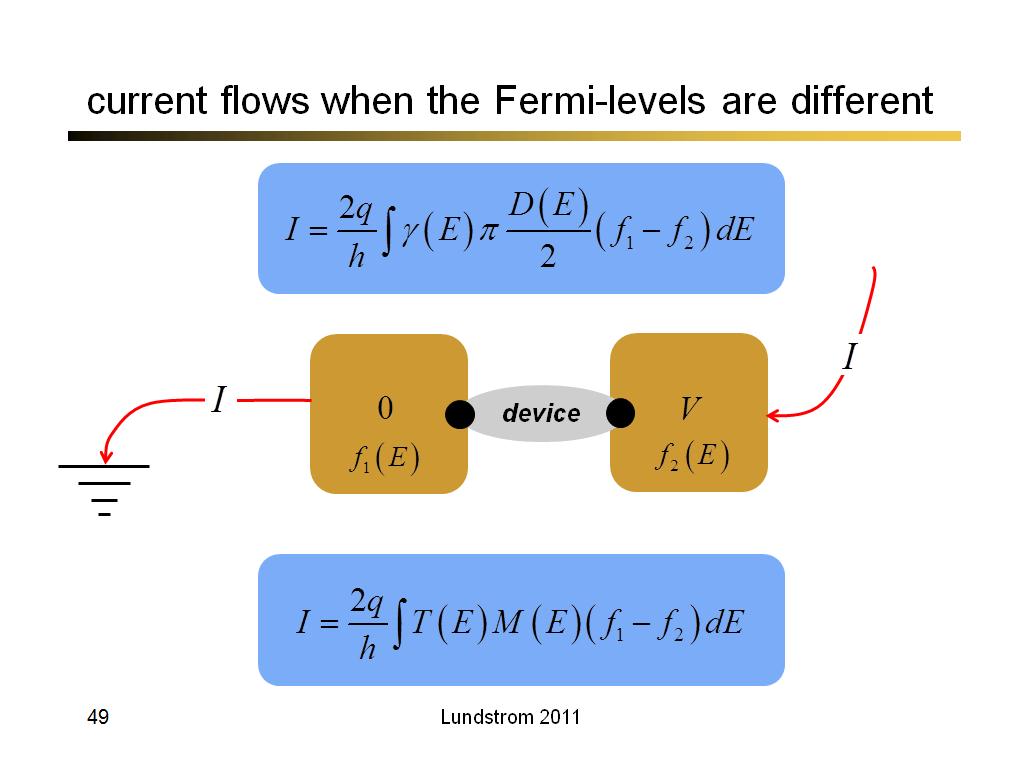
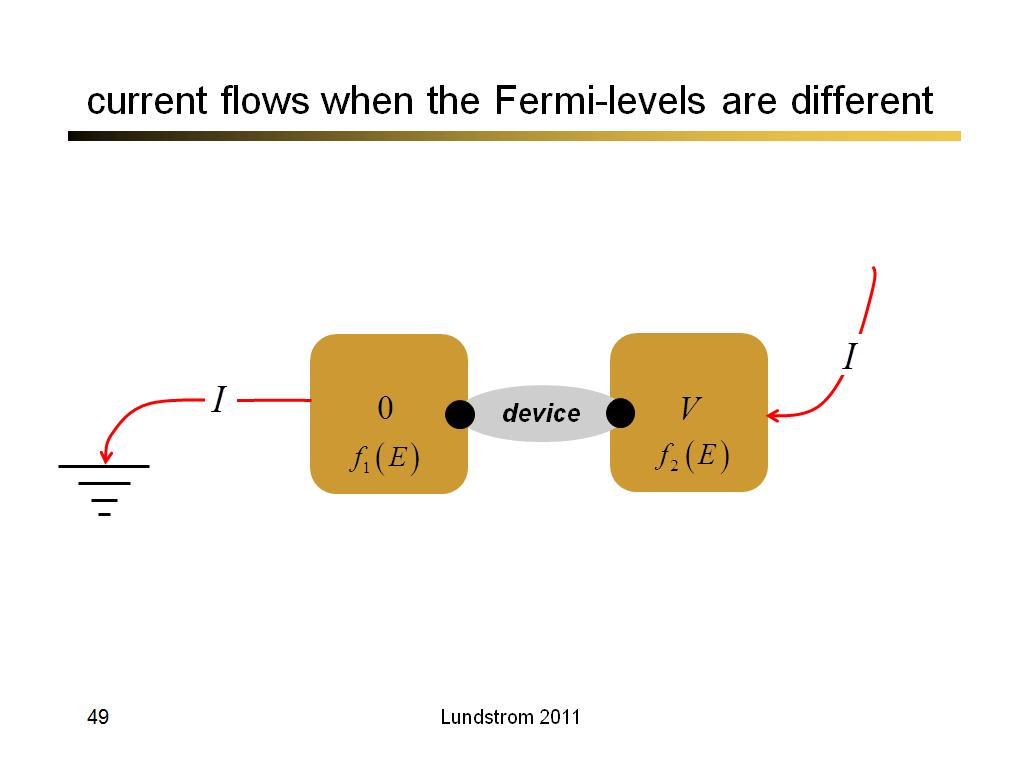 49. current flows when the Fermi-l…
3670.1666666666665
00:00/00:00
49. current flows when the Fermi-l…
3670.1666666666665
00:00/00:00 -
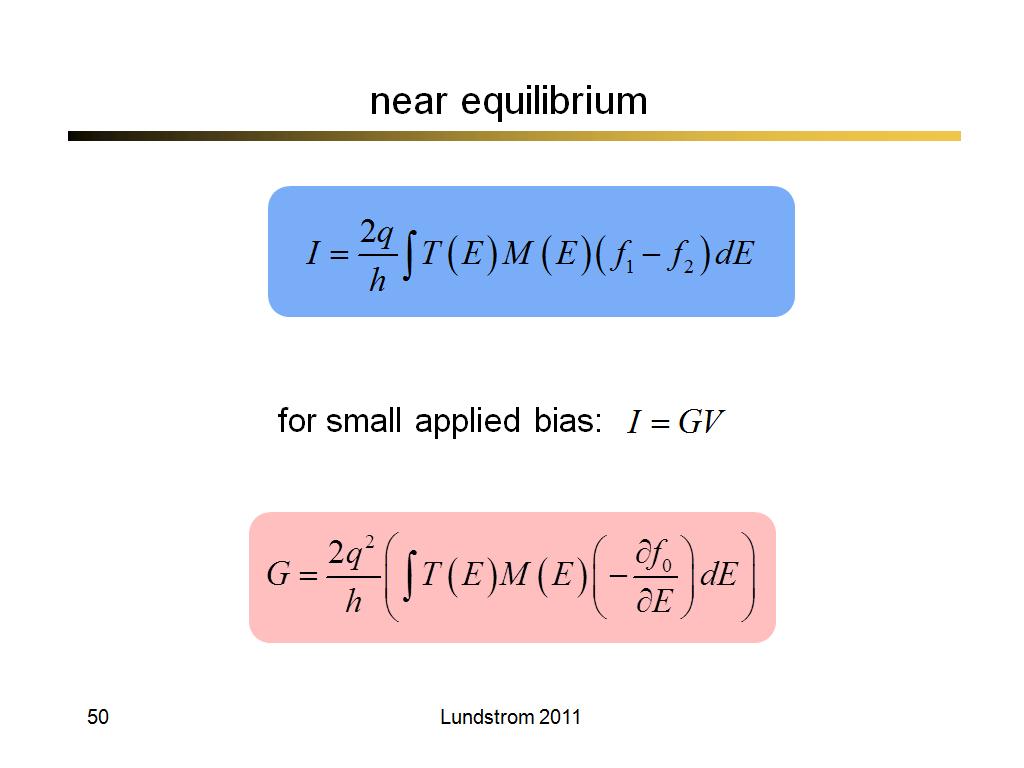
 50. near equilibrium
3711.2333333333331
00:00/00:00
50. near equilibrium
3711.2333333333331
00:00/00:00 -
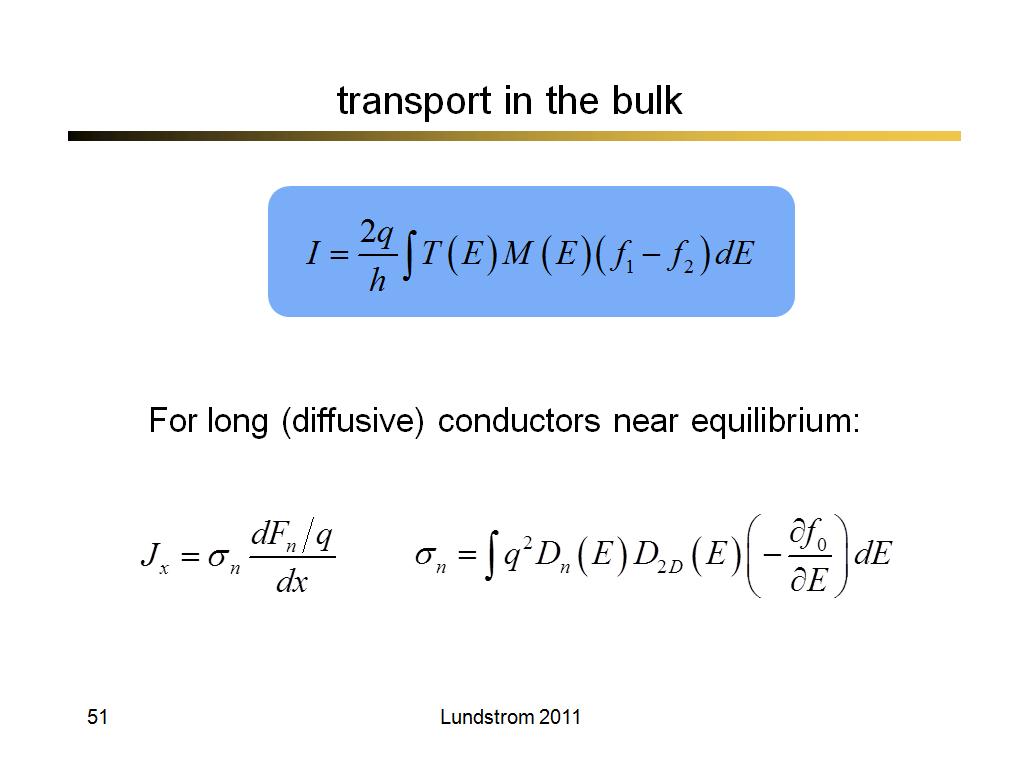
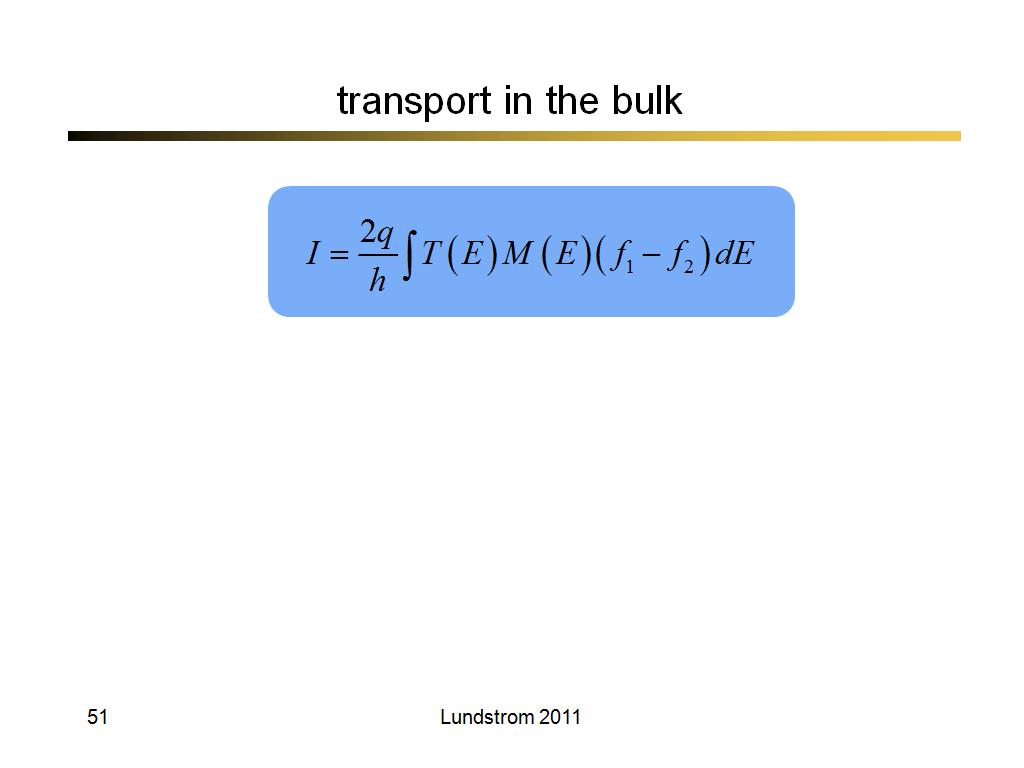 51. transport in the bulk
3731.5666666666666
00:00/00:00
51. transport in the bulk
3731.5666666666666
00:00/00:00 -
 52. outline
3747.1333333333332
00:00/00:00
52. outline
3747.1333333333332
00:00/00:00 -
 53. for more information
3748.9666666666667
00:00/00:00
53. for more information
3748.9666666666667
00:00/00:00 -
 54. for even more information
3783.1333333333332
00:00/00:00
54. for even more information
3783.1333333333332
00:00/00:00 -
 55. questions
3799.3333333333335
00:00/00:00
55. questions
3799.3333333333335
00:00/00:00